Abstract.
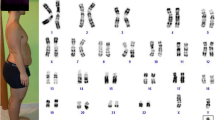
We report a mother and two daughters with partial Xp monosomy. Clinical assessment for Turner phenotype revealed that the three females manifested low-normal to mild short stature (–1.6 to approximately –2.3 SD) and variable degrees of skeletal features, such as cubitus valgus, short 4th matacarpals, and Madelung deformity, but no soft tissue or visceral anomalies or gonadal dysfunction. Cytogenetic studies for lymphocytes showed that the karyotype was 45,X[3]/46,X,del(X)(p21.1)[27] in the mother and non-mosaic 46,X,del(X)(p21.1) in the two daughters. Fluorescence in situ hybridization and microsatellite analyses for 19 loci/regions on the X chromosome demonstrated that the del(Xp) chromosome was missing SHOX and had the breakpoint between DMD and CYBB. The results are consistent with the recently proposed notion that haploinsufficiency of SHOX results in not only short stature, but also Turner skeletal features in association with maturational effects of gonadal estrogens. The lack of soft tissue or visceral anomalies suggests the presence of the putative lymphogenic gene on the del(Xp) chromosome; the preservation of ovarian function appears to be compatible with meiotic pairing failure being relatively mild.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Electronic Publication
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Adachi, M., Tachibana, K., Asakura, Y. et al. Del(X)(p21.1) in a mother and two daughters: genotype-phenotype correlation of Turner features. Hum Genet 106, 306–310 (2000). https://doi.org/10.1007/s004390000253
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s004390000253