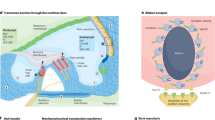
Abstract
Mutations to the OTOF gene are among the most common reasons for auditory neuropathy. Although cochlear implants are often effective in restoring sound transduction, there are currently no biological treatments for individuals with variants of OTOF. Previous studies have reported the rescue of hearing in DFNB9 mice using OTOF gene replacement although the efficacy needs improvement. Here, we developed a novel dual-AAV-mediated gene therapy system based on the principles of protein trans-splicing, and we show that this system can reverse bilateral deafness in Otof –/– mice after a single unilateral injection. The system effectively expressed exogenous mouse or human otoferlin after injection on postnatal day 0–2. Human otoferlin restored hearing to near wild-type levels for at least 6 months and restored the release of synaptic vesicles in inner hair cells. Our study not only provides a preferential clinical strategy for the treatment of OTOF-related auditory neuropathies, but also describes a route of development for other large-gene therapies and protein engineering techniques.





Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The datasets generated during and/or analyzed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
References
Adato A, Raskin L, Petit C, Bonne-Tamir B (2000) Deafness heterogeneity in a Druze isolate from the Middle East: novel OTOF and PDS mutations, low prevalence of GJB2 35delG mutation and indication for a new DFNB locus. Eur J Hum Genet 8:437–442. https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.ejhg.5200489
Akil O, Dyka F, Calvet C, Emptoz A, Lahlou G, Nouaille S, de Monvel JB, Hardelin JP, Hauswirth WW, Avan P, Petit C, Safieddine S, Lustig LR (2019) Dual AAV-mediated gene therapy restores hearing in a DFNB9 mouse model. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 116:4496–4501. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1817537116
Al-Moyed H, Cepeda AP, Jung SY, Moser T, Kugler S, Reisinger E (2019) A dual-AAV approach restores fast exocytosis and partially rescues auditory function in deaf otoferlin knock-out mice. EMBO Mol Med 11:1–13
Anzalone AV, Koblan LW, Liu DR (2020) Genome editing with CRISPR-Cas nucleases, base editors, transposases and prime editors. Nat Biotechnol 38:824–844. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41587-020-0561-9
Anzalone AV, Randolph PB, Davis JR, Sousa AA, Koblan LW, Levy JM, Chen PJ, Wilson C, Newby GA, Raguram A, Liu DR (2019) Search-and-replace genome editing without double-strand breaks or donor DNA. Nature 576:149–157. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41586-019-1711-4
Apgar J, Ross M, Zuo X, Dohle S, Sturtevant D, Shen BZ, de la Vega H, Lessard P, Lazar G, Raab RM (2012) A predictive model of intein insertion site for use in the engineering of molecular switches. PLoS ONE 7:1–14
Arentson-Lantz EJ, English KL, Paddon-Jones D (1985) Fry CS (2016) Fourteen days of bed rest induces a decline in satellite cell content and robust atrophy of skeletal muscle fibers in middle-aged adults. J Appl Physiol 120:965–975. https://doi.org/10.1152/japplphysiol.00799.2015
Bankoti K, Generotti C, Hwa T, Wang LL, O’Malley BW, Li DQ (2021) Advances and challenges in adeno-associated viral inner-ear gene therapy for sensorineural hearing loss. Mole Therapy-Methods Clin Develop 21:209–236. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.omtm.2021.03.005
Chan KY, Jang MJ, Yoo BB, Greenbaum A, Ravi N, Wu WL, Sanchez-Guardado L, Lois C, Mazmanian SK, Deverman BE, Gradinaru V (2017) Engineered AAVs for efficient noninvasive gene delivery to the central and peripheral nervous systems. Nat Neurosci 20:1172–1179. https://doi.org/10.1038/nn.4593
Chen JF, Liu K, Hu B, Li RR, Xin W, Chen H, Wang F, Chen L, Li RX, Ren SY, Xiao L, Chan JR, Mei F (2021) Enhancing myelin renewal reverses cognitive dysfunction in a murine model of Alzheimer’s disease. Neuron 109(2292–2307):e5. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuron.2021.05.012
Choi BY, Ahmed ZM, Riazuddin S, Bhinder MA, Shahzad M, Husnain T, Riazuddin S, Griffith AJ, Friedman TB (2009) Identities and frequencies of mutations of the otoferlin gene (OTOF) causing DFNB9 deafness in Pakistan. Clin Genet 75:237–243. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1399-0004.2008.01128.x
Ciuman RR (2009) Communication routes between intracranial spaces and inner ear: function, pathophysiologic importance and relations with inner ear diseases. Am J Otolaryngol 30:193–202. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.amjoto.2008.04.005
Davis H, Hirsh SK (1979) A slow brain stem response for low-frequency audiometry. Audiology 18:445–461. https://doi.org/10.3109/00206097909072636
Ding H, Zhang X, Zhu Z, Wang S, Xiong Y, Shang H, Liang G (2022) Membrane protein OTOF is a type I interferon-induced entry inhibitor of HIV-1 in macrophages. Mbio 13:1–15
Duman D, Tekin M (2012) Autosomal recessive nonsyndromic deafness genes: a review. Front Biosci (landmark Ed) 17:2213–2236. https://doi.org/10.2741/4046
Gaudelli NM, Komor AC, Rees HA, Packer MS, Badran AH, Bryson DI, Liu DR (2017) Programmable base editing of A.T to G.C in genomic DNA without DNA cleavage. Nature 551:464–471. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature24644
Gu X, Wang DQ, Xu ZJ, Wang JH, Guo L, Chai RJ, Li GL, Shu YL, Li HW (2021) Prevention of acquired sensorineural hearing loss in mice by in vivo Htra2 gene editing. Genome Biol 22:1–23
Guo JY, He L, Qu TF, Liu YY, Liu K, Wang GP, Gong SS (2018) Canalostomy as a surgical approach to local drug delivery into the inner ears of adult and neonatal mice. J vis Exp 135:1–8. https://doi.org/10.3791/57351
Holt JR, Geleoc GS (2019) Split otoferlins reunited. EMBO Mol Med 11:1–3. https://doi.org/10.15252/emmm.201809995
Hu XD, Wang JH, Yao X, Xiao QQ, Xue YY, Wang SR, Shi LY, Shu YL, Li HW, Yang H (2019) Screened AAV variants permit efficient transduction access to supporting cells and hair cells. Cell Discovery 5:1–4
Ide T, Mochiji S, Ueki N, Yamaguchi K, Shigenobu S, Hirono M, Wakabayashi KI (2016) Identification of the agg1 mutation responsible for negative phototaxis in a “wild-type” strain of Chlamydomonas reinhardtii. Biochem Biophys Rep 7:379–385. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbrep.2016.07.016
Ivanchenko MV, Hanlon KS, Hathaway DM, Klein AJ, Peters CW, Li Y, Tamvakologos PI, Nammour J, Maguire CA, Corey DP (2021) AAV-S: a versatile capsid variant for transduction of mouse and primate inner ear. Mol Ther Methods Clin Dev 21:382–398. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.omtm.2021.03.019
Iwasa Y, Nishio S, Yoshimura H, Kanda Y, Kumakawa K, Abe S, Naito Y, Nagai K, Usami S (2013) OTOF mutation screening in Japanese severe to profound recessive hearing loss patients. BMC Med Genet 14:1–7
Jia R, Song Z, Lin J, Li Z, Shan G, Huang C (2021) Gawky modulates MTF-1-mediated transcription activation and metal discrimination. Nucleic Acids Res 49:6296–6314. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gkab474
Johnson CP, Chapman ER (2010) Otoferlin is a calcium sensor that directly regulates SNARE-mediated membrane fusion. J Cell Biol 191:187–197. https://doi.org/10.1083/jcb.201002089
Komor AC, Kim YB, Packer MS, Zuris JA, Liu DR (2016) Programmable editing of a target base in genomic DNA without double-stranded DNA cleavage. Nature 533:420–424. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature17946
Kraus N, Ozdamar O, Stein L, Reed N (1984) Absent auditory brain stem response: peripheral hearing loss or brain stem dysfunction? Laryngoscope 94:400–406. https://doi.org/10.1288/00005537-198403000-00019
Landegger LD, Pan B, Askew C, Wassmer SJ, Gluck SD, Galvin A, Taylor R, Forge A, Stankovic KM, Holt JR, Vandenberghe LH (2017) A synthetic AAV vector enables safe and efficient gene transfer to the mammalian inner ear. Nat Biotechnol 35:280–284. https://doi.org/10.1038/nbt.3781
Li JJ, Hong SY, Chen WJ, Zuo EW, Yang H (2019) Advances in detecting and reducing off-target effects generated by CRISPR-mediated genome editing. J Genet Genomics 46:513–521. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jgg.2019.11.002
Liao Y, Li H, Pi Y, Li Z, Jin S (2019) Cardioprotective effect of IGF-1 against myocardial ischemia/reperfusion injury through activation of PI3K/Akt pathway in rats in vivo. J Int Med Res 47:3886–3897. https://doi.org/10.1177/0300060519857839
Manchaiah VK, Zhao F, Danesh AA, Duprey R (2011) The genetic basis of auditory neuropathy spectrum disorder (ANSD). Int J Pediatr Otorhinolaryngol 75:151–158. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijporl.2010.11.023
Michalski N, Goutman JD, Auclair SM, de Monvel JB, Tertrais M, Emptoz A, Parrin A, Nouaille S, Guillon M, Sachse M, Ciric D, Bahloul A, Hardelin JP, Sutton RB, Avan P, Krishnakumar SS, Rothman JE, Dulon D, Safieddine S, Petit C (2017) Otoferlin acts as a Ca2+ sensor for vesicle fusion and vesicle pool replenishment at auditory hair cell ribbon synapses. Elife 6:1–34
Mills KV, Johnson MA, Perler FB (2014) Protein splicing: how inteins escape from precursor proteins. J Biol Chem 289:14498–14505. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.R113.540310
Ng SS, Xiong A, Nguyen K, Masek M, No DY, Elazar M, Shteyer E, Winters MA, Voedisch A, Shaw K, Rashid ST, Frank CW, Cho NJ, Glenn JS (2017) Long-term culture of human liver tissue with advanced hepatic functions. JCI Insight 2:1–11. https://doi.org/10.1172/jci.insight.90853
Novikova O, Topilina N, Belfort M (2014) Enigmatic distribution, evolution, and function of inteins. J Biol Chem 289:14490–14497. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.R114.548255
Osborn MJ, Newby GA, McElroy AN, Knipping F, Nielsen SC, Riddle MJ, Xia LL, Chen WL, Eide CR, Webber BR, Wandall HH, Dabelsteen S, Blazar BR, Liu DR, Tolar J (2020) Base editor correction of COL7A1 in recessive dystrophic epidermolysis bullosa patient-derived fibroblasts and iPSCs. J Investig Dermatol 140:338–347. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jid.2019.07.701
Pangrsic T, Reisinger E, Moser T (2012) Otoferlin: a multi-C2 domain protein essential for hearing. Trends Neurosci 35:671–680. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tins.2012.08.002
Rabinowitz J, Chan YK, Samulski RJ (2019) Adeno-associated virus (AAV) versus immune response. Viruses 11:1–11. https://doi.org/10.3390/v11020102
Rance G, Beer DE, Cone-Wesson B, Shepherd RK, Dowell RC, King AM, Rickards FW, Clark GM (1999) Clinical findings for a group of infants and young children with auditory neuropathy. Ear Hear 20:238–252
Rankovic V, Vogl C, Dorje NM, Bahader I, Duque-Afonso CJ, Thirumalai A, Weber T, Kusch K, Strenzke N, Moser T (2020) Overloaded adeno-associated virus as a novel gene therapeutic tool for otoferlin-related deafness. Front Mol Neurosci 13:1–14. https://doi.org/10.3389/fnmol.2020.600051
Reisinger E (2020) Dual-AAV delivery of large gene sequences to the inner ear. Hear Res 394:1–10. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.heares.2019.107857
Rodriguez-Ballesteros M, Reynoso R, Olarte M, Villamar M, Morera C, Santarelli R, Arslan E, Meda C, Curet C, Volter C, Sainz-Quevedo M, Castorina P, Ambrosetti U, Berrettini S, Frei K, Tedin S, Smith J, Cruz Tapia M, Cavalle L, Gelvez N, Primignani P, Gomez-Rosas E, Martin M, Moreno-Pelayo MA, Tamayo M, Moreno-Barral J, Moreno F, del Castillo I (2008) A multicenter study on the prevalence and spectrum of mutations in the otoferlin gene (OTOF) in subjects with nonsyndromic hearing impairment and auditory neuropathy. Hum Mutat 29:823–831. https://doi.org/10.1002/humu.20708
Roux I, Safieddine S, Nouvian R, Grati M, Simmler MC, Bahloul I, Perfettini I, Le Gall M, Rostaing P, Hamard G, Triller A, Avan P, Moser T, Petit C (2006) Otoferlin, defective in a human deafness form, is essential for exocytosis at the auditory ribbon synapse. Cell 127:277–289. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cell.2006.08.040
Schmelas C, Grimm D (2018) Split Cas9, Not hairs - advancing the therapeutic index of CRISPR technology. Biotechnol J 13:1–17. https://doi.org/10.1002/biot.201700432
Shah NH, Eryilmaz E, Cowburn D, Muir TW (2013) Extein residues play an intimate role in the rate-limiting step of protein trans-splicing. J Am Chem Soc 135:5839–5847. https://doi.org/10.1021/ja401015p
Shubina-Oleinik O, Nist-Lund C, French C, Rockowitz S, Shearer AE, Holt JR (2021) Dual-vector gene therapy restores cochlear amplification and auditory sensitivity in a mouse model of DFNB16 hearing loss. Sci Adv 7:1–9
Sobkowicz HM, Rose JE, Scott GL, Levenick CV (1986) Distribution of synaptic ribbons in the developing organ of Corti. J Neurocytol 15:693–714. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01625188
Song L, McGee J, Walsh EJ (2006) Frequency- and level-dependent changes in auditory brainstem responses (ABRS) in developing mice. J Acoust Soc Am 119:2242–2257. https://doi.org/10.1121/1.2180533
Starr A, Picton TW, Sininger Y, Hood LJ, Berlin CI (1996) Auditory neuropathy. Brain 119:741–753
Stover T, Yagi M, Raphael Y (2000) Transduction of the contralateral ear after adenovirus-mediated cochlear gene transfer. Gene Ther 7:377–383. https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.gt.3301108
Strenzke N, Chakrabarti R, Al-Moyed H, Muller A, Hoch G, Pangrsic T, Yamanbaeva G, Lenz C, Pan KT, Auge E, Geiss-Friedlander R, Urlaub H, Brose N, Wichmann C, Reisinger E (2016) Hair cell synaptic dysfunction, auditory fatigue and thermal sensitivity in otoferlin Ile515Thr mutants. EMBO J 35:2519–2535. https://doi.org/10.15252/embj.201694564
Sun WC, Yang J, Liu XQ (2004) Synthetic two-piece and three-piece split inteins for protein trans-splicing. J Biol Chem 279:35281–35286. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M405491200
Suzuki J, Hashimoto K, Xiao R, Vandenberghe LH, Liberman MC (2017) Cochlear gene therapy with ancestral AAV in adult mice: complete transduction of inner hair cells without cochlear dysfunction (vol 7, 45524, 2017). Sci Rep 7:1–11
Tertrais M, Bouleau Y, Emptoz A, Belleudy S, Sutton RB, Petit C, Safieddine S, Dulon D (2019) Viral transfer of mini-otoferlins partially restores the fast component of exocytosis and uncovers ultrafast endocytosis in auditory hair cells of otoferlin knock-out mice. J Neurosci 39:3394–3411. https://doi.org/10.1523/JNEUROSCI.1550-18.2018
Tornabene P, Trapani I, Minopoli R, Centrulo M, Lupo M, de Simone S, Tiberi P, Dell’Aquila F, Marrocco E, Iodice C, Iuliano A, Gesualdo C, Rossi S, Giaquinto L, Albert S, Hoyng CB, Polishchuk E, Cremers FPM, Surace EM, Simonelli F, De Matteis MA, Polishchuk R, Auricchio A (2019) Intein-mediated protein trans-splicing expands adeno-associated virus transfer capacity in the retina. Sci Trans Med 11:1–13
Varga R, Avenarius MR, Kelley PM, Keats BJ, Berlin CI, Hood LJ, Morlet TG, Brashears SM, Starr A, Cohn ES, Smith RJH, Kimberling WJ (2006) OTOF mutations revealed by genetic analysis of hearing loss families including a potential temperature sensitive auditory neuropathy allele. J Med Genet 43:576–581. https://doi.org/10.1136/jmg.2005.038612
Villiger L, Grisch-Chan HM, Lindsay H, Ringnalda F, Pogliano CB, Allegri G, Fingerhut R, Haberle J, Matos J, Robinson MD, Thony B, Schwank G (2018) Treatment of a metabolic liver disease by in vivo genome base editing in adult mice. Nat Med 24:1519–1525. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41591-018-0209-1
Wang D, Tai PWL, Gao GP (2019a) Adeno-associated virus vector as a platform for gene therapy delivery. Nat Rev Drug Discovery 18:358–378. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41573-019-0012-9
Wang K, Luo L, He ZZ (2019b) The molecular mechanisms underpinning auditory neuropathy. Zhonghua Er Bi Yan Hou Tou Jing Wai Ke Za Zhi 54:149–156. https://doi.org/10.3760/cma.j.issn.1673-0860.2019.02.013
Wu YX, Liang D, Wang YH, Bai MZ, Tang W, Bao SM, Yan ZQ, Li DS, Li JS (2013) Correction of a genetic disease in mouse via use of CRISPR-Cas9. Cell Stem Cell 13:659–662. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.stem.2013.10.016
Xue YY, Hu XD, Wang DQ, Li D, Li YG, Wang F, Huang MQ, Gu X, Xu ZJ, Zhou JA, Wang JH, Chai RJ, Shen J, Chen ZY, Li GL, Yang H, Li HW, Zuo EW, Shu YL (2022) Gene editing in a Myo6 semi-dominant mouse model rescues auditory function. Mol Ther 30:105–118. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ymthe.2021.06.015
Yasunaga S, Grati M, Chardenoux S, Smith TN, Friedman TB, Lalwani AK, Wilcox ER, Petit C (2000) OTOF encodes multiple long and short isoforms: genetic evidence that the long ones underlie recessive deafness DFNB9. Am J Hum Genet 67:591–600. https://doi.org/10.1086/303049
Yasunaga S, Grati M, Cohen-Salmon M, El-Amraoui A, Mustapha M, Salem N, El-Zir E, Loiselet J, Petit C (1999) A mutation in OTOF, encoding otoferlin, a FER-1-like protein, causes DFNB9, a nonsyndromic form of deafness. Nat Genet 21:363–369. https://doi.org/10.1038/7693
Yeh WH, Shubina-Oleinik O, Levy JM, Pan BF, Newby GA, Wornow M, Burt R, Chen JC, Holt JR, Liu DR (2020) In vivo base editing restores sensory transduction and transiently improves auditory function in a mouse model of recessive deafness. Sci Trans Med 12:1–12
Zeng FG, Kong YY, Michalewski HJ, Starr A (2005) Perceptual consequences of disrupted auditory nerve activity. J Neurophysiol 93:3050–3063. https://doi.org/10.1152/jn.00985.2004
Zuris JA, Thompson DB, Shu Y, Guilinger JP, Bessen JL, Hu JH, Maeder ML, Joung JK, Chen ZY, Liu DR (2015) Cationic lipid-mediated delivery of proteins enables efficient protein-based genome editing in vitro and in vivo. Nat Biotechnol 33:73–80. https://doi.org/10.1038/nbt.3081
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the National Key Research and Development Program of China (2020YFA0908201), the National Natural Science Foundation of China (82171148), the Clinical Research Plan of SHDC (SHDC2020CR4083), the Science and Technology Commission of Shanghai Municipality (21S11905100), the Special Project for Clinical Research in Health Industry of Shanghai Municipal Health Commission (20224Z0003), the Excellent Doctors-Excellent Clinical Researchers Program of Eye & ENT Hospital of Fudan University (SYB202005), and the “Shuguang Program” supported by the Shanghai Education Development Foundation and the Shanghai Municipal Education Commission (20SG08). We thank Shanghai Refreshgene Therapeutics Co., Ltd. for suggestions and assistance with the experiments.
Funding
The National Key Research and Development Program of China, 2020YFA0908201, Yilai Shu, the National Natural Science Foundation of China, 82171148, Yilai Shu, the Clinical Research Plan of SHDC, SHDC2020CR4083, Yilai Shu, the Science and Technology Commission of Shanghai Municipality, 21S11905100, Yilai Shu, the Special Project for Clinical Research in Health Industry of Shanghai Municipal Health Commission, 20224Z0003, Yilai Shu, the Excellent Doctors-Excellent Clinical Researchers Program of Eye & ENT Hospital of Fudan University, SYB202005, Yilai Shu, the “Shuguang Program” supported by the Shanghai Education Development Foundation and the Shanghai Municipal Education Commission, 20SG08, Yilai Shu
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
YS, HL, and WW: developed and supervised the project. HT and YS: jointly conceived the project. HT designed experiments and analyzed the data. HW, JL, MX, and FW: performed the in vivo experiments and the partial data analysis. HT: conducted the structural prediction. SW, HT, and SH: conducted the in vitro experiments. HT, YS, and SH: wrote the manuscript. HT, YS, SH, HW, SW, KG, YC, and DW: reviewed and revised the manuscript. All the authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interests
All the authors declare no competing interests. Kaiyu Gao is currently an employee of Shanghai Refreshgene Therapeutics Co., Ltd.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Tang, H., Wang, H., Wang, S. et al. Hearing of Otof-deficient mice restored by trans-splicing of N- and C-terminal otoferlin. Hum Genet 142, 289–304 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00439-022-02504-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00439-022-02504-2