Abstract
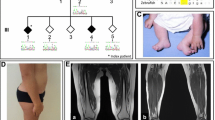
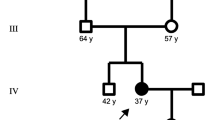
The motor neuron diseases (MND) are a group of related neurodegenerative diseases that cause the relative selective progressive death of motor neurons. These diseases range from slowly progressive forms including hereditary motor neuropathy (HMN), to the rapidly progressive disorder amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS). There is clinical and genetic overlap among these MNDs, implicating shared pathogenic mechanisms. We recruited a large family with a MND that was previously described as juvenile ALS and distal HMN. We identified a novel MND/HMN locus on chromosome 7q34-q36 following a genome-wide scan for linkage in this family. The disease causing mutation maps to a 26.2 cM (12.3 Mb) interval flanked by D7S2513 and D7S637 on chromosome 7q34-q36. Recombinant haplotype analysis including unaffected individuals suggests that the refined candidate interval spans 14.3 cM (6.3 Mb) flanked by D7S2511 and D7S798. One gene in the candidate interval, CDK5, was selected for immediate mutation analysis based upon its known association with an ALS-like phenotype in mice however, no mutations were identified. Identification of genes causing familial MND will lead to a greater understanding of the biological basis of both familial and sporadic motor neuron degeneration including ALS.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Antonellis A, Ellsworth RE, Sambuughin N, Puls I, Abel A, Lee-Lin SQ, Jordanova A, Kremensky I, Christodoulou K, Middleton LT, Sivakumar K, Ionasescu V, Funalot B, Vance JM, Goldfarb LG, Fischbeck KH, Green ED (2003) Glycyl tRNA synthetase mutations in Charcot-Marie-Tooth disease type 2D and distal spinal muscular atrophy type V. Am J Hum Genet 72:1293–1299
Bian F, Nath R, Sobocinski G, Booher RN, Lipinski WJ, Callahan MJ, Pack A, Wang KK, Walker LC (2002) Axonopathy, tau abnormalities, and dyskinesia, but no neurofibrillary tangles in p25-transgenic mice. J Comp Neurol 446:257–266
Blair IP, Kennerson ML, Nicholson GA (1995) Detection of Charcot-Marie-Tooth type 1A duplication by the polymerase chain reaction. Clin Chem 41:1105–1108
Blair IP, Bennett CL, Abel A, Rabin BA, Griffin JW, Fischbeck KH, Cornblath DR, Chance PF (2000) A gene for autosomal dominant juvenile amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS4) localizes to a 500-kb interval on chromosome 9q34. Neurogenetics 3:1–6
Chen YZ, Bennett CL, Huynh HM, Blair IP, Puls I, Irobi J, Dierick I, Abel A, Kennerson ML, Rabin BA, Nicholson GA, Auer-Grumbach M, Wagner K, De Jonghe P, Griffin JW, Fischbeck KH, Timmerman V, Cornblath DR, Chance PF (2004) DNA/RNA helicase gene mutations in a form of juvenile amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS4). Am J Hum Genet 74:1128–1135
De Jonghe P, Auer-Grumbach M, Irobi J, Wagner K, Plecko B, Kennerson M, Zhu D, De Vriendt E, Van Gerwen V, Nicholson G, Hartung HP, Timmerman V (2002) Autosomal dominant juvenile amyotrophic lateral sclerosis and distal hereditary motor neuronopathy with pyramidal tract signs: synonyms for the same disorder? Brain 125:1320–1325
Evgrafov OV, Mersiyanova I, Irobi J, Van Den Bosch L, Dierick I, Leung CL, Schagina O, Verpoorten N, Van Impe K, Fedotov V, Dadali E, Auer-Grumbach M, Windpassinger C, Wagner K, Mitrovic Z, Hilton-Jones D, Talbot K, Martin JJ, Vasserman N, Tverskaya S, Polyakov A, Liem RK, Gettemans J, Robberecht W, De Jonghe P, Timmerman V (2004) Mutant small heat-shock protein 27 causes axonal Charcot-Marie-Tooth disease and distal hereditary motor neuropathy. Nat Genet 36:602–606
Hanemann CO, Ludolph AC (2002) Hereditary motor neuropathies and motor neuron diseases: which is which. Amyotroph Lateral Scler Other Motor Neuron Disord 3:186–189
Harding AE, Thomas PK (1980) Hereditary distal spinal muscular atrophy. A report on 34 cases and a review of the literature. J Neurol Sci 45:337–348
Irobi J, Van Impe K, Seeman P, Jordanova A, Dierick I, Verpoorten N, Michalik A, De Vriendt E, Jacobs A, Van Gerwen V, Vennekens K, Mazanec R, Tournev I, Hilton-Jones D, Talbot K, Kremensky I, Van Den Bosch L, Robberecht W, Van Vandekerckhove J, Broeckhoven C, Gettemans J, De Jonghe P, Timmerman V (2004) Hot-spot residue in small heat-shock protein 22 causes distal motor neuropathy. Nat Genet 36:597–601
James PA, Talbot K (2006) The molecular genetics of non-ALS motor neuron diseases. Biochim Biophys Acta 1762:986–1000
Keller MP, Chance PF (1999) Inherited peripheral neuropathy. Semin Neurol 19:353–362
Lathrop GM, Lalouel J-M (1984) Easy calculations of lod scores and genetic risks on small computers. Am J Hum Genet 36:460–465
Munch C, Sedlmeier R, Meyer T, Homberg V, Sperfeld AD, Kurt A, Prudlo J, Peraus G, Hanemann CO, Stumm G, Ludolph AC (2004) Point mutations of the p150 subunit of dynactin (DCTN1) gene in ALS. Neurology 63:724–726
Neuromuscular Disorder Consortium (1997) Guidelines for CMT2 and distal HMN: workshop report. The Netherlands Neuromuscul Disord 8:426–431
Nguyen MD, Lariviere RC, Julien JP (2001) Deregulation of Cdk5 in a mouse model of ALS: toxicity alleviated by perikaryal neurofilament inclusions. Neuron 30:135–147
Nishimura AL, Mitne-Neto M, Silva HC, Richieri-Costa A, Middleton S, Cascio D, Kok F, Oliveira JR, Gillingwater T, Webb J, Skehel P, Zatz M (2004) A mutation in the vesicle-trafficking protein VAPB causes late-onset spinal muscular atrophy and amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Am J Hum Genet 75:822–831
Puls I, Jonnakuty C, LaMonte BH, Holzbaur EL, Tokito M, Mann E, Floeter MK, Bidus K, Drayna D, Oh SJ, Brown RH Jr, Ludlow CL, Fischbeck KH (2003) Mutant dynactin in motor neuron disease. Nat Genet 33:455–456
Sambuughin N, Sivakumar K, Selenge B, Lee HS, Friedlich D, Baasanjav D, Dalakas MC, Goldfarb LG (1998) Autosomal dominant distal spinal muscular atrophy type V (dSMA-V) and Charcot-Marie-Tooth disease type 2D (CMT2D) segregate within a single large kindred and map to a refined region on chromosome 7p15. J Neurol Sci 161:23–28
Shaw PJ (2005) Molecular and cellular pathways of neurodegeneration in motor neuron disease. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiat 76:1046–1057
Valdmanis PN, Gros-Louis F, Laurent S, Camu W, Meininger V, Rouleau GA (2005) VAPB mutations in ALS. Amyotroph Lateral Scler Other Motor Neuron Disord (Suppl 1) 6(Suppl 1):49–51
Van Den Bosch L, Timmerman V (2006) Genetics of motor neuron disease. Curr Neurol Neurosci Rep 6:423–431
Acknowledgments
We gratefully acknowledge the participation and contribution of patients and family members. We also thank Dr. D. Zhu for technical support and Dr. S. Reddel for assistance with neurological assessment of patients. This study was supported by a research grant (S.G.) and Bill Gole fellowship (I.P.B.) from the Motor Neurone Disease Research Institute of Australia Inc. (MNDRIA).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gopinath, S., Blair, I.P., Kennerson, M.L. et al. A novel locus for distal motor neuron degeneration maps to chromosome 7q34-q36. Hum Genet 121, 559–564 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00439-007-0348-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00439-007-0348-9