Abstract
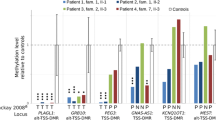
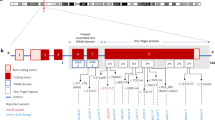
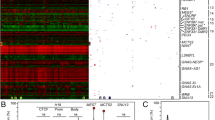
The expression of imprinted genes is mediated by allele-specific epigenetic modification of genomic DNA and chromatin, including parent of origin-specific DNA methylation. Dysregulation of these genes causes a range of disorders affecting pre- and post-natal growth and neurological function. We investigated a cohort of 12 patients with transient neonatal diabetes whose disease was caused by loss of maternal methylation at the TNDM locus. We found that six of these patients showed a spectrum of methylation loss, mosaic with respect to the extent of the methylation loss, the tissues affected and the genetic loci involved. Five maternally methylated loci were affected, while one maternally methylated and two paternally methylated loci were spared. These patients had higher birth weight and were more phenotypically diverse than other TNDM patients with different aetiologies, presumably reflecting the influence of dysregulation of multiple imprinted genes. We propose the existence of a maternal hypomethylation syndrome, and therefore suggest that any patient with methylation loss at one maternally-methylated locus may also manifest methylation loss at other loci, potentially complicating or even confounding the clinical presentation.



Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- BWS:
-
Beckwith–Wiedemann syndrome
- DMR:
-
differentially methylated region
- IUGR:
-
Intra-uterine growth retardation
- LOM:
-
Loss of methylation
- MS-PCR:
-
Methylation-specific PCR
- TNDM:
-
Transient neonatal diabetes mellitus
- UPD:
-
Uniparental disomy
- WRGL:
-
Wessex Regional Genetics Laboratory
References
Allegrucci C, Thurston A, Lucas E, Young L (2005) Epigenetics and the germline. Reproduction 129:137–149
Arima T, Kamikihara T, Hayashida T, Kato K, Inoue T, Shirayoshi, Oshimura M, Soejima H, Mukai T, Wake N (2005) ZAC, LIT1 (KCNQ1OT1) and p57 KIP2 (CDKN1C) are in an imprinted gene network that may play a role in Beckwith–Wiedemann syndrome. Nucl Acids Res 33:2650–2660
Arnaud P, MonkD, Hitchins M, Gordon E, Dean W, Beechey CV, Peters J, Craigen W, Preece M, Stanier P, Moore GE, Kelsey G (2003) Conserved methylation imprints in the human and mouse GRB10 genes with divergent allelic expression suggests differential reading of the same mark. Hum Mol Genet 12:1005–1019
Arnaud P, Hata K, Kaneda M, Li E, Sasaki H, Feil R, Kelsey G (2006) Stochastic imprinting in the progeny of Dnmt3L−/− females. Hum Mol Genet 15:589–598
Bliek J, Terhal P, van den Bogaard M-J, Maas S, Hamel B, Salieb-Beugelaar G, Simon M, Letteboer T, van der Smagt J, Kroes H, Mannens M (2006) Hypomethylation of the H19 gene causes not only Silver–Russell syndrome (SRS) but also isolated asymmetry or an SRS-like phenotype. Am J Hum Genet 78:604–614
Bestor T (2003) Imprinting errors and developmental asymmetry. Philos Trans R Soc Lond B 358:1411–1415
El-Maarri O, Buiting K, Peery EG, Kroisel PM, Balaban B, Wagner K, Urman B, Heyd J, Lich C, Brannan CI, Walter J, Horsthemke B (2001) Maternal methylation imprints on human chromosome 15 are established during or after fertilisation. Nature Genet 27:341–344
El-Maarri O, Seoud M, Coullin P, Herbiniaux U, Oldenburg J, Rouleau G, Slim R (2003) Maternal allales acquiring paternal methylation patterns in biparental complete hydatidiform moles. Hum Mol Genet. 12:1405–1413
Eggermann T, Meyer E, Schönherr N, Obermann C, Mavany M, Eggermann K, Ranke MB, Wollmann HA (2005) Epigenetic mutations in 11 p15 in Silver–Russell syndrome are restricted to the telomeric imprinting domain. J Med Genet 10.1136/jmg.2005.038687
Gardner RJ, Mackay DJ, Mungall AJ, Polychronakos C, Siebert R, Shield JP, Temple IK, Robinson DO (2000) An imprinted locus associated with transient neonatal diabetes mellitus. Hum Mol Genet 9:589–596
Gicquel C, Rossignol S, Cabrol S, Houang M, Steunou V, Barbu V, Danton F, Thibaud N, Le Merrer M, Burglen L, Bertrand A, Netchine I, Le Bouc Y (2005) Epimutation of the telomeric imprinting center region on chromosome 11 p15 in Silver–Russell syndrome. Nat Genet 37:1003–1007
Gloyn AL, Reimann F, Girard C, Edghill EL, Proks P, Pearson ER, Temple IK, Mackay DJ, Shield JP, Ellard S, Ashcroft FM, Gribble FM, Hattersley AT (2005) Relapsing diabetes can result from moderately activating mutations in KCNJ11. Hum Mol Genet 14:925–934
Howell C, Bestor TH, Ding F, Latham KE, Mertineit C, Trasler JM, Chaillet JR (2001) Genomic imprinting disrupted by a maternal-effect mutation in the Dnmt1 gene. Cell 104:829–838
Judson H, Hayward BE, Sheridan E, Bonthron DT (2002) A global disorder of imprinting in the human female germ line. Nature 416:539–42
Kant SG, van der Weij AM, Oostdijk W, Wit JM, Robinson DO, Temple IK, Mackay DJG (2005) Monozygous triplets discordant for transient neonatal diabetes mellitus and for imprinting of the TNDM DMR. Hum Genet 117:298–401
Lefebvre L, Viville S, Barton SC, Ishino F, Keverne EB, Surani MA (1998) Abnormal maternal behaviour and growth retardation associated with loss of the imprinted gene Mest. Nat Genet 20:163–169
Li L, Keverne EB, Aparicio SA, Ishino F, Barton SC, Surani MA (1999) Regulation of maternal behavior and offspring growth by paternally expressed Peg3. Science 284:330–333
Lucifero D, Mertineit C, Clarke HJ, Bestor TH, Trasler JM (2002) Methylation dynamics of imprinted genes in mouse germ cells. Genomics 79:530–538
Mackay DJG, Temple IK, Shield JPH, Robinson DO (2005) Bisulphite sequencing of the transient neonatal diabetes mellitus DMR facilitates a novel diagnostic test but reveals no methylation anomalies in patients of unknown aetiology. Hum Genet 116:255–261
Mackay DJG, Hahnemann JMD, Boonen SE, Poerksen S, Bunyan DJ, White HE, Durston VJ, Thomas NS, Robinson DO, Shield JPH, Clayton-Smith J, Temple IK (2006) Epimutation of the TNDM locus and the Beckwith–Wiedemann Syndrome centromeric locus in individuals with transient neonatal diabetes mellitus. Hum Gen 119:179–184
Moore MW, Dietz LG, Tirtorahardjo B, Cotter PD (2003) A multiplex methylation PCR assay for identification of uniparental disomy of chromosome 7. Hum Mut 21:645–648
Murphy SK, Wylie AA, Jirtle RL (2001) Imprinting of PEG3, the human homologue of a mouse gene involved in nurturing behavior. Genomics 7:110–7
Reik W, Walter J (2001) Genomic Imprinting: parental influence on the genome. Nat Rev Genet 2:21–32
Robertson KD (2005) DNA methylation and human disease. Nat Rev Genet 6:597–610
Temple IK, Shield JPH (2002) Transient neonatal diabetes, a disorder of imprinting. J Med Genet 39:872–875
Tycko B, Morison IM (2002) Physiological functions of imprinted genes. J Cell Physiol 192:245–258
Vu TH, Li T, Nguyen D, Nguyen BT, Yao X-M, Hu J-F, Hoffman AR (2000) Symmetric and asymmetric DNA methylation in the human IGF2-H19 imprinted region. Genomics 64:132–143
Waterland RA, Lin J-R, Smith CA, Jirtle RL (2006) Post-weaning diet affects genomic imprinting at the insulin-like growth factor 2 (Igf2) locus. Hum Mol Genet 15:705–716
Weksberg R, Shuman C, Caluseriu O, Smith AC, Fei Y, Nishikawa J, Stockley TL, Best L, Chitayat D, Olney A, Ives E, Schneider A, Bestor TH, Li M, Sadowski P, Squire D (2002) Discordant KCNQ1OT1 imprinting in sets of monozygotic twins discordant for Beckwith–Wiedemann syndrome. Hum Mol Genet 11:1317–1325
Weksberg R, Shuman C, Smith AC (2005) Beckwith–Wiedemann syndrome. Am J Med Genet 137C:12–23
Wylie AA, Murphy SK, Orton TC, Jirtle RL (2000) Novel imprinted DLK1/GTL2 domain on human chromosome 14 contains motifs that mimic those implicated in IGF2/H19 regulation. Genome Res 10:1711–1718
Zeschnigk M, Lich C, Buiting K, Doerfler W, Horsthemke B (1997) A single-tube PCR test for the diagnosis of Angelman and Prader–Willi syndrome based on allelic methylation differences at the SNRPN locus. Eur J Hum Genet 5:94–98
Acknowledgments
The authors thank Paul Strike for statistical analysis, Rinki Singh for helpful discussions, and Sven Poerksen (Department of Paediatrics, Glostrup Hospital, Glostrup, Denmark), Guy Hendrickx (Department of Paediatrics, Free University of Brussels, Jette, Belgium), Tracy Tinklin (Department of Paediatrics, Derby Children’s Hospital, UK). DJGM was funded by Diabetes UK, and PRN by the University of Bergen and Haukeland University Hospital.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mackay, D.J.G., Boonen, S.E., Clayton-Smith, J. et al. A maternal hypomethylation syndrome presenting as transient neonatal diabetes mellitus. Hum Genet 120, 262–269 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00439-006-0205-2
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00439-006-0205-2