Abstract
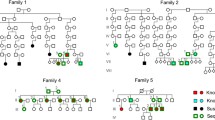
Basal Cell Nevus Syndrome (BCNS) is an autosomal dominant disease. PTCH1 gene mutations have been found responsible in many but not all pedigrees. Inflammatory Bowel Disease (IBD) is a complex genetic disorder, disproportionate in Ashkenazim, and characterized by chronic intestinal inflammation. We revisited a large Ashkenazim pedigree, first reported in 1968, with multiple diagnoses of BCNS and IBD, and with a common genetic cause for both disorders proposed. We expanded the pedigree to four generations and performed a genome-wide linkage study for BCNS and IBD traits. Twelve members with BCNS, seven with IBD, five with both diagnoses and eight unaffected were genotyped. Both non-parametric (GENEHUNTER 2.1) and parametric (FASTLINK) linkage analyses were performed and a validation through simulation was performed. BCNS linked to chromosome 9q22 (D9S1120) just proximal to the PTCH1 gene (NPL=3.26, P=0.003; parametric two-point LOD=2.4, parametric multipoint LOD=3.7). Novel IBD linkage evidence was observed at chromosome 1p13 (D1S420, NPL 3.92, P=0.0047; parametric two-point LOD=1.9). Linkage evidence was also observed to previously reported IBD loci on 4q, (D4S2623, NPL 3.02, P=0.012; parametric two-point LOD=2.15), 10q23 (D10S1225 near DLG5, NPL 3.33, P=0.0085; parametric two-point LOD=1.3), 12 overlapping the IBD2 locus (D12S313, NPL 2.6, P=0.018; parametric two-point LOD=1.52), and 7q (D7S510 and D7S3046, NPL 4.06, P=0.0035; parametric two-point LOD=2.18). In this pedigree affected by both BCNS and IBD, the two traits and their respective candidate genetic loci segregate independently; BCNS maps to the PTCH1 gene and IBD maps to several candidate regions, mostly overlapping previously observed IBD loci.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abecasis GR, Cherny SS, Cookson WO, Cardon LR (2002) Merlin-rapid analysis of dense genetic maps using sparse gene flow trees. Nat Genet 30:97–101
Bale AE (1997) The nevoid basal cell carcinoma syndrome: genetics and mechanism of carcinogenesis. Cancer Invest 15:180–186
Bonen DK, Cho JH (2003) The genetics of inflammatory bowel disease. Gastroenterology 124:521–536
Brant SR, Shugart YY (2004) Inflammatory bowel disease gene hunting by linkage analysis: rationale, methodology, and present status of the field. Inflamm Bowel Dis 10:300–311
Brant SR, Panhuysen CI, Bailey-Wilson JE, Rohal PM, Lee S, Mann J, Ravenhill G, Kirschner BS, Hanauer SB, Cho JH, Bayless TM (2000) Linkage heterogeneity for the IBD1 locus in Crohn’s disease pedigrees by disease onset and severity. Gastroenterology 119:1483–1490
Brant SR, Panhuysen CI, Nicolae D, Reddy DM, Bonen DK, Karaliukas R, Zhang L, Swanson E, Datta LW, Moran T, Ravenhill G, Duerr RH, Achkar JP, Karban AS, Cho JH (2003a) MDR1 Ala893 polymorphism is associated with inflammatory bowel disease. Am J Hum Genet 73:1282–1292
Brant SR, Picco MF, Achkar JP, Bayless TM, Kane SV, Brzezinski A, Nouvet FJ, Bonen D, Karban A, Dassopoulos T, Karaliukas R, Beaty TH, Hanauer SB, Duerr RH, Cho JH (2003b) Defining complex contributions of NOD2/CARD15 gene mutations, age at onset, and tobacco use on Crohn’s disease phenotypes. Inflamm Bowel Dis 9:281–289
Cavanaugh J, Consortium IBDIG (2001) International collaboration provides convincing linkage replication in complex disease through analysis of a large pooled data set: Crohn disease and chromosome 16. Am J Hum Genet 68:1165–1171
Cho JH, Nicolae DL, Gold LH, Fields CT, LaBuda MC, Rohal PM, Pickles MR, Qin L, Fu Y, Mann JS, Kirschner BS, Jabs EW, Weber J, Hanauer SB, Bayless TM, Brant SR (1998) Identification of novel susceptibility loci for inflammatory bowel disease on chromosomes 1p, 3q, and 4q: evidence for epistasis between 1p and IBD1. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 95:7502–7507
Cottingham RW, Idury RM, Schaffer AA (1993) Fast sequential genetic linkage computation. Am J Hum Genet 53:252–263
Curtis D, Sham PC (1995) Model-free linkage analysis using likelihoods. Am J Hum Genet 57:703–716
Curtis D, Zhao JH, Sham PC (1999) Comparison of GENEHUNTER and MFLINK for analysis of COGA linkage data. Genet Epidemiol 17(Suppl 1):S115–S120
Duerr RH, Barmada MM, Zhang L, Davis S, Preston RA, Chensny LJ, Brown JL, Ehrlich GD, Weeks DE, Aston CE (1998) Linkage and association between inflammatory bowel disease and a locus on chromosome 12. Am J Hum Genet 63:95–100
Economou M, Trikalinos TA, Loizou KT, Tsianos EV, Ioannidis JP (2004) Differential effects of NOD2 variants on Crohn’s disease risk and phenotype in diverse populations: a metaanalysis. Am J Gastroenterol 99:2393–2404
Farndon PA, Del Mastro RG, Evans DG, Kilpatrick MW (1992) Location of gene for Gorlin syndrome. Lancet 339:581–582
Fujii K, Miyashita T, Omata T, Kobayashi K, Takanashi J, Kouchi K, Yamada M, Kohno Y (2003) Gorlin syndrome with ulcerative colitis in a Japanese girl. Am J Med Genet 121:65–68
Gorlin RJ (1987) Nevoid basal-cell carcinoma syndrome. Medicine 66:98–113
Gorlin RJ, Goltz RW (1960) Multiple nevoid basal-cell epithelioma, jaw cysts and bifid rib: a syndrome. N Engl J Med 262:908–912
Hampe J, Schreiber S, Shaw SH, Lau KF, Bridger S, Macpherson AJ, Cardon LR, Sakul H, Harris TJ, Buckler A, Hall J, Stokkers P, van Deventer SJ, Nurnberg P, Mirza MM, Lee JC, Lennard-Jones JE, Mathew CG, Curran ME (1999) A genomewide analysis provides evidence for novel linkages in inflammatory bowel disease in a large European cohort. Am J Hum Genet 64:808–816
van Heel DA, Fisher SA, Kirby A, Daly MJ, Rioux JD, Lewis CM (2004) Inflammatory bowel disease susceptibility loci defined by genome scan meta-analysis of 1952 affected relative pairs. Hum Mol Genet 13:763–770
Hugot JP, Chamaillard M, Zouali H, Lesage S, Cezard JP, Belaiche J, Almer S, Tysk C, O’Morain CA, Gassull M, Binder V, Finkel Y, Cortot A, Modigliani R, Laurent-Puig P, Gower-Rousseau C, Macry J, Colombel JF, Sahbatou M, Thomas G (2001) Association of NOD2 leucine-rich repeat variants with susceptibility to Crohn’s disease [comment]. Nature 411:599–603
Johnson RL, Rothman AL, Xie J, Goodrich LV, Bare JW, Bonifas JM, Quinn AG, Myers RM, Cox DR, Epstein EH, Jr., Scott MP (1996) Human homolog of patched, a candidate gene for the basal cell nevus syndrome. Science 272:1668–1671
Karban A, Eliakim R, Brant SR (2002) Genetics of inflammatory bowel disease [comment]. Isr Med Assoc J 4:798–802
Katz J, Savin R, Spiro HM (1968) The basal cell nevus syndrome and inflammatory disease of the bowel. Am J Med 44:483–488
Kimonis VE, Goldstein AM, Pastakia B, Yang ML, Kase R, DiGiovanna JJ, Bale AE, Bale SJ (1997) Clinical manifestations in 105 persons with nevoid basal cell carcinoma syndrome. Am J Med Genet 69:299–308
Kruglyak L, Daly MJ, Reeve-Daly MP, Lander ES (1996) Parametric and nonparametric linkage analysis: a unified multipoint approach. Am J Hum Genet 58:1347–1363
Lander E, Kruglyak L (1995) Genetic dissection of complex traits: guidelines for interpreting and reporting linkage results. Nat Genet 11:241–247
Loftus EV Jr. (2004) Clinical epidemiology of inflammatory bowel disease: Incidence, prevalence, and environmental influences. Gastroenterology 126:1504–1517
Markianos K, Daly MJ, Kruglyak L (2001) Efficient multipoint linkage analysis through reduction of inheritance space. Am J Hum Genet 68:963–977
O’Connell JR, Weeks DE (1998) PedCheck: a program for identification of genotype incompatibilities in linkage analysis. Am J Hum Genet 63:259–66
Ogura Y, Bonen DK, Inohara N, Nicolae DL, Chen FF, Ramos R, Britton H, Moran T, Karaliuskas R, Duerr RH, Achkar JP, Brant SR, Bayless TM, Kirschner BS, Hanauer SB, Nunez G, Cho JH (2001) A frameshift mutation in NOD2 associated with susceptibility to Crohn’s disease [comment]. Nature 411:603–606
Orholm M, Munkholm P, Langholz E, Nielsen OH, Sorensen IA, Binder V (1991) Familial occurrence of inflammatory bowel disease. N Engl J Med 324:84–88
Ott J (1989) Computer-simulation methods in human linkage analysis. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 86:4175–4178
Parkes M, Barmada MM, Satsangi J, Weeks DE, Jewell DP, Duerr RH (2000) The IBD2 locus shows linkage heterogeneity between ulcerative colitis and Crohn disease. Am J Hum Genet 67:1605–1610
Podolsky DK (1991a) Inflammatory bowel disease (1). N Engl J Med 325:928–937
Podolsky DK (1991b) Inflammatory bowel disease (2). N Engl J Med 325:1008–1016
Risch N (1990) Linkage strategies for genetically complex traits. II. The power of affected relative pairs. Am J Hum Genet 46:229–241
Roth MP, Petersen GM, McElree C, Vadheim CM, Panish JF, Rotter JI (1989) Familial empiric risk estimates of inflammatory bowel disease in Ashkenazi Jews. Gastroenterology 96:1016–1020
Satsangi J, Parkes M, Louis E, Hashimoto L, Kato N, Welsh K, Terwilliger JD, Lathrop GM, Bell JI, Jewell DP (1996) Two stage genome-wide search in inflammatory bowel disease provides evidence for susceptibility loci on chromosome 3, 7 and 12. Nat Genet 14:199–202
Sawyer CS, Braverman IM (1969) Basal cell nevus syndrome with inflammatory disease of the bowel. Arch Dermatol 99:131–132
Stoll M, Corneliussen B, Costello CM, Waetzig GH, Mellgard B, Koch WA, Rosenstiel P, Albrecht M, Croucher PJ, Seegert D, Nikolaus S, Hampe J, Lengauer T, Pierrou S, Foelsch UR, Mathew CG, Lagerstrom-Fermer M, Schreiber S (2004) Genetic variation in DLG5 is associated with inflammatory bowel disease. Nat Genet 36:476–480
Tukel T, Shalata A, Present D, Rachmilewitz D, Mayer L, Grant D, Risch N, Desnick RJ (2004) Crohn disease: frequency and nature of CARD15 mutations in Ashkenazi and Sephardi/Oriental Jewish families. Am J Hum Genet 74:623–636
Vermeire S, Rutgeerts P (2005) Current status of genetics research in inflammatory bowel disease. Genes Immun 6:637–645
Weber JL, May PE (1989) Abundant class of human DNA polymorphisms which can be typed using the polymerase chain reaction. Am J Hum Genet 44:388–396
Weeks DE, Ott J, Lathrop GM (1990) SLINK: a general simulation program for linkage analysis. Am J Hum Genet 47:A204
Wicking C, Bale AE (1997) Molecular basis of the nevoid basal cell carcinoma syndrome. Curr Opin Pediatr 9:630–635
Wicking C, Gillies S, Smyth I, Shanley S, Fowles L, Ratcliffe J, Wainwright B, Chenevix-Trench G (1997) De novo mutations of the Patched gene in nevoid basal cell carcinoma syndrome help to define the clinical phenotype. Am J Med Genet 73:304–307
Yuan B, Vaske D, Weber JL, Beck J, Sheffield VC (1997) Improved set of short-tandem-repeat polymorphisms for screening the human genome. Am J Hum Genet 60:459–460
Zlotogora J, Zimmerman J, Rachmilewitz D (1991) Prevalence of inflammatory bowel disease in family members of Jewish Crohn’s disease patients in Israel. Dig Dis Sci 36:471–475
Acknowledgements
We would like to thank all the participating family members for their time and engagement to enhance our understanding of the etiology of IBD and BCNS. We thank Dr. Patrick Rohal and Mr. Franklin Nouvet for technical and recruitment assistance. We thank Dr Ethylin Wang Jabs for her critical review of the manuscript. This study was funded in part by National Institutes of Health Grants R01DK58189 (C.I.P, S.R.B.) and RR00052 (S.R.B.), The Harvey M. and Lyn P. Meyerhoff IBD Center (A.S.K., T.M.B., and S.R.B.); Israeli Society of Gastroenterology (A.S.K.), the Mammalian Genotyping Service (National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute) (RHD), and the Stewart W. Bainum family (S.R.B.).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Carolien I. Panhuysen and Amir Karban contributed equally to this work
Electronic supplementary material
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Panhuysen, C.I., Karban, A., Knodle Manning, A. et al. Identification of genetic loci for basal cell nevus syndrome and inflammatory bowel disease in a single large pedigree. Hum Genet 120, 31–41 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00439-006-0163-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00439-006-0163-8