Abstract
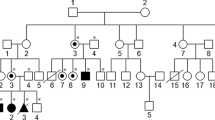
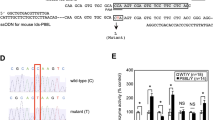
Nearly 300 different mutations underlying mucopolysaccharidosis type II (MPS II) have been identified worldwide. To investigate the molecular lesions underlying Taiwanese MPS II, probands and families were identified and screened for iduronate-2-sulfatase (IDS) mutation by single-strand conformation polymorphism and DNA sequencing. Five novel and five previously reported mutations were found. Together with those previously reported, a total of 17 identified missense, small deletion, and nonsense mutations were further characterized by transient expression studies. Transfection of COS-7 cells by the mutated cDNA did not yield active enzyme, demonstrating the deleterious nature of the mutations. A 57% decrease in IDS mRNA level was seen with the 231del6 mutation. Among the 11 missense mutations examined, K347E substitution showed apparent normal maturation and targeting on immunoblot and confocal fluorescence microscopy examination. The other 10 missense mutations showed apparent normal precursor with little or reduced mature forms, indicating normal maturation but incorrect targeting of the mutant enzymes. Among the six deletion and nonsense mutations examined, 1055del12 and E521X showed abnormal maturation. The staining pattern of the truncated W267X and 1184delG proteins suggested retention within early vacuolar compartments. The mutated 231del6 and 1421delAG proteins were unstable and largely degraded. Molecular analysis of the IDS gene will clearly identify the cause of the disease within patients and allow antenatal and family studies. The further characterization of gene mutations may delineate their functional consequences on IDS activity and processing and may enable future studies of genotype–phenotype correlation to estimate a prognosis and to lead to possible therapeutic interventions.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bonuccelli G, Di Natale P, Corsolini F, Villani G, Filocamo M (2001) The effect of four mutations on the expression of iduronate-2-sulfatase in mucopolysaccharidosis type II. Biochim Biophys Acta 1537:233–238
Bunge S, Steglich C, Beck M, Rosenkranz W, Schwinger E, Hopwood JJ, Gal A (1992) Mutation analysis of the iduronate-2-sulfatase gene in patients with mucopolysaccharidosis type II (Hunter syndrome). Hum Mol Genet 1:335–339
Cooper DN, Youssoufian H (1998) The CpG dinucleotide and human genetic disease (review). Hum Genet 78:151–155
Crotty PL, Braun SE, Anderson RA, Whitley CB (1992) Mutation R468W of the iduronate-2-sulfatase gene in mild Hunter syndrome (mucopolysaccharidosis type II) confirmed by in vitro mutagenesis and expression. Hum Mol Genet 1:755–757
Cudry S, Tigaud I, Froissart R, Bonnet V, Maire I, Bozon D (2000) MPS II in females: molecular basis of two different cases. J Med Genet 37:e29
Daniele A, Faust CJ, Herman GE, Di Natale P, Ballabio A (1993) Cloning and characterization of the cDNA for the murine iduronate sulfatase gene. Genomics 16:755–757
Flomen RH, Green EP, Green PM, Bentley DR, Giannelli F (1993) Determination of the organization of coding sequences within the iduronate sulphate sulphatase (IDS) gene. Hum Mol Genet 2:5–10
Froissart R, Millat G, Mathieu M, Bozon D, Maire IL (1995) Processing of iduronate-2-sulphatase in human fibroblasts. Biochem J 309:425–430
Froissart R, Maire I, Millat G, Cudry S, Birot AM, Bonnet V, Bouton O, Bozon D (1998) Identification of iduronate sulfatase gene alterations in 70 unrelated Hunter patients. Clin Genet 53:362–368
Lee-Chen GJ, Lin SP, Lin SZ, Chuang CK, Hsiao KT, Huang CF, Lien WC (2002) Identification and characterization of mutations underlying Sanfilippo syndrome type B (mucopolysaccharidosis type IIIB). J Med Genet 39:e3
Lin SP, Chuang CK, Tsai PJ, Chang JG, Wraith JE (2000) Molecular basis of mucopolysaccharidosis type II in Taiwan Chinese. Eur J Hum Genet 8:P-183
Millat G, Froissart R, Maire I, Bozon D (1997) Characterization of iduronate sulphatase mutants affecting N-glycosylation sites and the cysteine-84 residue. Biochem J 326:243–247
Millat G, Froissart R, Cudry S, Bonnet V, Maire I, Bozon D (1998) COS cell expression studies of P86L, P86R, P480L and P480Q Hunter’s disease-causing mutations. Biochim Biophys Acta 1406:214–218
Moskowitz SM, Tieu PT, Neufeld EF (1993) A deletion/insertion mutation in the IDUA gene in a Libyan Jewish patient with Hurler syndrome (mucopolysaccharidosis IH). Hum Mutat 2:71–73
Neufeld EF, Muenzer J (2001) The mucopolysaccharidoses. In: Scriver CR, Beaudet AL, Sly WS, Valle D, Childs B, Vogelstein B (eds) The metabolic and molecular bases of inherited disease, 8th edn. McGraw-Hill, New York, pp 3421–3452
Rathmann M, Bunge S, Beck M, Kresse H, Tylki-Szymanska A, Gal A (1996) Mucopolysaccharidosis type II (Hunter syndrome): mutation “hot spots” in the iduronate-2-sulfatase gene. Am J Hum Genet 59:1202–1209
Ricci V, Filocamo M, Regis S, Corsolini F, Stroppiano M, Duca MD, Gatti R (2003) Expression studies of two novel in CIS-mutations identified in an intermediate case of Hunter syndrome. Am J Med Genet 120A:84–87
Stenson PD, Ball EV, Mort M, Phillips AD, Shiel JA, Thomas NS, Abeysinghe S, Krawczak M, Cooper DN (2003) Human gene mutation database (HGMD): 2003 update. Hum Mutat 21:577–581
Sukegawa K, Tomatsu S, Fukao T, Iwata H, Song XQ, Yamada Y, Fukuda S, Isogai K, Orii T (1995) Mucopolysaccharidosis type II (Hunter disease): identification and characterization of eight point mutations in the iduronate-2-sulfatase gene in Japanese patients. Hum Mutat 6:136–143
Villani GRD, Daniele A, Balzano N, Di Natale P (2000) Expression of five iduronate-2-sulfatase site-directed mutations. Biochim Biophys Acta 1501:71–80
Wilson PJ, Morris CP, Anson DS, Occhiodoro T, Bielicki J, Clements PR, Hopwood JJ (1990) Hunter syndrome: isolation of an iduronate-2-sulfatase cDNA clone and analysis of patient DNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 87:8531–8535
Wilson PJ, Meaney CA, Hopwood JJ, Morris CP (1993) Sequence of the human iduronate-2-sulfatase (IDS) gene. Genomics 17:773–775
Acknowledgements
We thank the patients’ families for their support. We are also grateful to Dr. Mary Jeanne Buttrey for critical review of the manuscript. The Taiwan Foundation for Rare Disorders is specially acknowledged for providing a thesis scholarship. This work was supported by grants NSC-90-2311-B-003-004, NSC-91-2311-B-003-002, and NSC-92-2311-B-003-003 from the National Science Council, Executive Yuan, ROC.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Jui-Hung Chang and Shuan-Pei Lin contributed equally to this work
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chang, JH., Lin, SP., Lin, SC. et al. Expression studies of mutations underlying Taiwanese Hunter syndrome (mucopolysaccharidosis type II). Hum Genet 116, 160–166 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00439-004-1234-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00439-004-1234-3