Abstract
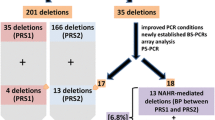
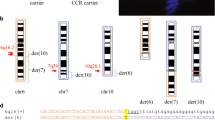
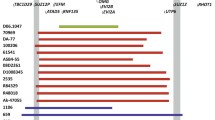
NF1 microdeletion syndrome is caused by haploinsufficiency of the NF1 gene and of gene(s) located in adjacent flanking regions. Most of the NF1 deletions originate by non-allelic homologous recombination between repeated sequences (REP-P and -M) mapped to 17q11.2, while the remaining deletions show unusual breakpoints. We performed high-resolution FISH analysis of 18 NF1 microdeleted patients with the aims of mapping non-recurrent deletion breakpoints and verifying the presence of additional recombination-prone architectural motifs. This approach allowed us to obtain the sequence of the first junction fragment of an atypical deletion. By conventional FISH, we identified 16 patients with REP-mediated common deletions, and two patients carrying atypical deletions of 1.3 Mb and 3 Mb. Following fibre-FISH, we identified breakpoint regions of 100 kb, which led to the generation of several locus-specific probes restricting the atypical deletion endpoint intervals to a few kilobases. Sequence analysis provided evidence of small blocks of REPs, clustered around the 1.3-Mb deletion breakpoints, probably involved in intrachromatid non-allelic homologous recombination (NAHR), while isolation and sequencing of the 3-Mb deletion junction fragment indicated that a non-homologous end joining (NHEJ) mechanism is implicated.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abeysinghe SS, Chuzhanova N, Krawczak M, Ball EV, Cooper DN (2003) Translocation and gross deletion breakpoints in human inherited disease and cancer. I: Nucleotide composition and recombination-associated motifs. Hum Mutat 22:229–244
Amati F, Conti E, Novelli A, Bengala M, Diglio MC, Marino B, Giannotti A, Gabrielli O, Novelli G, Dallapiccola B (1999) Atypical deletions suggest five 22q11.2 critical regions related to the DiGeorge/velo-cardio-facial syndrome. Eur J Hum Genet 7:903–909
Amos-Landgraf JM, Ji Y, Gottlieb W, Depinet T, Wandstrat AE, Cassidy SB, Driscoll DJ, Rogan PK, Schwartz S, Nicholls RD (1999) Chromosome breakage in the Prader-Willi and Angelman syndromes involves recombination between large, transcribed repeats at proximal and distal breakpoints. Am J Hum Genet 65:370–386
Bayes M, Magano LF, Rivera N, Flores R, A Perez Jurado L (2003) Mutational mechanisms of Williams-Beuren syndrome deletions Am J Hum Genet 73:131–151
Bentivegna A, Venturin M, Gervasini C, Corrado L, Larizza L, Riva P (2001) Identification of duplicated genes in 17q11.2 by using FISH on stretched chromosomes and DNA fibers. Hum Genet 109:48–54
Breen M, Arveiler B, Murray I, Gosden JR, Porteous DJ (1992) YAC mapping by FISH using Alu-PCR-generated probes. Genomics 13:726–730
Bromme D, Rossi AB, Smeekens SP, Anderson DC, Payan DG (1996) Human bleomycin hydrolase: molecular cloning, sequencing, functional expression, and enzymatic characterization. Biochemistry 35:6706–6714
Cnossen MH, van der Est MN, Breuning MH, van Asperen CJ, Breslau-Siderius EJ, van der Ploeg AT, de Goede-Bolder A, van den Ouweland AM, Halley DJ, Niermeijer MF (1997) Deletions spanning the neurofibromatosis type 1 gene: implications for genotype-phenotype correlations in neurofibromatosis type 1? Hum Mutat 9:458–464
Corrado L, Riva P, Venturin M, Bentivegna A, Gervasini C, Larizza L (2000) Mapping of genes and ESTs assigned to 17q11.2 to a YAC contig centered on the NF1 gene. Gene Screen 1:21–27
De Raedt T, Brems H, Wolkenstein P, Vidaud D, Pilotti S, Perrone F, Mautner V, Frahm S, Sciot R, Legius E (2003) Elevated risk for MPNST in NF1 microdeletion patients. Am J Hum Genet 72:1288–1292
Dorschner MO, Sybert VP, Weaver M, Pletcher BA, Stephens K (2000) NF1 microdeletion breakpoints are clustered at flanking repetitive sequences. Hum Mol Genet 9:35–46
Haaf T, Ward DC (1994) Structural analysis of α-satellite DNA and centromere proteins using extended chromatin and chromosomes. Hum Mol Genet 3:697–709
Huson SM, Hughes RC (1994) The neurofibromatosis: a clinical and pathogenetic overview. Chapman and Hall, London
Inoue K, Osaka H, Thurston VC, Clarke JTR, Yoneyama A, Rosenbark L, Bird TD, Hodes ME, Shaffer LG, Lupski JR (2002) Genomic Rearrangements resulting in PLP1 deletion occur by nonhomologous end joining and cause different dysmyelinating phenotipes in males and females Am J Hum Genet 71:838–853
Jenne DE, Tinschert S, Stegmann E, Reimann H, Nurnberg P, Horn D, Naumann I, Buske A, Thiel G (2000) A common set of at least 11 functional genes is lost in the majority of NF1 patients with gross deletions. Genomics 66:93–97
Jenne DE, Tinschert S, Reimann H, Lasinger W, Thiel G, Hameister H, Kehrer-Sawatzki H (2001) Molecular characterization and gene content of breakpoint boundaries in patients with neurofibromatosis type 1 with 17q11.2 microdeletions. Am J Hum Genet 69:516–527
Jenne DE, Tinschert S, Dorschner MO, Hameister H, Stephens K, Kehrer-Sawatzki H (2003) Complete physical map and gene content of the human NF1 tumor suppressor region in human and mouse. Genes Chromosomes Cancer 37:111–120
Kehrer-Sawatzki H, Tinschert S, Jenne DE (2003) Heterogeneity of breakpoints in non-LCR-mediated large constitutional deletions of the 17q11.2 NF1 tumor suppressor region. J Med Genet: e-letter e116
Kurahashi H, Tsuda E, Kohama R, Nakayama T, Masuno M, Imaizumi K, Kamiya T, Sano T, Okada S, Nishisho I (1997) Another critical region for deletion of 22q11: a study of 100 patients. Am J Med Genet 72:180–185
Kurahashi H, Shaikh T, Takata M, Toda T, Emanuel BS (2003) The constitutional t(17;22): another translocation mediated by palindromic AT-rich repeats. Am J Hum Genet 72:733–738
Leppig KA, Kaplan P, Viskochil D, Weaver M, Ortenberg J, Stephens K (1997) Familial neurofibromatosis 1 microdeletions: cosegregation with distinct facial phenotype and early onset of cutaneous neurofibroma. Am J Med Genet 73:197–204
Lichter P, Cremer T (1992) A pratical approach. In: Rooney DE Czipolkowski BH (eds) Human cytogenetics. IRL Press at Oxford University Press, Oxford, pp 157–192
Lopez Correa C, Brems H, Lazaro C, Marynen P, Legius E (2000) Unequal meiotic crossover: a frequent cause of NF1 microdeletions. Am J Hum Genet 66:1969–1974
Lopez Correa C, Dorschner M, Brems H, Lazaro C, Clementi M, Upadhyaya M, Dooijes D, Moog U, Kehrer-Sawatzki H, Rutkowski JL, Fryns JP, Marynen P, Stephens K, Legius E (2001) Recombination hotspot in NF1 microdeletion patients. Hum Mol Genet 10:1387–1392
McQuade L, Christodoulou J, Budarf ML, Sachdev R, Wilson M, Emanuel B, Colley A (1999) A further case of a 22q11.2 deletion with no overlap of the minimal DiGeorge Syndrome critical region (MDGCR). The involvement of the TBX1 and COMT genes in the deletion and the clinical phenotype. Am J Med Genet 86:27–33
Otto E, Betz R, Rensing C, Schätzle S, Kuntzen T, Vetsi T, Imm A, and Hildebrandt F (2000) A deletion distinct from the classical homologous recombination of juvenile nephronophthisis type 1 (NPH1) allows exact molecular definition of deletion breakpoints. Hum Mut 16:211–223
Passarge E (2000) A distinctive phenotype associated with an interstitial deletion 6q14 contained within a de novo pericentric inversion 6 (p112q15). Cytogenet Cell Genet 91:192–198
Petek E, Jenne DE, Smolle J, Binder B, Lasinger W, Windpassinger C, Wagner K, Kroisel PM, Kehrer-Sawatzki H (2003) Mitotic recombination mediated by the JJAZF1 (KIAA0160) gene causing somatic mosaicism and a new type of constitutional NF1 microdeletion in two children of a mosaic female with only few manifestations. J Med Genet 40:520–525
Povey S, Lovering R, Bruford E, Wright M, Lush M, Wain H (2001) The HUGO Gene Nomenclature Committee (HGNC). Hum Genet 109:678–680
Rasmussen SA, Colman SD, Ho VT, Abernathy CR, Arn PH, Weiss L, Schwartz C, Saul RA, Wallace MR (1998) Constitutional and mosaic large NF1 gene deletions in neurofibromatosis type 1. J Med Genet 35:468–471
Rauch A, Pfeiffer RA, Leipold G, Singer H, Tigges M and Hofbeck M. (1999) A novel 22q11.2 microdeletion in DiGeorge Syndrome. Am J Hum Genet 64:659–667
Riva P, Castorina P, Manoukian S, Dalpra L, Doneda L, Marini G, den Dunnen J, Larizza L (1996) Characterization of a cytogenetic 17q11.2 deletion in an NF1 patient with a contiguous gene syndrome. Hum Genet 98:646–650
Riva P, Corrado L, Colapietro P, Larizza L (1999) A rapid and simple method of generating locus-specific probes for FISH analysis. Technical Tips Online (http://tto.trends.com) T01618
Riva P, Corrado L, Natacci F,Castorina P,Wu BL, Schneider GH, Clementi M, Tenconi R, Korf BR, Larizza L (2000) NF1 microdeletion syndrome: refined fish characterization of sporadic and familial deletions with locus-specific probes. Am J Hum Genet 66:100–109
Shaikh TH, Kurahashi H, Saitta SC, O’Hare AM, Hu P, Roe BA, Driscoll DA, McDonald-McGinn DM, Zackai EH, Budarf ML, Emanuel BS (2000) Chromosome 22-specific low copy repeats and the 22q11.2 deletion syndrome: genomic organization and deletion endpoint analysis. Hum Mol Genet 9:489–501
Shaw CJ, Bi W, Lupski JR (2002) Genetic proof of unequal meiotic crossovers in reciprocal deletion and duplication of 17p11.2 Am J Hum Genet 71:1072–1081
Stankiewicz P, Shaw CJ, Dapper JD, Wakui K, Shaffer LG, Withers M, Elizondo L, Park SD Lupski JR (2003) Genome architecture catalyzes non recurrent chromosomal rearrangements. Am J Hum Genet 72:1101–1116
Thomas NS, Browne CE, Oley C, Haley S, Crolla JA (1999) Investigation of a cryptic interstitial duplication involving the Prader-Willi/Angelman syndrome critical region. Hum Genet 105:384–387
Tonsgard JH, Yelavarthi KK, Cushner S, Short MP, Lindgren V (1997) Do NF1 gene deletions result in a characteristic phenotype? Am J Med Genet 73:80–86
Upadhyaya M, Ruggieri M, Maynard J, Osborn M, Hartog C, Mudd S, Penttinen M, Cordeiro I, Ponder M, Ponder BA, Krawczak M, Cooper DN (1998) Gross deletions of the neurofibromatosis type 1 (NF1) gene are predominantly of maternal origin and commonly associated with a learning disability, dysmorphic features and developmental delay. Hum Genet 102:591–597
Van Roy N, Laureys G, Van Gele M, Opdenakker G, Miura R, van der Drift, Chan A, Versteeg R, Speleman F (1997) Analysis of 1;17 translocation breakpoints in neuroblastoma: implications for mapping of neuroblastoma genes. Eur J Cancer 33:1974–1978
Valero MC, Pascual-Castroviejo I, Velasco E, Moreno F, Hernandez-Chico C (1997) Identification of de novo deletions at the NF1 gene: no preferential paternal origin and phenotypic analysis of patients. Hum Genet 99:720–726
Valero MC, de Luis O, Cruces J, Perez Jurado LA (2000) Fine-scale comparative mapping of the human 7q11.23 region and the orthologous region on mouse chromosome 5G: the low-copy repeats that flank the Williams-Beuren syndrome deletion arose at breakpoint sites of an evolutionary inversion(s). Genomics 69:1–13
Van Roy N, Vandesompele J, Berx G, Staes K, Van Gele M, De Smet E, De Paepe A, Laureys G, van der Drift P, Versteeg R, Van Roy F, Speleman F (2002) Localization of the 17q breakpoint of a constitutional 1;17 translocation in a patient with neuroblastoma within a 25-kb segment located between the ACCN1 and TLK2 genes and near the distal breakpoints of two microdeletions in neurofibromatosis type 1 patients. Genes Chromosomes Cancer 35:113–120
Venturin M, Guanieri P, Natacci F, Stabile M, Tenconi R, Clementi M, Hernandez C, Thompson P, Upadhyaya M, Larizza L, Riva P (2004) Mental retardation and cardiovascular malformations in NF1-microdeleted patients point to candidate genes in 17q11.2. J Med Genet 41:35–41
Waldman AS, Liskay RM (1988) Dependence of intrachromosomal recombination in mammalian cells on uninterrupted homology. Mol Cell Biol 8:5350–5357
Acknowledgements
The authors thank Dr. C. Sala (YAC Screening Center HSR-DIBIT, Milan) for providing BAC and PAC clones, Dr. F. Natacci for valuable clinical evaluation of NF1 patients, Dr. D. Jenne for providing DJ2290 and DJ2314 primers and useful suggestions for REP-PCR assay. This work was supported by FIRST (P.R.) and Italian Ministry of Health on Neurofibromatosis 1 (1999–2000).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
M. Venturin and C. Gervasini contributed equally to the study
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Venturin, M., Gervasini, C., Orzan, F. et al. Evidence for non-homologous end joining and non-allelic homologous recombination in atypical NF1 microdeletions. Hum Genet 115, 69–80 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00439-004-1101-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00439-004-1101-2