Abstract
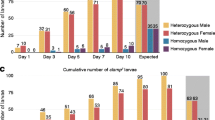
Stable activation of the Drosophila sex determination gene Sex-lethal in the female embryo is a multistep process. Early in embryogenesis Sex-lethal is regulated at the level of transcription, and then later in embryogenesis Sex-lethal regulation switches to an autoregulatory RNA splicing mechanism. Previous studies have shown that successful activation of Sxl requires both maternally and zygotically provided gene products, many of which are essential for viability and have other, non-sex specific functions. Using a screen for dosage-sensitive modifiers we identified a new maternally expressed gene, l(2)49Db, as a likely participant in Sxl activation. We show that the establishment of the Sxl autoregulatory splicing loop, but not the earlier steps in Sxl activation, is sensitive to the maternal dosage of l(2)49Db. We further demonstrate that l(2)49Db encodes an aspartyl tRNA synthetase. Finally we present evidence that this effect is indirect, by demonstrating that mutations in tryptophanyl tRNA synthetase are also dosage-sensitive maternal modifiers of Sex-lethal. These data suggest that stable activation of Sex-lethal in the embryo may be particularly sensitive to perturbation of the translational machinery.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Received: 10 September 1998 / Accepted: 20 October 1998
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Stitzinger, S., Pellicena-Palle, A., Albrecht, E. et al. Mutations in the predicted aspartyl tRNA synthetase of Drosophila are lethal and function as dosage-sensitive maternal modifiers of the sex determination gene Sex-lethal . Mol Gen Genet 261, 142–151 (1999). https://doi.org/10.1007/s004380050951
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s004380050951