Abstract
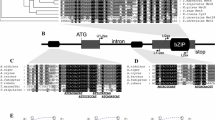
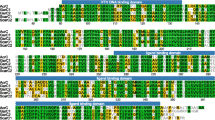
Genetic studies have indicated that the facB gene of Aspergillus nidulans is a major regulatory gene involved in acetamide and acetate utilisation. Sequencing of the facB gene revealed that it encodes a protein that contains an N-terminal GAL4-like Zn(II)2Cys6 (or C6 zinc) binuclear cluster for DNA binding, leucine zipper-like heptad repeat motifs and central and C-terminal acidic α-helical regions, consistent with a function as a DNA-binding transcriptional activator. The Zn(II)2Cys6 cluster shows strong similarity with those of the Saccharomyces cerevisiae carbon metabolism regulatory proteins CAT8 and SIP4. A significant level of similarity with CAT8 is found throughout the length of the protein, suggesting at least partial functional homology. The facB genes of Aspergillus oryzae and Aspergillus niger were also sequenced and found to be highly conserved. Deletion of the facB gene confirmed that it is required for growth on acetate as a sole carbon source. Functional dissection using deletion and fusion constructs and in vitro mutagenesis indicated that the Zn(II)2Cys6 cluster and the C-terminal end of the protein are required for function.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Received: 15 September 1996 / Accepted: 2 December 1996
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Todd, R., Murphy, R., Martin, H. et al. The acetate regulatory gene facB of Aspergillus nidulans encodes a Zn(II)2Cys6 transcriptional activator. Mol Gen Genet 254, 495–504 (1997). https://doi.org/10.1007/s004380050444
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s004380050444