Abstract
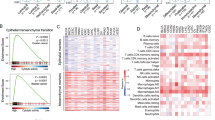
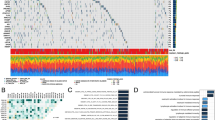
This study examines the prognostic role and immunological relevance of EMP1 (epithelial membrane protein-1) in a pan-cancer analysis, with a focus on ovarian cancer. Utilizing data from TCGA, CCLE, and GTEx databases, we assessed EMP1 mRNA expression and its correlation with tumor progression, prognosis, and immune microenvironment across various cancers. Our results indicate that EMP1 expression is significantly associated with poor prognosis in multiple cancer types, including ovarian, bladder, testicular, pancreatic, breast, brain, and uveal melanoma. Immune-related analyses reveal a positive correlation between EMP1 and immune cell infiltration, particularly neutrophils, macrophages, and dendritic cells, as well as high expression of immune checkpoint such as CD274, HAVCR2, IL10, PDCD1LG2, and TGFB1 in most tumors. In vivo experiments confirm that EMP1 promotes ovarian cancer cell proliferation, metastasis, and invasion. In conclusion, EMP1 emerges as a potential prognostic biomarker and therapeutic target in various cancers, particularly ovarian cancer, due to its influence on tumor progression and immune cell dynamics. Further research is warranted to elucidate the precise mechanisms of EMP1 in cancer biology and to translate these findings into clinical applications.









Similar content being viewed by others
Availability of data and materials
The RNA-sequencing data and corresponding clinical information were downloaded from The Cancer Genome Atlas (TCGA) database (https://portal.gdc.cancer.gov/), the Genotype-Tissue Expression (GTEx) (https://www.gtexportal.org/) and the Broad Institute Cancer Cell Line Encyclopedia (CCLE) (https://sites.broadinstitute.org/ccle/). The datasets used and/or analyzed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
References
Ariës IM, Jerchel IS, van den Dungen RE, van den Berk LC, Boer JM, Horstmann MA, Escherich G, Pieters R, den Boer ML (2014) EMP1, a novel poor prognostic factor in pediatric leukemia regulates prednisolone resistance, cell proliferation, migration and adhesion. Leukemia 28(9):1828–1837. https://doi.org/10.1038/leu.2014.80
Chen Y, Xu T, Xie F, Wang L, Liang Z, Li D, Liang Y, Zhao K, Qi X, Yang X, Jiao W (2021) Evaluating the biological functions of the prognostic genes identified by the Pathology Atlas in bladder cancer. Oncol Rep 45(1):191–201. https://doi.org/10.3892/or.2020.7853
Cheng S, Jiang Z, Xiao J, Guo H, Wang Z, Wang Y (2020) The prognostic value of six survival-related genes in bladder cancer. Cell Death Discov 6:58. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41420-020-00295-x
Dhodapkar MV, Dhodapkar KM (2020) Tissue-resident memory-like T cells in tumor immunity: Clinical implications. Semin Immunol 49:101415. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.smim.2020.101415
Echevarria MI, Awasthi S, Cheng CH, Berglund AE, Rounbehler RJ, Gerke TA, Takhar M, Davicioni E, Klein EA, Freedland SJ, Ross AE, Schaeffer EM, Den RB, Cleveland JL, Park JY, Rayford W, Yamoah K (2019) African American specific gene panel predictive of poor prostate cancer outcome. J Urol 202(2):247–255. https://doi.org/10.1097/ju.0000000000000193
Fruman DA, Rommel C (2014) PI3K and cancer: lessons, challenges and opportunities. Nat Rev Drug Discovery 13(2):140–156. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrd4204
Garner H, de Visser KE (2020) Immune crosstalk in cancer progression and metastatic spread: a complex conversation. Nat Rev Immunol 20(8):483–497. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41577-019-0271-z
Gyorffy B, Lánczky A, Szállási Z (2012) Implementing an online tool for genome-wide validation of survival-associated biomarkers in ovarian-cancer using microarray data from 1287 patients. Endocr Relat Cancer 19(2):197–208. https://doi.org/10.1530/erc-11-0329
Hinshaw DC, Shevde LA (2019) The tumor microenvironment innately modulates cancer progression. Can Res 79(18):4557–4566. https://doi.org/10.1158/0008-5472.Can-18-3962
Kaochar S, Dong J, Torres M, Rajapakshe K, Nikolos F, Davis CM, Ehli EA, Coarfa C, Mitsiades N, Poulaki V (2018) ICG-001 exerts potent anticancer activity against uveal melanoma cells. Invest Ophthalmol vis Sci 59(1):132–143. https://doi.org/10.1167/iovs.17-22454
Kennedy LB, Salama AKS (2020) A review of cancer immunotherapy toxicity. CA Cancer J Clin 70(2):86–104. https://doi.org/10.3322/caac.21596
Lai S, Wang G, Cao X, Li Z, Hu J, Wang J (2012) EMP-1 promotes tumorigenesis of NSCLC through PI3K/AKT pathway. J Huazhong Univ Sci Technolog Med Sci 32(6):834–838. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11596-012-1043-1
Lánczky A, Győrffy B (2021) Web-based survival analysis tool tailored for medical research (KMplot): development and implementation. J Med Internet Res 23(7):e27633. https://doi.org/10.2196/27633
Lei X, Lei Y, Li JK, Du WX, Li RG, Yang J, Li J, Li F, Tan HB (2020) Immune cells within the tumor microenvironment: Biological functions and roles in cancer immunotherapy. Cancer Lett 470:126–133. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.canlet.2019.11.009
Li H, Zhang X, Jiang X, Ji X (2017a) The expression and function of epithelial membrane protein 1 in laryngeal carcinoma. Int J Oncol 50(1):141–148. https://doi.org/10.3892/ijo.2016.3782
Li T, Fan J, Wang B, Traugh N, Chen Q, Liu JS, Li B, Liu XS (2017b) TIMER: a web server for comprehensive analysis of tumor-infiltrating immune cells. Cancer Res 77(21):e108–e110. https://doi.org/10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-17-0307
Li TW, Fu JX, Zeng ZX, Cohen D, Li J, Chen QM, Li B, Liu XS (2020) TIMER2.0 for analysis of tumor-infiltrating immune cells. Nucleic Acids Res 48(W1):W509–W514. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gkaa407
Liao Y, Wang J, Jaehnig EJ, Shi Z, Zhang B (2019) WebGestalt 2019: gene set analysis toolkit with revamped UIs and APIs. Nucleic Acids Res 47(W1):W199–W205. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gkz401
Lin B, Zhang T, Ye X, Yang H (2020a) High expression of EMP1 predicts a poor prognosis and correlates with immune infiltrates in bladder urothelial carcinoma. Oncol Lett 20(3):2840–2854. https://doi.org/10.3892/ol.2020.11841
Lin SY, Miao YR, Hu FF, Hu H, Zhang Q, Li Q, Chen Z, Guo AY (2020b) A 6-Membrane Protein Gene score for prognostic prediction of cytogenetically normal acute myeloid leukemia in multiple cohorts. J Cancer 11(1):251–259. https://doi.org/10.7150/jca.35382
Liu SH, Shen PC, Chen CY, Hsu AN, Cho YC, Lai YL, Chen F-H, Li C-Y, Wang S-C, Chen M, Chung I-F, Cheng WC (2020a) DriverDBv3: a multi-omics database for cancer driver gene research. Nucleic Acids Res 48(D1):D863–D870. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gkz964
Liu Y, Ding Y, Nie Y, Yang M (2020b) EMP1 promotes the proliferation and invasion of ovarian cancer cells through activating the MAPK pathway. Onco Targets Ther 13:2047–2055. https://doi.org/10.2147/OTT.S240028
Morad G, Helmink BA, Sharma P, Wargo JA (2021) Hallmarks of response, resistance, and toxicity to immune checkpoint blockade. Cell 184(21):5309–5337. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cell.2021.09.020
Newman AM, Liu CL, Green MR, Gentles AJ, Feng W, Xu Y, Hoang CD, Diehn M, Alizadeh AA (2015) Robust enumeration of cell subsets from tissue expression profiles. Nat Methods 12(5):453–457. https://doi.org/10.1038/nmeth.3337
Ru BB, Wong CN, Tong Y, Zhong JY, Zhong SSW, Wu WC, Chu KC, Wong CY, Lau CY, Chen I, Chan NW, Zhang JW (2019) TISIDB: an integrated repository portal for tumor-immune system interactions. Bioinformatics 35(20):4200–4202. https://doi.org/10.1093/bioinformatics/btz210
Shah S, Brock EJ, Ji K, Mattingly RR (2019) Ras and Rap1: a tale of two GTPases. Semin Cancer Biol 54:29–39. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.semcancer.2018.03.005
Singh J, Kumari S, Arora M, Verma D, Palanichamy JK, Kumar R, Sharma G, Bakhshi S, Pushpam D, Ali MS, Ranjan A, Tanwar P, Chauhan SS, Singh A, Chopra A (2021) Prognostic relevance of expression of EMP1, CASP1, and NLRP3 genes in pediatric B-lineage acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Front Oncol 11:606370. https://doi.org/10.3389/fonc.2021.606370
Sun G, Zhao G, Lu Y, Wang Y, Yang C (2014a) Association of EMP1 with gastric carcinoma invasion, survival and prognosis. Int J Oncol 45(3):1091–1098. https://doi.org/10.3892/ijo.2014.2488
Sun GG, Lu YF, Fu ZZ, Cheng YJ, Hu WN (2014b) EMP1 inhibits nasopharyngeal cancer cell growth and metastasis through induction apoptosis and angiogenesis. Tumour Biol 35(4):3185–3193. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13277-013-1416-5
Sun L, Kees T, Almeida AS, Liu B, He XY, Ng D, Han X, Spector DL, McNeish IA, Gimotty P, Adams S, Egeblad M (2021) Activating a collaborative innate-adaptive immune response to control metastasis. Cancer Cell 39(10):1361-1374.e1369. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ccell.2021.08.005
Sung H, Ferlay J, Siegel RL, Laversanne M, Soerjomataram I, Jemal A, Bray F (2021) Global Cancer Statistics 2020: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA Cancer J Clin 71(3):209–249. https://doi.org/10.3322/caac.21660
Vasaikar SV, Straub P, Wang J, Zhang B (2018) LinkedOmics: analyzing multi-omics data within and across 32 cancer types. Nucleic Acids Res 46(D1):D956–D963. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gkx1090
Wang HT, Kong JP, Ding F, Wang XQ, Wang MR, Liu LX, Wu M, Liu ZH (2003) Analysis of gene expression profile induced by EMP-1 in esophageal cancer cells using cDNA microarray. World J Gastroenterol 9(3):392–398. https://doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v9.i3.392
Wang YW, Cheng HL, Ding YR, Chou LH, Chow NH (2017) EMP1, EMP 2, and EMP3 as novel therapeutic targets in human cancer. Biochim Biophys Acta Rev Cancer 1868(1):199–211. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbcan.2017.04.004
Wang J, Li X, Wu H, Wang H, Yao L, Deng Z, Zhou Y (2019) EMP1 regulates cell proliferation, migration, and stemness in gliomas through PI3K-AKT signaling and CD44. J Cell Biochem 120(10):17142–17150. https://doi.org/10.1002/jcb.28974
Wang M, Liu T, Hu X, Yin A, Liu J, Wang X (2020) EMP1 promotes the malignant progression of osteosarcoma through the IRX2/MMP9 axis. Panminerva Med 62(3):150–154. https://doi.org/10.23736/s0031-0808.20.03913-0
Yan Z, Wang Q, Zhao S, Xie L, Zhang L, Han Y, Zhang B, Li H, Guo X (2021) OSov: an interactive web server to evaluate prognostic biomarkers for ovarian cancer. Biology (basel) 11(1):23. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology11010023
Zhang G, Fan E, Yue G, Zhong Q, Shuai Y, Wu M, Feng G, Chen Q, Gou X (2019) Five genes as a novel signature for predicting the prognosis of patients with laryngeal cancer. J Cell Biochem. https://doi.org/10.1002/jcb.29535
Zou X, Wei Y, Qi T, Wang X, Zuo W, Wang T, Zhu W, Zhou X (2021) A novel 6-gene signature derived from tumor-infiltrating T cells and neutrophils predicts survival of bladder urothelial carcinoma. Aging (albany NY) 13(23):25496–25517. https://doi.org/10.18632/aging.203770
Acknowledgements
We would like to gratefully acknowledge contributions from TCGA, CCLE and GTEx.
Funding
This work was supported by funds including the National Key Research and Development Program of China (grant nos. 2018YFC1002804 and 2016YFC1000600), the National Natural Science Foundation of China (grant nos. 81771618, 81971356).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
BY and JZ conceived and designed the research. JZ and XL collected and conducted data under the instruction of BY. JY supervised the study and provided funds. BY, LM, YZ participant in vivo experiments. JZ wrote the initial paper and BY revised the paper. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval
All related experiments were performed in accordance with the Declaration of Helsinki and ethical approval was obtained from the Ethics Committee of the Renmin Hospital of Wuhan University. All patients provided written informed consent.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Additional information
Communicated by Wenfei Jin.
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, J., Yang, J., Li, X. et al. EMP1 correlated with cancer progression and immune characteristics in pan-cancer and ovarian cancer. Mol Genet Genomics 299, 51 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00438-024-02146-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00438-024-02146-1