Abstract
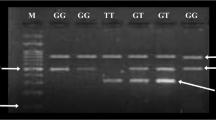
Polymorphism of transcription factor 7-like 2 (TCF7L2) has a link with type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM) through β cell dysfunction that causes defect in blood glucose homeostasis. This case–control study recruited 67 T2DM as cases and 65 age-matched healthy individuals as controls to determine whether the polymorphism rs12255372 (G > T) in the TCF7L2 gene have an association with T2DM in Bangladeshi population. Genomic DNA was purified from peripheral whole blood sample and direct Sanger sequencing was done for genotyping of SNP. Bivariate logistic regression was done to find out the association between genetic variant and T2DM. In our study, the minor T allele frequency was significantly more frequent in T2DM group than healthy controls (29.1% vs. 16.9%). After adjusting with confounding factors, heterozygous-genotype GT had higher odds of developing T2DM (OR 2.4; 95% CI: 1.0–5.5; p value = 0.04) and in dominant model, having SNP in TCF7L2 increased the risk of T2DM 2.3 times (95% CI: 1.0–5.2; p value = 0.04). In interaction model, genetic susceptible SNP cases interacted significantly with increasing age and BMI, female gender, and having family history of diabetes mellitus to develop T2DM (pinteraction < 0.001). Having minor T allele either in heterozygous or homozygous variant form of rs12255372 (G > T) TCF7L2 had significant association with T2DM. In conclusion, TCF7L2 gene variant increases risk of developing T2DM among the Bangladeshi population.


Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The data underlying this article are available in the article and its online supplementary material (https://doi.org/10.17632/fmf9r9hhmr.2). Fasta sequence files/chromatograms are available upon request.
References
Afroz A, Alam K, Ali L et al (2019) Type 2 diabetes mellitus in Bangladesh: a prevalence based cost-of-illness study. BMC Health Serv Res 19(1):1–12. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12913-019-4440-3
Alami FM, Ahmadi M, Bazrafshan H et al (2012) Association of the TCF7L2 rs12255372 (G/T) variant with type 2 diabetes mellitus in an Iranian population. Genet Mol Biol 35(2):413–417. https://doi.org/10.1590/S1415-47572012005000029
Alsmadi O, Al-Rubeaan K, Mohamed G et al (2008) Weak or no association of TCF7L2 variants with Type 2 diabetes risk in an Arab population. BMC Med Genet 9:e72. https://doi.org/10.1186/1471-2350-9-72
Atlas D (2015) International diabetes federation. IDF Diabetes Atlas, 7th edn. Brussels, Belgium: International Diabetes Federation, 33.
Banglapedia: National Encyclopedia of Bangladesh. (2021). Bengali Nation: Asiatic Society of Bangladesh. Retrieved from: https://en.banglapedia.org/index.php/Bangali_Nation. Accessed 23 June 2022
Beaudry KM, Devries MC (2019) Nutritional strategies to combat type 2 diabetes in aging adults: the importance of protein. Front Nutr 6:138. https://doi.org/10.3389/fnut.2019.00138
Berumen J, Orozco L, Betancourt-Cravioto M et al (2019) Influence of obesity, parental history of diabetes, and genes in type 2 diabetes: a case–control study. Sci Rep 9(1):1–5. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-019-39145-x
Bessenyei B, Márka M, Urbán L et al (2004) Single nucleotide polymorphisms: aging and diseases. Biogerontology 5:291–303. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10522-004-2567-y
Bińkowski J, Miks S (2018) Hardy-Weinberg Equilibrium—Gene-Calc. https://gene-calc.pl/hardy-weinberg-page. Accessed 24 Mar 2022
Bodhini D, Radha V, Dhar M et al (2007) The rs12255372 (G/T) and rs7903146 (C/T) polymorphisms of the TCF7L2 gene are associated with type 2 diabetes mellitus in Asian Indians. Metab 56(9):1174–1178. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.metabol.2007.04.012
Chandak GR, Janipalli CS, Bhaskar S et al (2007) Common variants in the TCF7L2 gene are strongly associated with type 2 diabetes mellitus in the Indian population. Diabetologia 50(1):63–67. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00125-006-0502-2
Chiang YT, Ip W, Jin T (2012) The role of the Wnt signaling pathway in incretin hormone production and function. Front Physio 3:273. https://doi.org/10.3389/fphys.2012.00273
Dedoussis GV, Kaliora AC, Panagiotakos DB (2007) Genes, diet and type 2 diabetes mellitus: a review. Rev Diabet Stud 4(1):13–24. https://doi.org/10.3906/sag-1507-160
Duval A, Rolland S, Tubacher E et al (2000) The human T-cell transcription factor-4 gene: structure, extensive characterization of alternative splicings, and mutational analysis in colorectal cancer cell lines. Cancer Res 60:3872–3879
Federation ID (2019) IDF diabetes atlas. 1st ed. Brussels, Belgium: International Diabetes Federation
Friedewald WT, Levy RI, Fredrickson DS (1972) Estimation of low density lipoprotein cholesterol without the use of the preparative ultracentrifuge. Clin Chem 18:499–502. https://doi.org/10.1093/clinchem/18.6.499
Grant SF, Thorleifsson G, Reynisdottir I et al (2006) Variant of transcription factor 7-like 2 (TCF7L2) gene confers risk of type 2 diabetes. Nat Genet 38(3):320–323. https://doi.org/10.1038/ng1732
Guo T, Hanson RL, Traurig M et al (2007) TCF7L2 is not a major susceptibility gene for type 2 diabetes in Pima Indians: analysis of 3,501 individuals. Diabetes 56:3082–3088. https://doi.org/10.2337/db07-0621
Guo J, Huang X, Dou L et al (2022) Aging and aging-related diseases: from molecular mechanisms to interventions and treatments. Sig Transduct Target Ther 7:391. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41392-022-01251-0
Hameed T, Khan Z, Imran M et al (2021) Associations of transcription factor 7-Like 2 (TCF7L2) gene polymorphism in patients of type 2 diabetes mellitus from Khyber Pakhtunkhwa population of Pakistan. Afr Health Sci 21(1):15–22. https://doi.org/10.4314/ahs.v21i1.4
Hasan M, Hasanat M, Hasan K et al (2016) TCF7L2 gene rs7903146 polymorphism is observed in gestational diabetes mellitus in Bangladesh. Integr Obes Diabetes 2(4). https://doi.org/10.15761/IOD.1000155
Hayashi T, Iwamoto Y, Kaku K et al (2007) Replication study for the association of TCF7L2 with susceptibility to type 2 diabetes in a Japanese population. Diabetologia 50(5):980–984. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00125-007-0618-z
Hossain MB, Khan MN, Oldroyd JC et al (2022) Prevalence of, and risk factors for, diabetes and prediabetes in Bangladesh: evidence from the national survey using a multilevel Poisson regression model with a robust variance. PLOS Glob Public Health. 2(6):e0000461. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pgph.0000461
Jin T, Liu L (2008) Minireview: the Wnt signaling pathway effector TCF7L2 and type 2 diabetes mellitus. Mol Endocrinol 22(11):2383–2392. https://doi.org/10.1210/me.2008-0135
Kaya DE, Arikoğlu H, Kayiş SA et al (2017) Transcription factor 7-like 2 (TCF7L2) gene polymorphisms are strong predictors of type 2 diabetes among nonobese diabetics in the Turkish population. Turk J Med Sci 47(1):22–28. https://doi.org/10.3906/sag-1507-160
Koichiro T, Glen S, Kumar S (2021) MEGA11: molecular evolutionary genetics analysis version 11. Mol Biol Evol 38(7):3022–3027. https://doi.org/10.1093/molbev/msab120
Kota SK, Meher LK, Jammula S (2012) Genetics of type 2 diabetes mellitus and other specific types of diabetes; its role in treatment modalities. Diabetes Metab Syndr Clin Res Rev 6(1):54–58. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.dsx.2012.05.014
Lovic D, Piperidou A, Zografou I et al (2020) The growing epidemic of diabetes mellitus. Curr Vasc Pharmacol 18(2):104–109. https://doi.org/10.2174/1570161117666190405165911
Mondal AK, Das SK, Baldini G et al (2010) Genotype and tissue-specific effects on alternative splicing of the transcription factor 7-like 2 gene in humans. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 95(3):1450–1457. https://doi.org/10.1210/jc.2009-2064
Nanfa D, Sobngwi E, Atogho-Tiedeu B et al (2015) Association between the TCF7L2 rs12255372 (G/T) gene polymorphism and type 2 diabetes mellitus in a Cameroonian population: a pilot study. Clin Trans Med 4(1):1–5. https://doi.org/10.1186/s40169-015-0058-1
Online Sample Size Estimator (OSSE), 2006. http://osse.bii.a-star.edu.sg/. Accessed 12 Feb 2021
Papier K, D’Este C, Bain C et al (2017) Body mass index and type 2 diabetes in Thai adults: defining risk thresholds and population impacts. BMC Public Health 17(1):1–10. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12889-017-4708-7
Pearson ER, Donnelly LA, Kimber C et al (2007) Variation in TCF7L2 influences therapeutic response to sulfonylureas: a GoDARTs study. Diabetes 56(8):2178–2182. https://doi.org/10.2337/db07-0440
Peng S, Zhu Y, Lü B et al (2013) TCF7L2 gene polymorphisms and type 2 diabetes risk: a comprehensive and updated meta-analysis involving 121 174 subjects. Mutagenesis 28(1):25–37. https://doi.org/10.1093/mutage/ges048
Pickering TG, Hall JE, Appel LJ et al (2005) Recommendations for blood pressure measurement in humans: an AHA scientific statement from the Council on High Blood Pressure Research Professional and Public Education Subcommittee. J Clin Hypertens 7(2):102–109. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1524-6175.2005.04377.x
Prokunina-Olsson L, Kaplan LM, Schadt EE (2009) Alternative splicing of TCF7L2 gene in omental and subcutaneous adipose tissue and risk of type 2 diabetes. PLoS ONE 4(9):e7231. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0007231
Schäfer SA, Tschritter O, Machicao F (2007) Impaired glucagon-like peptide-1-induced insulin secretion in carriers of transcription factor 7-like 2 (TCF7L2) gene polymorphisms. Diabetologia 50(12):2443–2450. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00125-007-0753-6
Shokouhi S, Delpisheh A, Haghani K et al (2014) Association of rs7903146, rs12255372, and rs290487 polymorphisms in TCF7L2 gene with type 2 diabetes in an Iranian Kurdish ethnic group. Clin Lab 60(8):1269–1276. https://doi.org/10.7754/Clin.Lab.2013.130809
Sun H, Saeedi P, Karuranga S et al (2022) IDF Diabetes Atlas: global, regional and country-level diabetes prevalence estimates for 2021 and projections for 2045. Diabetes Res Clin Pract 183:109119. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.diabres.2021.109119
Tong Y, Lin Y, Zhang Y et al (2009) Association between TCF7L2gene polymorphisms and susceptibility to Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus: a large Human Genome Epidemiology (HuGE) review and meta-analysis. BMC Med Genet 10:15. https://doi.org/10.1186/1471-2350-10-15
Vcelak J, Vejrakova D, Vaňkova M et al (2012) T2D Risk haplotypes of the TCF7L2 gene in the Czech population sample: the association with free fatty acids composition. Physiol Res 61(3):229–240
Wang GS, Cooper TA (2007) Splicing in disease: disruption of the splicing code and the decoding machinery. Nat Rev Genet 8(10):749–761. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrg2164
Waterhouse AM, Procter JB, Martin DM et al (2009) Jalview Version 2—a multiple sequence alignment editor and analysis workbench. Bioinformatics 25(9):1189–1191. https://doi.org/10.1093/bioinformatics/btp033
Weise A, Bruser K, Elfert S et al (2010) Alternative splicing of Tcf7l2 transcripts generates protein variants with differential promoter-binding and transcriptional activation properties at Wnt/β-catenin targets. Nucleic Acids Res 38(6):1964–1981. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gkp1197
Yi F, Brubaker PL, Jin T (2005) TCF-4 mediates cell type-specific regulation of proglucagon gene expression by β-catenin and glycogen synthase kinase-3β. J Biol Chem 280(2):1457–1464. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M411487200
Acknowledgements
This study received partial funding support from the Ministry of Science and Technology, Government of Bangladesh. We are also thankful to Santi Sir Memorial Diabetic Center of Sirajdikhan, Munshiganj for assisting us in data collection. We also thank Zubair Ahmed Ratan, Department of Biomedical Engineering, Khulna University of Engineering and Technology, Bangladesh, for critical reviewing of the manuscript and helpful suggestion.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
ABMMKI and NB conceived the project. NB, MF, MAY collected the data. NB and MAI performed statistical analysis. NB performed genetic analysis. NB drafted the manuscript. ABMMKI and MAI supervised the study. The manuscript was reviewed and approved by all authors.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethical approval
This study design was approved from the Ethical Review Committee at the Faculty of Biological Sciences of University of Dhaka, Bangladesh (Ref. No. 152/Biol. Scs. 2021). We obtained informed written consent from all the candidates who participated in this study. At the same time, we followed all the principles of Helsinki Declaration.
Conflict of interests
The authors declare that there is no competing interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Barman, N., Atiqul Haque, M., Firoz, M. et al. Association of transcription factor 7-like 2 rs12255372 polymorphism with susceptibility of type 2 diabetes mellitus in Bangladeshi population. Mol Genet Genomics 298, 1201–1209 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00438-023-02049-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00438-023-02049-7