Abstract
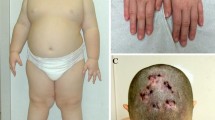
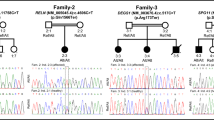
Early childhood obesity is a real public health problem worldwide. Identifying the etiologies, especially treatable and preventable causes, can direct health professionals toward proper management. Measurement of serum leptin levels is helpful in the diagnosis of congenital leptin and leptin receptor deficiencies which are considered important rare causes of early childhood obesity. The main aim of this study was to investigate the frequency of LEP, LEPR, and MC4R gene variants among a cohort of Egyptian patients with severe early onset obesity. The current cross-sectional study included 30 children who developed obesity during the first year of life with BMI > 2SD (for age and sex). The studied patients were subjected to full medical history taking, anthropometric measurements, serum leptin and insulin assays, and genetic testing of LEP, LEPR and MC4R. Disease causing variants in LEP and LEPR were identified in 10/30 patients with a detection rate of 30%. Eight different homozygous variants (two pathogenic, three likely pathogenic, and three variants of uncertain significant) were identified in the two genes, including six previously unreported LEPR variants. Of them, a new frameshift variant in LEPR gene (c.1045delT, p.S349Lfs*22) was recurrent in two unrelated families and seems to have a founder effect in our population. In conclusion, we reported ten new patients with leptin and leptin receptor deficiencies and identified six novel LEPR variants expanding the mutational spectrum of this rare disorder. Furthermore, the diagnosis of these patients helped us in genetic counseling and patients’ managements specially with the availability of drugs for LEP and LEPR deficiencies.



Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The data supporting the findings of this study are available with the corresponding author upon request.
References
Akıncı A, Türkkahraman D, Tekedereli İ et al (2019) Novel mutations in obesity-related genes in turkish children with non-syndromic early onset severe obesity: a multicentre study. J Clin Res Pediatr Endocrinol 11(4):341–349. https://doi.org/10.4274/jcrpe.galenos.2019.2019.0021
Albuquerque D, Estévez MN, Víbora PB et al (2014) Novel variants in the MC4R and LEPR genes among severely obese children from the Iberian population. Ann Hum Genet 78(3):195–207. https://doi.org/10.1111/ahg.12058
Algariri N, Alhabib M, Alsaheel A (2017) A novel mutation leading to leptin receptor deficiency and subsequent childhood morbid obesity. J Endocrinol Diab 4(4):1–2. https://doi.org/10.15226/2374-6890/4/4/00187
Andiran N, Celik N, Andiran F (2011) Homozygosity for two missense mutations in the leptin receptor gene (P316:W646C) in a Turkmenian girl with severe early-onset obesity. J Pediatr Endocrinol Metab 24(11–12):1043–1045. https://doi.org/10.1515/JPEM.2011.313
Armağan C, Yılmaz C, Koç A et al (2019) A toddler with a novel LEPR mutation. Hormones (athens) 18(2):237–240. https://doi.org/10.1007/s42000-019-00097-6
Le Beyec-Le Bihan J, Poitou-Bernert C, et al (2019) Variants in genes of the leptin/melanocortin pathway are involved in 3% of cases of early-onset severe obesity. Endocrine Abstracts 2019 63 GP132.
Bhatt A, Purani C, Bhargava P et al (2019) Whole exome sequencing reveals novel LEPR frameshift mutation in severely obese children from Western India. Mol Genet Genomic Med 7(7):e00692. https://doi.org/10.1002/mgg3.692
Bişgin A (2018) LEPR deficiency: prevalence and importance of a novel mutation and significant genetic variants, usually underestimated. Turk J Endocrinol Metab. https://doi.org/10.2579/tjem.2018-59842
Chekhranova MK, Karpova SK, Yatsyshina SB et al (2008) A new mutation c.422C>G (p. S141C) in homoand heterozygous forms of the human leptin gene. Russ J Bioorg Chem 34:768–770. https://doi.org/10.1134/S1068162008060198
Clément K, Vaisse C, Lahlou N et al (1998) A mutation in the human leptin receptor gene causes obesity and pituitary dysfunction. Nature 392(6674):398–401. https://doi.org/10.1038/32911
Clément K, Biebermann H, Farooqi IS et al (2018) MC4R agonism promotes durable weight loss in patients with leptin receptor deficiency. Nat Med 24(5):551–555. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41591-018-0015-9
Dayal D, Seetharaman K, Panigrahi I, Muthuvel B, Agarwal A (2018) Severe early onset obesity due to a novel missense mutation in exon 3 of the Leptin gene in an infant from northwest India. J Clin Res Pediatr Endocrinol 10(3):274–278. https://doi.org/10.4274/jcrpe.5501
Dehghani MR, Mehrjardi MYV, Dilaver N et al (2018) Potential role of gender specific effect of leptin receptor deficiency in an extended consanguineous family with severe early-onset obesity. Eur J Med Genet 61(8):465–467. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejmg.2018.03.006
ElSaeed G, Mousa N, El-Mougy F et al (2020) Monogenic leptin deficiency in early childhood obesity. Pediatr Obes 15(1):e12574. https://doi.org/10.1111/ijpo.12574
Farooqi IS, Keogh JM, Yeo GS, Lank EJ, Cheetham T, O’Rahilly S (2003) Clinical spectrum of obesity and mutations in the melanocortin 4 receptor gene. N Engl J Med 348(12):1085–1095. https://doi.org/10.1056/NEJMoa022050
Farooqi IS, Wangensteen T, Collins S et al (2007) Clinical and molecular genetic spectrum of congenital deficiency of the leptin receptor. N Engl J Med 356(3):237–247. https://doi.org/10.1056/NEJMoa063988
Fatima W, Shahid A, Imran M et al (2011) Leptin deficiency and leptin gene mutations in obese children from Pakistan. Int J Pediatr Obes 6(5–6):419–427. https://doi.org/10.3109/17477166.2011.608431
Fischer-Posovszky P, von Schnurbein J, Moepps B et al (2010) A new missense mutation in the leptin gene causes mild obesity and hypogonadism without affecting T cell responsiveness. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 95(6):2836–2840. https://doi.org/10.1210/jc.2009-2466
Gibson WT, Farooqi IS, Moreau M et al (2004) Congenital leptin deficiency due to homozygosity for the Delta133G mutation: report of another case and evaluation of response to four years of leptin therapy. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 89(10):4821–4826. https://doi.org/10.1210/jc.2004-0376
Gill R, Cheung YH, Shen Y et al (2014) Whole-exome sequencing identifies novel LEPR mutations in individuals with severe early onset obesity. Obesity (silver Spring) 22(2):576–584. https://doi.org/10.1002/oby.20492
Hannema SE, Wit JM, Houdijk ME et al (2016) Novel leptin receptor mutations identified in two girls with severe obesity are associated with increased bone mineral density. Horm Res Paediatr 85(6):412–420. https://doi.org/10.1159/000444055
Huvenne H, Le Beyec J, Pépin D et al (2015) Seven novel deleterious LEPR mutations found in early-onset obesity: a ΔExon6-8 shared by subjects from reunion Island, France, suggests a founder effect. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 100(5):E757–E766. https://doi.org/10.1210/jc.2015-1036
Huvenne H, Dubern B, Clément K, Poitou C (2016) Rare genetic forms of obesity: clinical approach and current treatments in 2016. Obes Facts 9(3):158–173. https://doi.org/10.1159/000445061
Kakar N, Ahmad J, Kubisch C, Borck G (2013) Exon skipping and severe childhood-onset obesity caused by a leptin receptor mutation. Am J Med Genet A 161A(10):2672–2674. https://doi.org/10.1002/ajmg.a.36125
Kleinendorst L, van Haelst MM, van den Akker ELT (2017) Young girl with severe early-onset obesity and hyperphagia. BMJ Case Rep. https://doi.org/10.1136/bcr-2017-221067
Kleinendorst L, Massink MPG, Cooiman MI et al (2018) Genetic obesity: next-generation sequencing results of 1230 patients with obesity. J Med Genet 55(9):578–586. https://doi.org/10.1136/jmedgenet-2018-105315
Kleinendorst L, Abawi O, van der Kamp HJ et al (2020a) Leptin receptor deficiency: a systematic literature review and prevalence estimation based on population genetics. Eur J Endocrinol 182(1):47–56. https://doi.org/10.1530/EJE-19-0678
Kleinendorst L, Abawi O, van der Voorn B et al (2020b) Identifying underlying medical causes of pediatric obesity: Results of a systematic diagnostic approach in a pediatric obesity center. PLoS ONE 15(5):e0232990. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0232990
Kohlsdorf K, Nunziata A, Funcke JB et al (2018) Early childhood BMI trajectories in monogenic obesity due to leptin, leptin receptor, and melanocortin 4 receptor deficiency. Int J Obes (lond) 42(9):1602–1609. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41366-018-0049-6
Le Beyec J, Cugnet-Anceau C, Pépin D et al (2013) Homozygous leptin receptor mutation due to uniparental disomy of chromosome 1: response to bariatric surgery. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 98(2):E397–E402. https://doi.org/10.1210/jc.2012-2779
Loos RJF, Yeo GSH (2022) The genetics of obesity: from discovery to biology. Nat Rev Genet 23(2):120–133. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41576-021-00414-z
Martinelli CE, Keogh JM, Greenfield JR et al (2011) Obesity due to melanocortin 4 receptor (MC4R) deficiency is associated with increased linear growth and final height, fasting hyperinsulinemia, and incompletely suppressed growth hormone secretion. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 96(1):E181–E188. https://doi.org/10.1210/jc.2010-1369
Mazen I, El-Gammal M, Abdel-Hamid M, Amr K (2009) A novel homozygous missense mutation of the leptin gene (N103K) in an obese Egyptian patient. Mol Genet Metab 97(4):305–308. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ymgme.2009.04.002
Mazen I, El-Gammal M, Abdel-Hamid M, Farooqi IS, Amr K (2011) Homozygosity for a novel missense mutation in the leptin receptor gene (P316T) in two Egyptian cousins with severe early onset obesity. Mol Genet Metab 102(4):461–464. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ymgme.2010.12.013
Mazen I, Amr K, Tantawy S, Farooqi IS, El Gammal M (2014) A novel mutation in the leptin gene (W121X) in an Egyptian family. Mol Genet Metab Rep 1:474–476. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ymgmr.2014.10.002
Montague CT, Farooqi IS, Whitehead JP et al (1997) Congenital leptin deficiency is associated with severe early-onset obesity in humans. Nature 387(6636):903–908. https://doi.org/10.1038/43185
Nalbantoğlu Ö, Hazan F, Acar S, Gürsoy S, Özkan B (2022) Screening of non-syndromic early-onset child and adolescent obese patients in terms of LEP, LEPR, MC4R and POMC gene variants by next-generation sequencing. J Pediatr Endocrinol Metab 35(8):1041–1050. https://doi.org/10.1515/jpem-2022-0027
Niazi RK, Gjesing AP, Hollensted M et al (2018) Identification of novel LEPR mutations in Pakistani families with morbid childhood obesity. BMC Med Genet 19(1):199. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12881-018-0710-x
Niv-Spector L, Shpilman M, Grupi A, Gertler A (2010) The obese phenotype-inducing N82K mutation in human leptin disrupts receptor-binding and biological activity. Mol Genet Metab 100(2):193–197. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ymgme.2010.02.015
Nunziata A, Funcke JB, Borck G et al (2018) Functional and phenotypic characteristics of human leptin receptor mutations. J Endocr Soc 3(1):27–41. https://doi.org/10.1210/js.2018-00123
O’Rahilly S, Farooqi IS (2008) Human obesity as a heritable disorder of the central control of energy balance. Int J Obes (lond) 32(Suppl 7):S55–S61. https://doi.org/10.1038/ijo.2008.239
Paz-Filho G, Wong ML, Licinio J (2011) Ten years of leptin replacement therapy. Obes Rev 12(5):e315–e323. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1467-789X.2010.00840.x
Saeed S, Bonnefond A, Manzoor J et al (2014) Novel LEPR mutations in obese Pakistani children identified by PCR-based enrichment and next generation sequencing. Obesity (silver Spring) 22(4):1112–1117. https://doi.org/10.1002/oby.20667
Saeed S, Bonnefond A, Manzoor J et al (2015) Genetic variants in LEP, LEPR, and MC4R explain 30% of severe obesity in children from a consanguineous population. Obesity (silver Spring) 23(8):1687–1695. https://doi.org/10.1002/oby.21142
Shabana S (2016) The p N103K mutation of leptin (LEP) gene and severe early onset obesity in Pakistan. Biol Res. https://doi.org/10.1186/s40659-016-0082-7
Strobel A, Issad T, Camoin L, Ozata M, Strosberg AD (1998) A leptin missense mutation associated with hypogonadism and morbid obesity. Nat Genet 18(3):213–215. https://doi.org/10.1038/ng0398-213
Temtamy S, Aglan M (2012) Consanguinity and genetic disorders in Egypt. Middle East J Med Genet 1(1):12–17. https://doi.org/10.1097/01.MXE.0000407744.14663.d8
Thakur S, Kumar A, Dubey S, Saxena R, Peters AN, Singhal A (2014) A novel mutation of the leptin gene in an Indian patient. Clin Genet 86(4):391–393. https://doi.org/10.1111/cge.12289
Timper K, Brüning JC (2017) Hypothalamic circuits regulating appetite and energy homeostasis: pathways to obesity. Dis Model Mech 10(6):679–689. https://doi.org/10.1242/dmm.026609
Vauthier V, Jaillard S, Journel H, Dubourg C, Jockers R, Dam J (2012) Homozygous deletion of an 80 kb region comprising part of DNAJC6 and LEPR genes on chromosome 1P313 is associated with early onset obesity, mental retardation and epilepsy [published correction appears in Mol Genet Metab. A;114(4):613]. Mol Genet Metab 106(3):345–350. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ymgme.2012.04.026
Voigtmann F, Wolf P, Landgraf K et al (2021) Identification of a novel leptin receptor (LEPR) variant and proof of functional relevance directing treatment decisions in patients with morbid obesity. Metabolism. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.metabol.2020.154438
Wabitsch M, Funcke JB, Lennerz B et al (2015a) Biologically inactive leptin and early-onset extreme obesity. N Engl J Med 372(1):48–54. https://doi.org/10.1056/NEJMoa1406653
Wabitsch M, Funcke JB, von Schnurbein J et al (2015b) Severe early-onset obesity due to bioinactive leptin caused by a p.N103K mutation in the Leptin Gene. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 100(9):3227–3230. https://doi.org/10.1210/jc.2015-2263
Wade KH, Lam BYH, Melvin A et al (2021) Loss-of-function mutations in the melanocortin 4 receptor in a UK birth cohort. Nat Med 27(6):1088–1096. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41591-021-01349-y
Yang Y, Xu Y (2020) The central melanocortin system and human obesity. J Mol Cell Biol 12(10):785–797. https://doi.org/10.1093/jmcb/mjaa048
Yupanqui-Lozno H, Bastarrachea RA, Yupanqui-Velazco ME et al (2019) Congenital Leptin deficiency and Leptin Gene missense mutation found in two colombian sisters with severe obesity. Genes (basel) 10(5):342. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes10050342
Zorn S, von Schnurbein J, Kohlsdorf K, Denzer C, Wabitsch M (2020) Diagnostic and therapeutic odyssey of two patients with compound heterozygous leptin receptor deficiency. Mol Cell Pediatr 7(1):15. https://doi.org/10.1186/s40348-020-00107-3
Acknowledgements
We are deeply thankful for the late Prof. Mona Elruby for referring one of the families.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
All authors contributed to the study. Recruitment of patients and writing the clinical data were performed by IHM, Mona AEG, AAE, GMA, and EAA. Molecular analysis was performed by MS. A-H and SF. AG. The first draft of the manuscript was written by MS. A-H, AAE, and IHM, and all authors commented on previous versions of the manuscript. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
Authors declare no conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
This study was approved by the Medical Research Ethical Committee of the National Research Centre (NRC), Cairo, Egypt, and conducted in accordance with the Declaration of Helsinki ethical principles for medical research involving human subjects.
Consent for participation
An informed consent was obtained from the patients and or their guardians for participation in the study (available with the corresponding author upon request).
Consent for publication
An informed consent was obtained from the patients and or their guardians for publication of the study and any accompanying images (available with the corresponding author upon request).
Additional information
Communicated by Shuhua Xu.
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Mazen, I.H., El-Gammal, M.A., Elaidy, A.A. et al. Congenital leptin and leptin receptor deficiencies in nine new families: identification of six novel variants and review of literature. Mol Genet Genomics 298, 919–929 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00438-023-02025-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00438-023-02025-1