Abstract
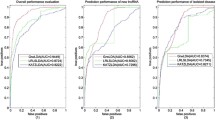
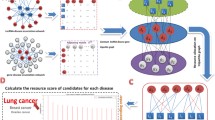
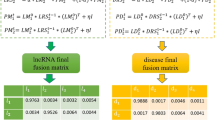
Accumulating evidence indicates that the regulation of long non-coding RNAs (lncRNAs) is closely related to a variety of diseases. Identifying meaningful lncRNA–disease associations will help to contribute to the understanding of the molecular mechanisms underlying these diseases. However, only a limited number of associations between lncRNAs and diseases have been inferred from traditional biological experiments due to the high cost and highly specialized. Therefore, computational methods are increasingly used to reduce time of biological experiments and complement biological research. In this paper, a computational method called HBRWRLDA is proposed to predict lncRNA–disease associations. First, HBRWRLDA models the relationships between multiple nodes using hypergraphs, which allows HBRWRLDA to integrate the expression similarity of lncRNAs and the semantic similarity of diseases to construct hypergraphs. Then, a bi-random walk on hypergraphs is used to predict potential lncRNA–disease associations. HBRWRLDA achieves a higher area under the curve value of 0.9551 and \(0.9488\pm 0.0013\), respectively, compared with the other five advanced methods under the framework of one-leave cross validation (LOOCV) and five-fold cross-validation (5-fold CV). In addition, the prediction effect of HBRWRLDA was confirmed case studies of three diseases: renal cell carcinoma, gastric cancer, and hepatocellular carcinoma. Case studies demonstrates the capacity of HBRWRLDA to identify potentially disease-associated lncRNAs. Overall, HBRWRLDA is excellent at predicting potential lncRNA–disease associations and could be useful in conducting further biological experiments by helping researchers identify candidates of lncRNA–disease association.








Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The source codes used in this work could be freely downloaded at https://github.com/yeyetuowoyi/HBRWRLDA.
References
Aksoy SG, Joslyn C, Marrero CO, Praggastis B, Purvine E (2020) Hypernetwork science via high-order hypergraph walks. EPJ Data Sci 9(1):16. https://doi.org/10.1140/epjds/s13688-020-00231-0
Bao Z, Yang Z, Huang Z, Zhou Y, Cui Q, Dong D (2019) LncRNADisease 2.0: an updated database of long non-coding RNA-associated diseases. Nucleic Acids Res 47(D1):1034–1037. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gky905
Bin X, Hongjian Y, Xiping Z, Bo C, Shifeng Y, Binbin T (2018) Research progresses in roles of lncRNA and its relationships with breast cancer. Cancer Cell Int 18(1):1–12. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12935-018-0674-0
Chang H-L, Bamodu OA, Ong J-R, Lee W-H, Yeh C-T, Tsai J-T (2020) Targeting the epigenetic non-coding RNA MALAT1/Wnt signaling axis as a therapeutic approach to suppress stemness and metastasis in hepatocellular carcinoma. Cells 9(4):1020. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells9041020
Chen X, Yan G-Y (2013) Novel human lncRNA-disease association inference based on lncRNA expression profiles. Bioinformatics 29(20):2617–2624. https://doi.org/10.1093/bioinformatics/btt426
Chen X, You ZH, Yan GY, Gong DW (2016) IRWRLDA: improved random walk with restart for lncRNA-disease association prediction. Oncotarget 7(36):57919. https://doi.org/10.18632/oncotarget.11141
Chen X, Sun YZ, Zhang DH, Li JQ, Yan GY, An JY, You ZH (2017) NRDTD: a database for clinically or experimentally supported non-coding RNAs and drug targets associations. Database. https://doi.org/10.1093/database/bax057
Chen Q, Lai D, Lan W, Wu X, Chen B, Chen Y-PP, Wang J (2021) ILDMSF: inferring associations between long non-coding RNA and disease based on multi-similarity fusion. IEEE/ACM Trans Comput Biol Bioinform 18(3):1106–1112. https://doi.org/10.1109/TCBB.2019.2936476
Cui Z, Liu J-X, Gao Y-L, Zhu R, Yuan S-S (2020) LncRNA-disease associations prediction using bipartite local model with nearest profile-based association inferring. IEEE J Biomed Health Inform 24(5):1519–1527. https://doi.org/10.1109/JBHI.2019.2937827
de Martel C, Georges D, Bray F, Ferlay J, Clifford GM (2020) Global burden of cancer attributable to infections in 2018: a worldwide incidence analysis. Lancet Glob Health 8(2):180–190. https://doi.org/10.1016/S2214-109X(19)30488-7
Deleuze A, Saout J, Dugay F, Peyronnet B, Mathieu R, Verhoest G, Bensalah K, Crouzet L, Laguerre B, Belaud-Rotureau M-A (2020) Immunotherapy in renal cell carcinoma: the future is now. Int J Mol Sci 21(7):2532. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21072532
Ding L-J, Li Y, Wang S-D, Wang X-S, Fang F, Wang W-Y, Lv P, Zhao D-H, Wei F, Qi L (2016) Long noncoding RNA LNCCAMTA1 promotes proliferation and cancer stem cell-like properties of liver cancer by inhibiting CAMTA1. Int J Mol Sci 17(10):1617. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms17101617
Dong D, Lun Y, Sun B, Sun H, Wang Q, Yuan G, Quan J (2020) Silencing of long non-coding RNA PCAT6 restrains gastric cancer cell proliferation and epithelial-mesenchymal transition by targeting microRNA-15A. Gen Physiol Biophys 39(1):1–12. https://doi.org/10.4149/gpb_2019044
Ezzat A, Wu M, Li X-L, Kwoh C-K (2016) Drug-target interaction prediction via class imbalance-aware ensemble learning. BMC Bioinform 17(19):267–276. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12859-016-1377-y
Fan Y, Chen M, Pan X (2022) GCRFLDA: scoring lncRNA-disease associations using graph convolution matrix completion with conditional random field. Brief Bioinform 23(1):bbab361. https://doi.org/10.1093/bib/bbab361
Fu G, Wang J, Domeniconi C, Yu G (2018) Matrix factorization-based data fusion for the prediction of lncRNA-disease associations. Bioinformatics 34(9):1529–1537. https://doi.org/10.1093/bioinformatics/btx794
Gao Y, Shang S, Guo S, Li X, Zhou H, Liu H, Sun Y, Wang J, Wang P, Zhi H, Li X, Ning S, Zhang Y (2020) LNC2Cancer 3.0: an updated resource for experimentally supported lncRNA/circRNA cancer associations and web tools based on RNA-seq and scRNA-seq data. Nucleic Acids Res 49(D1):1251–1258. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gkaa1006
Hao NB, He YF, Li XQ, Wang K, Wang RL (2017) The role of miRNA and lncRNA in gastric cancer. Oncotarget 8(46):81572. https://doi.org/10.18632/oncotarget.19197
Hu Y-W, Kang C-M, Zhao J-J, Nie Y, Zheng L, Li H-X, Li X, Wang Q, Qiu Y-R (2020) LncRNA PLAC2 down-regulates RPL36 expression and blocks cell cycle progression in glioma through a mechanism involving stat1. J Cell Mol Med 22:497–510. https://doi.org/10.1111/jcmm.13338
Ju C, Liu R, Zhang Y-W, Zhang Y, Zhou R, Sun J, Lv X-B, Zhang Z (2019) Mesenchymal stem cell-associated lncRNA in osteogenic differentiation. Biomed Pharmacother 115:108912. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biopha.2019.108912
Kong Q, Liang C, Jin Y, Pan Y, Tong D, Kong Q, Zhou J (2019) The lncRNA miR4435-2HG is upregulated in hepatocellular carcinoma and promotes cancer cell proliferation by upregulating miRNA-487A. Cell Mol Biol Lett 24(1):1–7. https://doi.org/10.1186/s11658-019-0148-y
Lan W, Li M, Zhao K, Liu J, Wu F-X, Pan Y, Wang J (2017) LDAP: a web server for lncRNA-disease association prediction. Bioinformatics 33(3):458–460. https://doi.org/10.1093/bioinformatics/btw639
Lan W, Wu X, Chen Q, Peng W, Wang J, Chen YP (2022) GANLDA: graph attention network for lncRNA-disease associations prediction. Neurocomputing 469:384–393. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neucom.2020.09.094
Li J, Zhao H, Xuan Z, Yu J, Feng X, Liao B, Wang L (2021) A novel approach for potential human lncRNA-disease association prediction based on local random walk. IEEE/ACM Trans Comput Biol Bioinform 18(3):1049–1059. https://doi.org/10.1109/TCBB.2019.2934958
Liu G, Zhao X, Zhou J, Cheng X, Ye Z, Ji Z (2018) LncRNA TP73-AS1 promotes cell proliferation and inhibits cell apoptosis in clear cell renal cell carcinoma through repressing KISS1 expression and inactivation of PI3K/Akt/mTOR signaling pathway. Cell Physiol Biochem 48(1):371–384. https://doi.org/10.1159/000491767
Liu L, Pang X, Shang W, Xie H, Feng Y, Feng G (2019) Long non-coding RNA GAS5 sensitizes renal cell carcinoma to sorafenib via miR-21/SOX5 pathway. Cell Cycle 18(3):257–263. https://doi.org/10.1080/15384101.2018.1475826
Liu J-X, Gao M-M, Cui Z, Gao Y-L, Li F (2021) DSCMF: prediction of lncRNA-disease associations based on dual sparse collaborative matrix factorization. BMC Bioinform 22:241. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12859-020-03868-w
Long Y, Luo J, Zhang Y, Xia Y (2020) Predicting human microbe-disease associations via graph attention networks with inductive matrix completion. Brief Bioinform 22(3):bbaa146. https://doi.org/10.1093/bib/bbaa146
Lu C, Yang M, Luo F, Wu F-X, Li M, Pan Y, Li Y, Wang J (2018) Prediction of lncRNA-disease associations based on inductive matrix completion. Bioinformatics 34(19):3357–3364. https://doi.org/10.1093/bioinformatics/bty327
Lu R, Zhao G, Yang Y, Jiang Z, Cai J, Zhang Z, Hu H (2019) Long noncoding RNA HOTAIRM1 inhibits cell progression by regulating miR-17-5P/PTEN axis in gastric cancer. J Cell Biochem 120(4):4952–4965. https://doi.org/10.1002/jcb.27770
Lu C, Yang M, Li M, Li Y, Wu F-X, Wang J (2020) Predicting human lncRNA-disease associations based on geometric matrix completion. IEEE J Biomed Health Inform 24(8):2420–2429. https://doi.org/10.1109/JBHI.2019.2958389
Mishra P, Kumar S (2021) Association of lncRNA with regulatory molecular factors in brain and their role in the pathophysiology of schizophrenia. Metab Brain Dis 36:849–858. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11011-021-00692-w
Ning L, Cui T, Zheng B, Wang N, Luo J, Yang B, Du M, Cheng J, Dou Y, Wang D (2021) MNDR V3.0: mammal ncRNA-disease repository with increased coverage and annotation. Nucleic Acids Res 49(D1):160–164. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gkaa707
Niu Y-W, Qu C-Q, Wang G-H, Yan G-Y (2019) RWHMDA: random walk on hypergraph for microbe-disease association prediction. Front Microbiol 10(2):1578. https://doi.org/10.3389/fmicb.2019.01578
Qu Y, Xiao H, Xiao W, Xiong Z, Hu W, Gao Y, Ru Z, Wang C, Bao L, Wang K (2018) Upregulation of MIAT regulates LOXL2 expression by competitively binding miR-29C in clear cell renal cell carcinoma. Cell Physiol Biochem 48(3):1075–1087. https://doi.org/10.1159/000491974
Ranganathan S, Lopez-Terrada D, Alaggio R (2020) Hepatoblastoma and pediatric hepatocellular carcinoma: an update. Pediatr Dev Pathol 23(2):79–95. https://doi.org/10.1177/1093526619875228
Ren Y, Huang W, Weng G, Cui P, Liang H, Li Y (2019) LncRNA PVT1 promotes proliferation, invasion and epithelial-mesenchymal transition of renal cell carcinoma cells through downregulation of miR-16-5P. Oncotargets Ther 12:2563. https://doi.org/10.2147/OTT.S190239
Safa A, Gholipour M, Dinger ME, Taheri M, Ghafouri-Fard S (2020) The critical roles of lncRNAs in the pathogenesis of melanoma. Exp Mol Pathol 117:104558. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.yexmp.2020.104558
Sheng N, Cui H, Zhang T, Xuan P (2021) Attentional multi-level representation encoding based on convolutional and variance autoencoders for lncRNA-disease association prediction. Brief Bioinform 22(3):bbaa067. https://doi.org/10.1093/bib/bbaa067
Shi Z, Zhang H, Jin C, Quan X, Yin Y (2020) A representation learning model based on variational inference and graph autoencoder for predicting lncRNA-disease associations. BMC Bioinform 22(1):1–20. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12859-021-04073-z
Slifka MK, Whitton JL (2020) LncRNA regulation: new frontiers in epigenetic solutions to drug chemoresistance. Biochem Pharmacol 23:114228. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bcp.2020.114228
Slifka MK, Whitton JL (2020) Long non-coding RNA BACE1-AS modulates isoflurane-induced neurotoxicity to Alzheimer’s disease through sponging miR-214-3p. Neurochem Res 45(10):2324–2335. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11064-020-03091-2
Smyth EC, Nilsson M, Grabsch HI, van Grieken NC, Lordick F (2020) Gastric cancer. Lancet 396(10251):635–648. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0140-6736(20)31288-5
Sun L, Tu J, Liu C, Pan A, Xia X, Chen X (2010) Analysis of lncRNA expression profiles by sequencing reveals that lnc-AL9287683 and lnc-AC0914931 are novel biomarkers for disease risk and activity of rheumatoid arthritis. Inflammopharmacology 28(2):437–450. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10787-019-00666-6
Sun J, Shi H, Wang Z, Zhang C, Liu L, Wang L, He W, Hao D, Liu S, Zhou M (2014) Inferring novel lncRNA-disease associations based on a random walk model of a lncRNA functional similarity network. Mol Biosyst 10(8):2074–2081. https://doi.org/10.1039/c3mb70608g
Sun Z, Xue S, Zhang M, Xu H, Hu X, Chen S, Liu Y, Guo M, Cui H (2020) Aberrant NSUN2-mediated m5C modification of H19 lncRNA is associated with poor differentiation of hepatocellular carcinoma. Oncogene 39(45):6906–6919. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12943-020-01188-4
Wang D, Wang J, Lu M, Song F, Cui Q (2010) Inferring the human microRNA functional similarity and functional network based on microRNA-associated diseases. Bioinformatics 26(13):1644–1650. https://doi.org/10.1093/bioinformatics/btq241
Wu X, Lan W, Chen Q, Dong Y, Liu J, Peng W (2020) Inferring lncRNA-disease associations based on graph autoencoder matrix completion. Comput Biol Chem 87:107282. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compbiolchem.2020.107282
Xiao Q, Luo J, Liang C, Cai J, Ding P (2018) A graph regularized non-negative matrix factorization method for identifying microRNA-disease associations. Bioinformatics 34(2):239–248. https://doi.org/10.1093/bioinformatics/btx545
Xuan Z, Li J, Yu J, Feng X, Zhao B, Wang L (2019) A probabilistic matrix factorization method for identifying lncRNA-disease associations. Genes 10(2):126. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes10020126
Xuan P, Zhan L, Cui H, Zhang T, Nakaguchi T, Zhang W (2021) Graph triple-attention network for disease-related lncRNA prediction. IEEE J Biomed Health Inform 26(6):2839–2849. https://doi.org/10.1109/JBHI.2021.3130110
Yu G, Fu G, Lu C, Ren Y, Wang J (2017) BRWLDA: bi-random walks for predicting lncRNA-disease associations. Oncotarget 8(36):604. https://doi.org/10.18632/oncotarget.19588
Zhai H, Li Y (2019) BCYRN1 is correlated with progression and prognosis in gastric cancer. Biosci Rep 39(11):20190505. https://doi.org/10.1042/BSR20190505
Zhao Y, Chen X, Yin J (2018) A novel computational method for the identification of potential miRNA-disease association based on symmetric non-negative matrix factorization and kronecker regularized least square. Front Genet 9:324. https://doi.org/10.3389/fgene.2018.00324
Zhao L, Wang J, Li Y, Song T, Wu Y, Fang S, Bu D, Li H, Sun L, Pei D (2021a) NONCODEV6: an updated database dedicated to long non-coding RNA annotation in both animals and plants. Nucleic Acids Res 49(D1):165–171. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gkaa1046
Zhao X, Yang Y, Yin M (2021b) MHRWR: prediction of lncRNA-disease associations based on multiple heterogeneous networks. IEEE/ACM Trans Comput Biol Bioinform 8(6):2577–2585. https://doi.org/10.1109/TCBB.2020.2974732
Zhou M, Wang X, Li J, Hao D, Wang Z, Shi H, Han L, Zhou H, Sun J (2015) Prioritizing candidate disease-related long non-coding RNAs by walking on the heterogeneous lncRNA and disease network. Mol Biosyst 11(3):760–769. https://doi.org/10.1039/c4mb00511b
Funding
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (62002070, 61802072); the Science and Technology Plan Project of Guangzhou City (201902020012, 202102021236, 201902020006); the 315 Opening Project of Guangdong Province Key Laboratory of Computational Science at the Sun Yat-seUniversity (2021013).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Ethics approval
This article does not contain any studies with human participants or animals performed by any of the authors.
Additional information
Communicated by Shuhua Xu.
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Xie, G., Zhu, Y., Lin, Z. et al. HBRWRLDA: predicting potential lncRNA–disease associations based on hypergraph bi-random walk with restart. Mol Genet Genomics 297, 1215–1228 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00438-022-01909-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00438-022-01909-y