Abstract
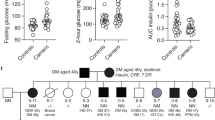
Monogenic diabetes is a rare type of diabetes resulting from mutations in a single gene. To date, most cases remain genetically unexplained, posing a challenge for accurate diabetes treatment, which leads to on a molecular diagnosis. Therefore, a trio exome scan was performed in a lean, nonsyndromic Caucasian girl with diabetes onset at 2½ years who was negative for autoantibodies. The lean father had diabetes from age 11 years. A novel heterozygous mutation in EDEM2, c.1271G > A; p.Arg424His, was found in the proband and father. Downregulation of Edem2 in rat RIN-m β-cells resulted in a decrease in insulin genes Ins1 to 67.9% (p = 0.006) and Ins2 to 16.8% (p < 0.001) and reduced insulin secretion by 60.4% (p = 0.0003). Real-time PCR revealed a major disruption of endocrine pancreas-specific genes, including Glut2 and Pxd1, with mRNA suppression to 54% (p < 0.001) and 85.7% (p = 0.01), respectively. No other expression changes related to stress or apoptotic genes were observed. Extended clinical follow-up involving ten family members showed that two healthy individuals carried the same mutation with no sign of diabetes in the clinical screen except for a slight increase in IA-2 antibody in one of them, suggesting incomplete penetrance. In conclusion, we describe EDEM2 as a likely/potential novel diabetes gene, in which inhibition in vitro reduces the expression of β-cell genes involved in the glucose‐stimulated insulin secretion (GSIS) pathway, leading to an overall suppression of insulin secretion but not apoptosis.




Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The datasets generated during and/or analyzed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
References
Ahlgren U, Jonsson J, Edlund H (1996) The morphogenesis of the pancreatic mesenchyme is uncoupled from that of the pancreatic epithelium in IPF1/PDX1-deficient mice. Development 122:1409–1416
Ahlgren U, Jonsson J, Jonsson L, Simu K, Edlund H (1998) beta-cell-specific inactivation of the mouse Ipf1/Pdx1 gene results in loss of the beta-cell phenotype and maturity onset diabetes. Genes Dev 12:1763–1768
Fajans SS, Bell GI, Polonsky KS (2001) Molecular mechanisms and clinical pathophysiology of maturity-onset diabetes of the young. N Engl J Med 345:971–980
Gregersen N, Bolund L, Bross P (2005) Protein misfolding, aggregation, and degradation in disease. Mol Biotechnol 31:141–150
Hani H, Allaudin ZN, Mohd-Lila MA, et al (2017) Improvement of isolated caprine islet survival and functionality in vitro by enhancing of PDX1 gene expression. Xenotransplantation 24(3). https://doi.org/10.1111/xen.12302
Hosokawa N, Wada I, Hasegawa K, Yorihuzi T, Tremblay LO, Herscovics A, Nagata K (2001) A novel ER alpha-mannosidase-like protein accelerates ER-associated degradation. EMBO Rep 2:415–422
Irgens HU, Molnes J, Johansson BB, Ringdal M, Skrivarhaug T, Undlien DE, Sovik O, Joner G, Molven A, Njolstad PR (2013) Prevalence of monogenic diabetes in the population-based Norwegian Childhood Diabetes Registry. Diabetologia 56:1512–1519
Johnson JH, Newgard CB, Milburn JL, Lodish HF, Thorens B (1990) The high Km glucose transporter of islets of Langerhans is functionally similar to the low affinity transporter of liver and has an identical primary sequence. J Biol Chem 265:6548–6551
Kaneto H, Miyagawa J, Kajimoto Y, Yamamoto K, Watada H, Umayahara Y, Hanafusa T, Matsuzawa Y, Yamasaki Y, Higashiyama S, Taniguchi N (1997) Expression of heparin-binding epidermal growth factor-like growth factor during pancreas development. A potential role of PDX-1 in transcriptional activation. J Biol Chem 272:29137–29143
Kaneto H, Xu G, Fujii N, Kim S, Bonner-Weir S, Weir GC (2002) Involvement of c-Jun N-terminal kinase in oxidative stress-mediated suppression of insulin gene expression. J Biol Chem 277:30010–30018
Kubo A, Stull R, Takeuchi M, Bonham K, Gouon-Evans V, Sho M, Iwano M, Saito Y, Keller G, Snodgrass R (2011) Pdx1 and Ngn3 overexpression enhances pancreatic differentiation of mouse ES cell-derived endoderm population. PLoS ONE 6:e24058
Mangrum C, Rush E, Shivaswamy V (2015) Genetically targeted dipeptidyl peptidase-4 inhibitor use in a patient with a novel mutation of MODY type 4. Clin Med Insights Endocrinol Diabetes 8:83–86
Mast SW, Diekman K, Karaveg K, Davis A, Sifers RN, Moremen KW (2005) Human EDEM2, a novel homolog of family 47 glycosidases, is involved in ER-associated degradation of glycoproteins. Glycobiology 15:421–436
Miedzybrodzka Z, Hattersley AT, Ellard S, Pearson D, de Silva D, Harvey R, Haites N (1999) Non-penetrance in a MODY 3 family with a mutation in the hepatic nuclear factor 1alpha gene: implications for predictive testing. Eur J Hum Genet 7:729–732
Murphy R, Ellard S, Hattersley AT (2008) Clinical implications of a molecular genetic classification of monogenic beta-cell diabetes. Nat Clin Pract Endocrinol Metab 4:200–213
Ninagawa S, Okada T, Sumitomo Y, Horimoto S, Sugimoto T, Ishikawa T, Takeda S, Yamamoto T, Suzuki T, Kamiya Y, Kato K, Mori K (2015) Forcible destruction of severely misfolded mammalian glycoproteins by the non-glycoprotein ERAD pathway. J Cell Biol 211:775–784
Olivari S, Galli C, Alanen H, Ruddock L, Molinari M (2005) A novel stress-induced EDEM variant regulating endoplasmic reticulum-associated glycoprotein degradation. J Biol Chem 280:2424–2428
Oyadomari S, Araki E, Mori M (2002) Endoplasmic reticulum stress-mediated apoptosis in pancreatic beta-cells. Apoptosis 7:335–345
Samali A, Fitzgerald U, Deegan S, Gupta S (2010) Methods for monitoring endoplasmic reticulum stress and the unfolded protein response. Int J Cell Biol 2010:830307
Shields BM, Hicks S, Shepherd MH, Colclough K, Hattersley AT, Ellard S (2010) Maturity-onset diabetes of the young (MODY): how many cases are we missing? Diabetologia 53:2504–2508
Slingerland AS, Shields BM, Flanagan SE, Bruining GJ, Noordam K, Gach A, Mlynarski W, Malecki MT, Hattersley AT, Ellard S (2009) Referral rates for diagnostic testing support an incidence of permanent neonatal diabetes in three European countries of at least 1 in 260,000 live births. Diabetologia 52:1683–1685
Tanahashi T, Osabe D, Nomura K, Shinohara S, Kato H, Ichiishi E, Nakamura N, Yoshikawa T, Takata Y, Miyamoto T, Shiota H, Keshavarz P, Yamaguchi Y, Kunika K, Moritani M, Inoue H, Itakura M (2006) Association study on chromosome 20q11.21-13.13 locus and its contribution to type 2 diabetes susceptibility in Japanese. Hum Genet 120:527–542
Thomas SE, Dalton L, Malzer E, Marciniak SJ (2011) Unravelling the story of protein misfolding in diabetes mellitus. World J Diabetes 2:114–118
Thorens B (2015) GLUT2, glucose sensing and glucose homeostasis. Diabetologia 58:221–232
Wang H, Maechler P, Ritz-Laser B, Hagenfeldt KA, Ishihara H, Philippe J, Wollheim CB (2001) Pdx1 level defines pancreatic gene expression pattern and cell lineage differentiation. J Biol Chem 276:25279–25286
Watada H, Kajimoto Y, Miyagawa J, Hanafusa T, Hamaguchi K, Matsuoka T, Yamamoto K, Matsuzawa Y, Kawamori R, Yamasaki Y (1996) PDX-1 induces insulin and glucokinase gene expressions in alphaTC1 clone 6 cells in the presence of betacellulin. Diabetes 45:1826–1831
World-Health-Organization (2016) Global Report on Diabetes. In. World Health Organization, https://www.who.int/, p 88
Zong WX, Li C, Hatzivassiliou G, Lindsten T, Yu QC, Yuan J, Thompson CB (2003) Bax and Bak can localize to the endoplasmic reticulum to initiate apoptosis. J Cell Biol 162:59–69
Acknowledgments
We thank our laboratory staff: Martin J. Larsen for performing the sequencing alignment, Jette Møller, Trine Jørgensen, and Flemming Bergholdt for performing the laboratory work.
Funding
This study was funded by The Research Fund, Region of Southern Denmark; The University of Southern Denmark, and King Abdullah International Research Centre.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
KB, HC, and MB were involved in planning and supervising the project. HC, and KH collected and provided the clinical data. YA and KB designed the experiments. YA performed the experiments. YA and KB analyzed the data. YA drafted the manuscript. All authors discussed the results and contributed to the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
Yazeid Alhaidan declares that he has no conflict of interest. Henrik Thybo Christesen declares that he has no conflict of interest. Kurt Højlund declares that he has no conflict of interest. Mohammed A. Al Balwi declares that he has no conflict of interest. Klaus Brusgaard declares that he has no conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
All procedures performed in studies involving human participants were in accordance with the ethical standards of the institutional and national research committee and with the 1964 Helsinki Declaration and its later amendments or comparable ethical standards. The study was approved by the regional ethical committee of southern Denmark (sagnr. S-VF-20040235).
Informed consent
Informed consent was obtained from all individual participants included in the study.
Additional information
Communicated by Stefan Hohmann.
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Alhaidan, Y., Christesen, H.T., Højlund, K. et al. A novel gene in early childhood diabetes: EDEM2 silencing decreases SLC2A2 and PXD1 expression, leading to impaired insulin secretion. Mol Genet Genomics 295, 1253–1262 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00438-020-01695-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00438-020-01695-5