Abstract
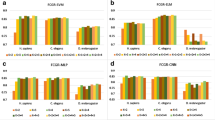
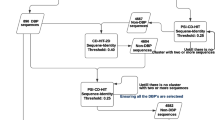
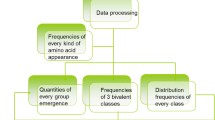
Nucleosome is a central element of eukaryotic chromatin, which composes of histone proteins and DNA molecules. It performs vital roles in many eukaryotic intra-nuclear processes, for instance, chromatin structure and transcriptional regulation formation. Identification of nucleosome positioning via wet lab is difficult; so, the attention is diverted towards the accurate intelligent automated prediction. In this regard, a novel intelligent automated model “iNuc-ext-PseTNC” is developed to identify the nucleosome positioning in genomes accurately. In this predictor, the sequences of DNA are mathematically represented by two different discrete feature extraction techniques, namely pseudo-tri-nucleotide composition (PseTNC) and pseudo-di-nucleotide composition. Several contemporary machine learning algorithms were examined. Further, the predictions of individual classifiers were integrated through an evolutionary genetic algorithm. The success rates of the ensemble model are higher than individual classifiers. After analyzing the prediction results, it is noticed that iNuc-ext-PseTNC model has achieved better performance in combination with PseTNC feature space, which are 94.3%, 93.14%, and 88.60% of accuracies using six-fold cross-validation test for the three benchmark datasets S1, S2, and S3, respectively. The achieved outcomes exposed that the results of iNuc-ext-PseTNC model are prominent compared to the existing methods so far notifiable in the literature. It is ascertained that the proposed model might be more fruitful and a practical tool for rudimentary academia and research.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ahmad J, Javed F, Hayat M (2017) Intelligent computational model for classification of sub-Golgi protein using oversampling and fisher feature selection methods. Artif Intell Med 78:14–22
Athey BD, Smith MF, Rankert DA, Williams SP, Langmore JP (1990) The diameters of frozen-hydrated chromatin fibers increase with DNA linker length: evidence in support of variable diameter models for chromatin. J Cell Biol 111:795–806
Awazu A (2017) Prediction of nucleosome positioning by the incorporation of frequencies and distributions of three different nucleotide segment lengths into a general pseudo k-tuple nucleotide composition. Bioinformatics 33:42–48
Berbenetz NM, Nislow C, Brown GW (2010) Diversity of eukaryotic DNA replication origins revealed by genome-wide analysis of chromatin structure. PLoS Genet 6:e1001092
Cao D-S, Xu Q-S, Liang Y-Z (2013) Propy: a tool to generate various modes of Chou’s PseAAC. Bioinformatics 29:960–962
Che Y, Ju Y, Xuan P, Long R, Xing F (2016) Identification of multi-functional enzyme with multi-label classifier. PLoS One 11:e0153503
Chen Y-K, Li K-B (2013) Predicting membrane protein types by incorporating protein topology, domains, signal peptides, and physicochemical properties into the general form of Chou’s pseudo amino acid composition. J Theor Biol 318:1–12
Chen W, Feng P-M, Lin H, Chou K-C (2013a) iRSpot-PseDNC: identify recombination spots with pseudo dinucleotide composition. Nucleic Acids Res 41(6):e68
Chen W, Feng P, Lin H, Chou K (2013b) iRSpot-PseDNC: identify recombination spots with pseudo dinucleotide composition. Nucleic Acids Res gks1450
Chen W, Lei T-Y, Jin D-C, Lin H, Chou K-C (2014) PseKNC: a flexible web server for generating pseudo K-tuple nucleotide composition. Anal Biochem 456:53–60
Chen W, Zhang X, Brooker J, Lin H, Zhang L, Chou K-C (2015) PseKNC-general: a cross-platform package for generating various modes of pseudo nucleotide compositions. Bioinformatics 31:119–120
Chen W, Ding H, Feng P, Lin H, Chou K-C (2016) iACP: a sequence-based tool for identifying anticancer peptides. Oncotarget 7:16895
Chen W, Feng P, Yang H, Ding H, Lin H, Chou K-C (2017) iRNA-AI: identifying the adenosine to inosine editing sites in RNA sequences. Oncotarget 8:4208
Cheng X, Xiao X, Chou K-C (2017a) pLoc-mGneg: predict subcellular localization of Gram-negative bacterial proteins by deep gene ontology learning via general PseAAC. Genomics 110:231–239
Cheng X, Xiao X, Chou K-C (2017b) pLoc-mHum: predict subcellular localization of multi-location human proteins via general PseAAC to winnow out the crucial GO information. Bioinformatics 34:1448–1456
Cheng X, Xiao X, Chou K-C (2017c) pLoc-mPlant: predict subcellular localization of multi-location plant proteins by incorporating the optimal GO information into general PseAAC. Mol Biosyst 13:1722–1727
Cheng X, Xiao X, Chou K-C (2017d) pLoc-mVirus: predict subcellular localization of multi-location virus proteins via incorporating the optimal GO information into general PseAAC. Gene 628:315–321
Cheng X, Xiao X, Chou K-C (2018) pLoc-mEuk: predict subcellular localization of multi-label eukaryotic proteins by extracting the key GO information into general PseAAC. Genomics 110:50–58
Chou KC (2001a) Prediction of protein cellular attributes using pseudo-amino acid composition. Proteins Struct Funct Bioinform 43:246–255
Chou K-C (2001b) Prediction of signal peptides using scaled window. Peptides 22:1973–1979
Chou K-C (2005) Using amphiphilic pseudo amino acid composition to predict enzyme subfamily classes. Bioinformatics 21:10–19
Chou K-C (2015) Impacts of bioinformatics to medicinal chemistry. Med Chem 11:218–234
Chou K-C (2017) An unprecedented revolution in medicinal chemistry driven by the progress of biological science. Curr Top Med Chem 17:2337–2358
Chou K-C, Shen H-B (2007a) Euk-mPLoc: a fusion classifier for large-scale eukaryotic protein subcellular location prediction by incorporating multiple sites. J Proteome Res 6:1728–1734
Chou K-C, Shen H-B (2007b) Recent progress in protein subcellular location prediction. Anal Biochem 370:1–16
Chou K-C, Shen H-B (2007c) Signal-CF: a subsite-coupled and window-fusing approach for predicting signal peptides. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 357:633–640
Dong C, Yuan Y-Z, Zhang F-Z, Hua H-L, Ye Y-N, Labena AA, Lin H, Chen W, Guo F-B (2016) Combining pseudo dinucleotide composition with the Z curve method to improve the accuracy of predicting DNA elements: a case study in recombination spots. Mol BioSyst 12:2893–2900
Eddy SR (1996) Hidden markov models. Curr Opin Struct Biol 6:361–365
Ehsan A, Mahmood K, Khan YD, Khan SA, Chou K-C (2018) A novel modeling in mathematical biology for classification of signal peptides. Sci Rep 8:1039
Feng P, Ding H, Yang H, Chen W, Lin H, Chou K-C (2017) iRNA-PseColl: identifying the occurrence sites of different RNA modifications by incorporating collective effects of nucleotides into PseKNC. Mol Ther Nucleic Acids 7:155–163
Feng P, Yang H, Ding H, Lin H, Chen W, Chou K-C (2018) iDNA6mA-PseKNC: identifying DNA N6-methyladenosine sites by incorporating nucleotide physicochemical properties into PseKNC. Genomics. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ygeno.2018.01.005
Field Y, Kaplan N, Fondufe-Mittendorf Y, Moore IK, Sharon E, Lubling Y, Widom J, Segal E (2008) Distinct modes of regulation by chromatin encoded through nucleosome positioning signals. PLoS Comput Biol 4:e1000216
Gabdank I, Barash D, Trifonov EN (2010) Single-base resolution nucleosome mapping on DNA sequences. J Biomol Struct Dyn 28:107–121
Goñi JR, Fenollosa C, Pérez A, Torrents D, Orozco M (2008) DNAlive: a tool for the physical analysis of DNA at the genomic scale. Bioinformatics 24:1731–1732
Guo S-H, Deng E-Z, Xu L-Q, Ding H, Lin H, Chen W, Chou K-C (2014) iNuc-PseKNC: a sequence-based predictor for predicting nucleosome positioning in genomes with pseudo k-tuple nucleotide composition. Bioinformatics 30(11):1522–1529
Hayat M, Khan A (2012) Discriminating outer membrane proteins with fuzzy K-nearest neighbor algorithms based on the general form of Chou’s PseAAC. Protein Pept Lett 19:411–421
Hayat M, Tahir M (2015) PSOFuzzySVM-TMH: identification of transmembrane helix segments using ensemble feature space by incorporated fuzzy support vector machine. Mol BioSyst 11:2255–2262
Ioshikhes I, Bolshoy A, Derenshteyn K, Borodovsky M, Trifonov EN (1996) Nucleosome DNA sequence pattern revealed by multiple alignment of experimentally mapped sequences. J Mol Biol 262:129–139
Isami S, Sakamoto N, Nishimori H, Awazu A (2015) Simple elastic network models for exhaustive analysis of long double-stranded DNA dynamics with sequence geometry dependence. PLoS One 10:e0143760
Jia J, Liu Z, Xiao X, Liu B, Chou K-C (2016) pSuc-Lys: predict lysine succinylation sites in proteins with PseAAC and ensemble random forest approach. J Theor Biol 394:223–230
Kabir M, Hayat M (2016) iRSpot-GAEnsC: identifying recombination spots via ensemble classifier and extending the concept of Chou’s PseAAC to formulate DNA samples. Mol Genet Genom 291:285–296
Kaplan N, Moore IK, Fondufe-Mittendorf Y, Gossett AJ, Tillo D, Field Y, LeProust EM, Hughes TR, Lieb JD, Widom J (2009) The DNA-encoded nucleosome organization of a eukaryotic genome. Nature 458:362–366
Levitsky VG (2004) RECON: a program for prediction of nucleosome formation potential. Nucleic Acids Res 32:W346–W349
Li W-C, Deng E-Z, Ding H, Chen W, Lin H (2015) iORI-PseKNC: a predictor for identifying origin of replication with pseudo k-tuple nucleotide composition. Chemom Intell Lab Syst 141:100–106
Li D, Luo L, Zhang W, Liu F, Luo F (2016) A genetic algorithm-based weighted ensemble method for predicting transposon-derived piRNAs. BMC Bioinform 17:329
Lin H, Deng E-Z, Ding H, Chen W, Chou K-C (2014) iPro54-PseKNC: a sequence-based predictor for identifying sigma-54 promoters in prokaryote with pseudo k-tuple nucleotide composition. Nucleic Acids Res 42:12961–12972
Liu B, Zhang D, Xu R, Xu J, Wang X, Chen Q, Dong Q, Chou K-C (2014a) Combining evolutionary information extracted from frequency profiles with sequence-based kernels for protein remote homology detection. Bioinformatics 30:472–479
Liu B, Xu J, Lan X, Xu R, Zhou J, Wang X, Chou K-C (2014b) iDNA-Prot| dis: identifying DNA-binding proteins by incorporating amino acid distance-pairs and reduced alphabet profile into the general pseudo amino acid composition. PLoS One 9:e106691
Liu B, Liu F, Fang L, Wang X, Chou K-C (2015a) repDNA: a Python package to generate various modes of feature vectors for DNA sequences by incorporating user-defined physicochemical properties and sequence-order effects. Bioinformatics 31:1307–1309
Liu Z, Xiao X, Qiu W-R, Chou K-C (2015c) iDNA-Methyl: identifying DNA methylation sites via pseudo trinucleotide composition. Anal Biochem 474:69–77
Liu B, Fang L, Liu F, Wang X, Chen J, Chou K-C (2015d) Identification of real microRNA precursors with a pseudo structure status composition approach. PLoS One 10:e0121501
Liu G-H, Shen H-B, Yu D-J (2016a) Prediction of protein–protein interaction sites with machine-learning-based data-cleaning and post-filtering procedures. J Membr Biol 249:141–153
Liu B, Long R, Chou K-C (2016b) iDHS-EL: identifying DNase I hypersensitive sites by fusing three different modes of pseudo nucleotide composition into an ensemble learning framework. Bioinformatics 32(16):2411–2418
Liu B, Wang S, Long R, Chou K-C (2016c) iRSpot-EL: identify recombination spots with an ensemble learning approach. Bioinformatics 33:35–41
Liu B, Yang F, Huang D-S, Chou K-C (2017a) iPromoter-2L: a two-layer predictor for identifying promoters and their types by multi-window-based PseKNC. Bioinformatics 34:33–40
Liu B, Yang F, Chou K-C (2017b) 2L-piRNA: a two-layer ensemble classifier for identifying Piwi-interacting RNAs and their function. Mol Ther Nucleic Acids 7:267–277
Liu B, Wu H, Zhang D, Wang X, Chou K-C (2017c) Pse-Analysis: a python package for DNA/RNA and protein/peptide sequence analysis based on pseudo components and kernel methods. Oncotarget 8:13338
Liu B, Li K, Huang D-S, Chou K-C (2018) iEnhancer-EL: identifying enhancers and their strength with ensemble learning approach. Bioinformatics. https://doi.org/10.1093/bioinformatics/bty458
Luo L, Li D, Zhang W, Tu S, Zhu X, Tian G (2016) Accurate prediction of transposon-derived piRNAs by integrating various sequential and physicochemical features. PLoS One 11:e0153268
Manavalan B, Shin TH, Lee G (2018) PVP-SVM: sequence-based prediction of phage virion proteins using a support vector machine. Front Microbiol 9:476
Mavrich TN, Jiang C, Ioshikhes IP, Li X, Venters BJ, Zanton SJ, Tomsho LP, Qi J, Glaser RL, Schuster SC (2008a) Nucleosome organization in the Drosophila genome. Nature 453:358–362
Mavrich TN, Ioshikhes IP, Venters BJ, Jiang C, Tomsho LP, Qi J, Schuster SC, Albert I, Pugh BF (2008b) A barrier nucleosome model for statistical positioning of nucleosomes throughout the yeast genome. Genome Res 18:1073–1083
Mavrich TN, Ioshikhes IP, Venters BJ, Jiang C, Tomsho LP, Qi J, Schuster SC, Albert I, Pugh BF (2008c) A barrier nucleosome model for statistical positioning of nucleosomes throughout the yeast genome. Genome Res
Nikolaou C, Althammer S, Beato M, Guigó R (2010) Structural constraints revealed in consistent nucleosome positions in the genome of S. cerevisiae. Epigenetics Chromatin 3:20
Peckham HE, Thurman RE, Fu Y, Stamatoyannopoulos JA, Noble WS, Struhl K, Weng Z (2007) Nucleosome positioning signals in genomic DNA. Genome Res 17:1170–1177
Qiu W-R, Xiao X, Chou K-C (2014) iRSpot-TNCPseAAC: identify recombination spots with trinucleotide composition and pseudo amino acid components. Int J Mol Sci 15:1746–1766
Satchwell SC, Drew HR, Travers AA (1986) Sequence periodicities in chicken nucleosome core DNA. J Mol Biol 191:659–675
Schwartz S, Meshorer E, Ast G (2009) Chromatin organization marks exon–intron structure. Nat Struct Mol Biol 16:990
Segal E, Fondufe-Mittendorf Y, Chen L, Thåström A, Field Y, Moore IK, Wang J-PZ, Widom J (2006) A genomic code for nucleosome positioning. Nature 442:772–778
Stolz RC, Bishop TC (2010) ICM Web: the interactive chromatin modeling web server. Nucleic Acids Res 38:W254–W261
Tahir M, Hayat M (2016) iNuc-STNC: a sequence-based predictor for identification of nucleosome positioning in genomes by extending the concept of SAAC and Chou’s PseAAC. Mol BioSyst 12:2587–2593
Thoma F, Koller T, Klug A (1979) Involvement of histone H1 in the organization of the nucleosome and of the salt-dependent superstructures of chromatin. J Cell Biol 83:403–427
Tian K, Yang X, Kong Q, Yin C, He RL, Yau SS-T (2015) Two dimensional Yau-hausdorff distance with applications on comparison of DNA and protein sequences. PLoS One 10:e0136577
Tolstorukov MY, Choudhary V, Olson WK, Zhurkin VB, Park PJ (2008) nuScore: a web-interface for nucleosome positioning predictions. Bioinformatics 24:1456–1458
Xi L, Fondufe-Mittendorf Y, Xia L, Flatow J, Widom J, Wang J-P (2010) Predicting nucleosome positioning using a duration Hidden Markov Model. BMC Bioinform 11:1
Xiang S, Liu K, Yan Z, Zhang Y, Sun Z (2016) RNAMethPre: a web server for the prediction and query of mRNA m 6 A sites. PLoS One 11:e0162707
Xiao X, Wang P, Lin W-Z, Jia J-H, Chou K-C (2013) iAMP-2L: a two-level multi-label classifier for identifying antimicrobial peptides and their functional types. Anal Biochem 436:168–177
Xiao X, Cheng X, Su S, Mao Q, Chou K-C (2017) pLoc-mGpos: incorporate key gene ontology information into general PseAAC for predicting subcellular localization of Gram-positive bacterial proteins. Nat Sci 9:330
Xiao X, Cheng X, Chen G, Mao Q, Chou K-C (2018) pLoc-mGpos: predict subcellular localization of Gram-positive bacterial proteins by quasi-balancing training dataset and PseAAC. Genomics. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ygeno.2018.05.017
Xu Y, Shao X-J, Wu L-Y, Deng N-Y, Chou K-C (2013a) iSNO-AAPair: incorporating amino acid pairwise coupling into PseAAC for predicting cysteine S-nitrosylation sites in proteins. PeerJ 1:e171
Xu Y, Ding J, Wu L-Y, Chou K-C (2013b) iSNO-PseAAC: predict cysteine S-nitrosylation sites in proteins by incorporating position specific amino acid propensity into pseudo amino acid composition. PLoS One 8:e55844
Xu Y, Wen X, Wen L-S, Wu L-Y, Deng N-Y, Chou K-C (2014) iNitro-Tyr: prediction of nitrotyrosine sites in proteins with general pseudo amino acid composition. PLoS One 9:e105018
Yasuda T, Sugasawa K, Shimizu Y, Iwai S, Shiomi T, Hanaoka F (2005) Nucleosomal structure of undamaged DNA regions suppresses the non-specific DNA binding of the XPC complex. DNA Repair 4:389–395
YongE F, GaoShan K (2015) Identify beta-hairpin motifs with quadratic discriminant algorithm based on the chemical shifts. PLoS One 10:e0139280
Yuan G-C, Liu JS (2008) Genomic sequence is highly predictive of local nucleosome depletion. PLoS Comput Biol 4:e13
Yuan G-C, Liu Y-J, Dion MF, Slack MD, Wu LF, Altschuler SJ, Rando OJ (2005) Genome-scale identification of nucleosome positions in S. cerevisiae. Science 309:626–630
Zhang W, Niu Y, Xiong Y, Zhao M, Yu R, Liu J (2012) Computational prediction of conformational B-cell epitopes from antigen primary structures by ensemble learning. PLoS One 7:e43575
Zhang W, Liu F, Luo L, Zhang J (2015a) Predicting drug side effects by multi-label learning and ensemble learning. BMC Bioinform 16:365
Zhang W, Niu Y, Zou H, Luo L, Liu Q, Wu W (2015b) Accurate prediction of immunogenic T-cell epitopes from epitope sequences using the genetic algorithm-based ensemble learning. PLoS one 10:e0128194
Zhang W, Zou H, Luo L, Liu Q, Wu W, Xiao W (2016a) Predicting potential side effects of drugs by recommender methods and ensemble learning. Neurocomputing 173:979–987
Zhang C-J, Tang H, Li W-C, Lin H, Chen W, Chou K-C (2016b) iOri-Human: identify human origin of replication by incorporating dinucleotide physicochemical properties into pseudo nucleotide composition. Oncotarget 7:69783
Zhang W, Shi J, Tang G, Wu W, Yue X, Li D (2017) Predicting small RNAs in bacteria via sequence learning ensemble method. In: Bioinformatics and biomedicine (BIBM), 2017 IEEE international conference on, IEEE, pp 643–647
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Communicated by S. Hohmann.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Tahir, M., Hayat, M. & Khan, S.A. iNuc-ext-PseTNC: an efficient ensemble model for identification of nucleosome positioning by extending the concept of Chou’s PseAAC to pseudo-tri-nucleotide composition. Mol Genet Genomics 294, 199–210 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00438-018-1498-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00438-018-1498-2