Abstract
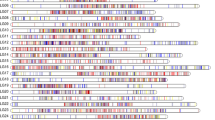
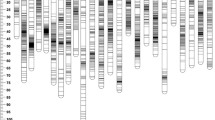
The Kuruma prawn, Marsupenaeus japonicus, is one of the most promising marine invertebrates in the industry in Asia, Europe and Australia. However, the increasing global temperatures result in considerable economic losses in M. japonicus farming. In the present study, to select genetically improved animals for the sustainable development of the Kuruma prawn industry, a high-resolution genetic linkage map and quantitative trait locus (QTL) identification were performed using the RAD technology. The maternal map contained 5849 SNP markers and spanned 3127.23 cM, with an average marker interval of 0.535 cM. Instead, the paternal map contained 3927 SNP markers and spanned 3326.19 cM, with an average marker interval of 0.847 cM. The consensus map contained 9289 SNP markers and spanned 3610.90 cM, with an average marker interval of 0.388 cM and coverage of 99.06 % of the genome. The markers were grouped into 41 linkage groups in the maps. Significantly, negative correlation was detected between high-temperature tolerance (UTT) and body weight (BW). The QTL mapping revealed 129 significant QTL loci for UTT and four significant QTL loci for BW at the genome-wide significance threshold. Among these QTLs, 129 overlapped with linked SNPs, and the remaining four were located in regions between contiguous SNPs. They explained the total phenotypic variance ranging from 8.9 to 12.4 %. Because of a significantly negative correlation between growth and high-temperature tolerance, we demonstrate that this high-resolution linkage map and QTLs would be useful for further marker-assisted selection in the genetic improvement of M. japonicus.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bouza C, Hermida M, Pardo BG, Vera M, Fernández C, de la Herran R et al (2012) An expressed sequence tag (EST)-enriched genetic map of turbot (Scophthalmus maximus): a useful framework for comparative genomics across model and farmed teleosts. BMC Genet 13:54
Catchen JM, Amores A, Hohenlohe P, Cresko W, Postlethwait JH (2011) building and genotyping loci de novo from short-read sequences. G3-Genes Genom Genet 1(3):171–182
Chow S, Dougherty WJ, Sandifer PA (1990) Meiotic chromosome complements and nuclear DNA contents of four species of shrimps of the genus Penaeus. J Crustac Biol 10:29–36
Dall W (1986) Estimation of routine metabolic rate in a penaeid prawn, Penaeus esculentus Haswell. J Exp Mar Biol Ecol 96:57–74
Davey JW, Blaxter ML (2011) RADSeq: next-generation population genetics. Brief Funct Genom 9:416–423
Etter PD, Preston JL, Bassham S, Cresko WA, Johnson EA (2011) Local de novo assembly of RAD paired-end contigs using short sequencing reads. PLoS One 6(4):e18561
Fishman L, Kelly AJ, Morgan E, Willis JH (2001) A genetic map in the Mimulus guttatus species complex reveals transmission ratio distortion due to heteros pecific interactions. Genetics 159:1701–1716
Furusho S, Umezaki Y, Ishida K, Honda A (1988) Changes in the concentration of ATP-related compoundsand lactic acid in muscle of live prawn Penaeus japonicus during storage in sawdust. Nippon Suisan Gakk 54:1209–1212
Gonen S, Lowe NR, Cezard T, Gharbi K, Bishop SC, Houston RD (2014) Linkage maps of the Atlantic salmon (Salmo salar) genome derived from RAD sequencing. BMC Genom 14:166
Hayashi KI, Fujiwara Y (1988) A new method for obtaining metaphase chromosomes from the regeneration blastema of Penaeus (Marsupenaeus) japonicus. Nippon Suisan Gakk 54:1563–1565
Hewitt DR, Duncan PF (2001) Effect of high water temperature on the survival moulting and food consumption of Penaeus (Marsupenaeus) japonicus (Bate, 1888). Aquac Res 32:305–313
Hohenlohe PA, Bassham S, Etter PD, Stiffler N, Johnson EA, Cresko WA (2010) Population genomics of parallel adaptation in three spine stickleback using sequenced RAD tags. PLoS Genet 6(2):e1000862
Holthuis LB (1980) FAO species catalogue. Vol. 1. Shrimps and prawns of the World. An annotated catalogue of species of interest to fisheries. FAO Fisheries Synopsis 125, 1. Food and Agricultural Organisation of the United Nations, p 271
Hu LY (2014) The application of molecular markers in the selective breeding of Marsupenaeus japonicus (Master Thesis). Shanghai Ocean University, Shanghai, p 26
Hubert S, Higgins B, Borza T, Bowman S (2011) Development of a SNP resource and a genetic linkage map for Atlantic cod (Gadus morhua). BMC Genom 11:191
Jansen RC, Stam P (1994) High resolution of quantitative traits into multiple loci via interval mapping. Genetics 136:1447–1455
Jiao WQ, Fu XT, Dou JZ, Li HD, Su HL, Mao JX, Yu Q, Zhang LL, Hu XL, Huang XT, Wang YF, Wang S, Bao ZM (2014) High-resolution linkage and quantitative trait locus mapping aided by genome survey sequencing: building up an integrative genomic framework for a bivalve mollusc. DNA Res 21:85–101
Kinne O (1970) (ed) Temperature. Marine Ecology, vol 1 Part 1. Wiley-Interscience, London, p 35
Lan X, Pan C, Zhang L, Zhao M, Zhang C, Lei C, Chen H (2009) A novel missense (A79V) mutation of goat PROP1 gene and its association with production traits. Mol Biol Rep 36:2069–2073
Li YT, Byrne K, Miggiano E, Whan V, Moore S, Keys S, Crocos P, Preston N, Lehnert S (2003) Genetic mapping of the kuruma prawn Penaeus japonicus using AFLP markers. Aquaculture 219:143–156
Liao IC, Chien YH (1994) Culture of Kuruma prawn (Penaeus japonicus Bate) in Asia. J World Aquacult Soc 25(1):18–33
Lu X, Luan S, Kong J, Hu LY, Mao Y, Zhong SP (2015) Genome-wide mining, characterization, and development of microsatellite markers in Marsupenaeus japonicus by genome survey sequencing. Chin J Oceanol Limnol. doi:10.1007/s00343-016-5250-7
MOA (Ministry of Agriculture of the People’s Republic of China) (2011) China fishery statistical yearbook. In: Department of fishery of the Ministry of Agriculture. China Agricultural Press, Beijing, p 25
MOA (Ministry of Agriculture of the People’s Republic of China) (2014) China fishery statistical yearbook. In: Department of fishery of the Ministry of Agriculture. China Agricultural Press, Beijing, p 28
Niiyama H (1948) Cytogenetics, Oguma conference. Oguma commemoration volume on cytology and genetics, In: Biology DataBook, vol 1, 2nd edn, Federation of American Societies for Experimental Biology, Bethesda, Maryland, pp 19–20
Palaiokostas C, Bekaert M, Davie A, Cowan ME, Oral M, Taggart JB et al (2013a) Mapping the sex determination locus in the Atlantic halibut (Hippoglossus hippoglossus) using RAD sequencing. BMC Genom 14:566
Palaiokostas C, Bekaert M, Khan MG, Taggat JB, Gharbi K, McAndrew BJ et al (2013b) Mapping and validation of the major sex-determining region in Nile Tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus L.) using RAD sequencing. PLoS One 8(7):1–9
Peterson BK, Weber JN, Kay EH, Fisher HS, Hoekstra HE (2012) Double digest RAD-seq: an inexpensive method for De Novo SNP discovery and genotyping in model and non-model species. PLoS One 7(5):e37135
Piepho HP (2001) A quick method for computing approximate thresholds for quantitative trait loci detection. Genetics 157:425–432
Schmidt-Nielsen K (1964) Desert animals: physiological problems of heat and water. Oxford University Press, Oxford
Schmidt-Nielsen K (1997) Animal physiology: adaptation and environment, 5th edn. Cambridge University Press, New York
Somorjai IML, Danzmann RG, Ferguson MM (2003) Distribution of temperature tolerance quantitative trait loci in arctic charr (Salvelinus alpinus) and inferred homologies in rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss). Genetics 165:1443–1456
Subramanian P, Krishnamurthy K (1986) Effects of salinity and body size on metabolism and growth of penaeid prawns. Indian J Exp Biol 54:773–778
Takeuchi T, KawashimaT Koyanagi R et al (2012) Draft genome of the pearl oyster Pinctada fucata: a platform forunder standing bivalve biology. DNA Res 19:117–130
Tao HH, Ma WX, Wu YZ, Zhao YZ (2014) High-density genetic map construction and QTLs analysis of grain yield-related traits in Sesame (Sesamum indicum L.) based on RAD-Seq techonology. BMC Plant Biol 14:274
Thomas MG, Enns RM, Shirley KL, Garcia MD, Garrett AJ, Silver GA (2007) Associations of DNA polymorphisms in growth hormone and its transcriptional regulators with growth and carcass traits in two populations of Brangus bulls. Genet Mol Res 6:222–237
Van Ooijen (2004) MapQTL, Software for the mapping of quantitative trait loci in experimental populations. Kyazma B. V., Wageningen
Van Ooijen JW (2006) JoinMap4, Software for the calculation of genetic linkage maps in experiment population. Kyazma B. V., Wageningen
Van Ooijen JW (2011) Multipoint maximum likelihood mapping in a full-sib family of an out breeding species. Genet Res 93(5):343–349
Wang WJ, Kong J, Dong SR (2006) Genetic mapping of the Chinese shrimp Fenneropenaeus chinensis using AFLP markers. Curr Zool 52:575–584
Wang S, Meyer E, McKay J, Matz MV (2012) 2b-RAD: a simple and flexible method for genome-wide genotyping. Nat Methods 9:808–810
Wang W, Hu Y, Ma Y, Xu L, Guan J, Kong J (2015) High-density genetic linkage mapping in Turbot (Scophthalmus maximus L.) based on SNP markers and major Sex- and growth-related regions detection. PLoS One 10(3):e0120410
Xiang JH, Liu RY. Zhou LH (1991) The chromosomes of three shrimp Penaeus penicillatus, P. semisulcatus and P. japonicas. Mar Sci 4:72–73
Xu TS, Liu JB, Yao DW, Cai HF, Chen H, Zhou HL et al (2010) The prophet of PIT1 gene variation and its effect on growth traits in Chinese indigeous goat. J Anim Vet Adv 9:2940–2946
Xu P, Xu S, Wu X, Tao Y, Wang B, Wang S et al (2014) Population genomic analyses from low-coverage RAD-Seq data: a case study on the non-model cucurbit bottle gourd. Plant J 77(3):430–442
Zeng XC, Chen HY, Jia B, Zhao ZS, Hui WQ, Wang ZB et al (2011) Identification of SNPs within the sheep PROP1 gene and their effects on wool traits. Mol Biol Rep 38:2723–2728
Zhang G, Fang X, Guo X et al (2012) The oyster genome reveals stress adaptation and complexity of shell formation. Nature 490:49–54
Zhang XJ, Yu Y, Li FH, Xiang JH, Liu DY (2014) Construction of a high-density SNP genetic map for pacific white shrimp Litopenaeus vannamei. Plant and Animal Genome, San Diego, CA
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by grants of National Hi-Tech R&D program of China (2012AA10A409) and the Taishan Scholar Program For Seed Industry.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Funding
This work was funded by the grants of National Hi-Tech R&D program of China (2012AA10A409) and the Taishan Scholar Program For Seed Industry.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no potential conflicts of interest.
Ethical approval
This article does not contain any studies with human participants or animals performed by the authors.
Additional information
Communicated by S. Hohmann.
X. Lu and S. Luan: co-first authors, contributed equally to this work.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lu, X., Luan, S., Hu, L.Y. et al. High-resolution genetic linkage mapping, high-temperature tolerance and growth-related quantitative trait locus (QTL) identification in Marsupenaeus japonicus . Mol Genet Genomics 291, 1391–1405 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00438-016-1192-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00438-016-1192-1