Abstract
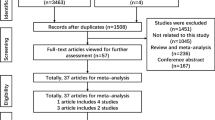
Five polymorphisms, rs2293152, rs4796793, rs12949918, rs6503695, rs744166, in the STAT3 gene have been implicated in susceptibility to cancer, but the results were inconclusive. The aim of this meta-analysis is to investigate the association between the five polymorphisms and cancer risk. All eligible case–control studies published up to March 2015 were identified by searching PubMed, Web of Science, Wanfang, VIP, and CNKI. Effect sizes of odds ratio (OR) and 95 % confidence interval (95 % CI) were calculated by using a fixed- or random-effect model. A total of 15 articles were included. Overall, a significantly decreased risk was found for rs12949918 polymorphism (dominant model: OR = 0.83, 95 % CI: 0.75–0.91, recessive model: OR = 0.77, 95 % CI: 0.68–0.87, TC vs. TT: OR = 0.87, 95 % CI: 0.79–0.96, CC vs. TT: OR = 0.71, 95 % CI: 0.62–0.81), and for rs744166 polymorphism (recessive model: OR = 0.75, 95 % CI: 0.58–0.98; GG vs. AA: OR = 0.68, 95 % CI: 0.51–0.90), while there was no significant association for other three polymorphisms under all genetic models. In subgroup analysis by ethnicity, for rs12949918 polymorphism, similar results were detected among Caucasians, similarly, a significant decreased risk was observed in Asians under dominant and CC vs. TT model; for rs2293152 polymorphism, significant association was detected among Asians under recessive model. This meta-analysis suggests that the STAT3 rs12949918 and rs744166 polymorphisms, but not other three polymorphisms, may be an important protective factor for cancer.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Begg CB, Mazumdar M (1994) Operating characteristics of a rank correlation test for publication bias. Biometrics 50:1088–1101
Bredberg A (2011) Cancer: more of polygenic disease and less of multiplemutations? A quantitative viewpoint. Cancer 117:440–445
Butterbach K, Beckmann L, de Sanjosé S, Benavente Y, Becker N, Foretova L, Maynadie M, Cocco P, Staines A, Boffetta P, Brennan P, Nieters A (2011) Association of JAK-STAT pathway related genes with lymphoma risk: results of a Europeancase-control study (EpiLymph). Br J Haematol 153:318–333
Chen Y, Lan Q, Zheng T, Zhao N, Holford TR, Lerro C, Dai M, Huang H, Liang J, Ma S, Leaderer B, Boyle P, Chanock S, Rothman N, Zhang Y (2013) Polymorphisms inJAK/STAT signaling pathway genes and risk of non-Hodgkin lymphoma. Leuk Res 37:1120–1124
Darnell JE Jr (1997) STATs and gene regulation. Science 277:1630–1635
DerSimonian R, Laird N (1986) Meta-analysis in clinical trials. Control Clin Trials 7:177–188
Domańska D, Antczak A, Pastuszak-Lewandoska D, Górski P, Kordiak J, Czarnecka K, Migdalska-Sęk M, Nawrot E, Kiszałkiewcz J, Brzeziańska E (2013) STAT3 rs3816769polymorphism correlates with gene expression level and may predispose to nonsmallcell lung cancer: a preliminary study. Pol Arch Med Wewn 123:672–679
Egger M, Davey Smith G, Schneider M, Minder C (1997) Bias in meta-analysis detected by a simple, graphical test. BMJ 315:629–634
Huang KD, Lou KX, Xia L, Huang Y, Xu XY (2014) Association between STAT3 gene polymorphism and colorectal cancer susceptibility. J Pract Med 30:770–772
Ito N, Eto M, Nakamura E, Takahashi A, Tsukamoto T, Toma H, Nakazawa H, Hirao Y, Uemura H, Kagawa S, Kanayama H, Nose Y, Kinukawa N, Nakamura T, Jinnai N, Seki T, Takamatsu M, Masui Y, Naito S, Ogawa O (2007) STAT3 polymorphism predicts interferon-alfa response in patientswith metastatic renal cell carcinoma. J Clin Oncol 25:2785–2791
Jiang B, Zhu ZZ, Liu F, Yang LJ, Zhang WY, Yuan HH, Wang JG, Hu XH, Huang G (2011) STAT3 gene polymorphisms and susceptibility to non-small cell lung cancer. Genet Mol Res 10:1856–1865
Judd LM, Menheniott TR, Ling H, Jackson CB, Howlett M, Kalantzis A, Priebe W, Giraud AS (2014) Inhibition of the JAK2/STAT3 pathway reduces gastric cancer growth in vitro and in vivo. PLoS One 9:e95993
Kim SM, Kwon OJ, Hong YK, Kim JH, Solca F, Ha SJ, Soo RA, Christensen JG, Lee JH, Cho BC (2012) Activation of IL-6R/JAK1/STAT3 signaling induces de novo resistanceto irreversible EGFR inhibitors in non-small cell lung cancer with T790M resistance mutation. Mol Cancer Ther 11:2254–2264
Kim MJ, Nam HJ, Kim HP, Han SW, Im SA, Kim TY, Oh DY, Bang YJ (2013) OPB-31121, a novel small molecular inhibitor, disrupts the JAK2/STAT3 pathway and exhibits an antitumor activity in gastric cancer cells. Cancer Lett 335:145–152
Kreil S, Waghorn K, Ernst T, Chase A, White H, Hehlmann R, Reiter A, Hochhaus A, Cross NC (2010) German CML Study Group: apolymorphism associated with STAT3 expression and responseof chronic myeloid leukemia to interferon a. Haematologica 95:148–152
Kwon EM, Salinas CA, Kolb S, Fu R, Feng Z, Stanford JL, Ostrander EA (2011) Genetic polymorphisms in inflammation pathway genes and prostate cancer risk. Cancer Epidemiol Biomark Prev 20:923–933
Lau J, Ioannidis JP, Schmid CH (1997) Quantitative synthesis in systematic reviews. Ann Intern Med 127:820–826
Levy DE, Darnell JE Jr (2002) STATs: transcriptional controland biological impact. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 3:651–662
Lin Q, Lai R, Chirieac LR, Li C, Thomazy VA, Grammatikakis I, Rassidakis GZ, Zhang W, Fujio Y, Kunisada K, Hamilton SR, Amin HM (2005) Constitutive activation of JAK3/STAT3 in colon carcinoma tumors and cell lines: inhibition of JAK3/STAT3 signaling induces apoptosis and cell cycle arrest of colon carcinoma cells. Am J Pathol 167:969–980
Liu Y, Yu D, Pan M, Bi Y, Zhou Y (2014) A case-control study on the relationship between polymorphisms of STAT3 and XRCC4 gene and the risk of hepatocellular carcinoma. Int J Lab Med 35:850–852
Lutticken C, Wegenka UM, Yuan JP, Buschmann J, Schindler C, Ziemiecki A (1994) Association of transcription factor APRF and protein kinase Jak1 with the interleukin-6 signal transducer gp130. Science 263:89–92
Mantel N, Haenszel W (1959) Statistical aspects of the analysis of data from retrospective studies of disease. J Natl Cancer Inst 22:719–748
Okamoto W, Okamoto I, Arao T, Yanagihara K, Nishio K, Nakagawa K (2011) Differentialroles of STAT3 depending on the mechanism of STAT3 activation in gastric cancercells. Br J Cancer 105:407–412
Pharoah PD, Dunning AM, Ponder BA, Easton DF (2004) Association studiesfor finding cancer-susceptibility genetic variants. Nat Rev Cancer 4:850–860
Slattery ML, Lundgreen A, Kadlubar SA, Bondurant KL, Wolff RK (2013) JAK/STAT/SOCS-signaling pathway and colon and rectal cancer. Mol Carcinog 52:155–166
Torre LA, Bray F, Siegel RL, Ferlay J, Lortet-Tieulent J, Jemal A (2015) Global cancer statistics, 2012. CA Cancer J Clin 65:87–108
Vaclavicek A, Bermejo JL, Schmutzler RK, Sutter C, Wappenschmidt B, Meindl A, Kiechle M, Arnold N, Weber BH, Niederacher D, Burwinkel B, Bartram CR, HemminkiK Försti A (2007) Polymorphisms in the Janus kinase 2 (JAK)/signal transducer andactivator of transcription (STAT) genes: putative association of the STAT generegion with familial breast cancer. Endocr Relat Cancer 14:267–277
Wang Z (2013) Association of signal transducer and activator of transcription 3/5b genes polymorphisms with breast cancer in Chinese women. Master Thesis. China Medical University
Wang K, Zhou B, Zhang J, Xin Y, Lai T, Wang Y, Hou Q, Song Y, Chen Y, Quan Y, Xi M, Zhang L (2011) Association of signal transducer and activator of transcription 3 gene polymorphisms with cervical cancer in Chinese women. DNA Cell Biol 30:931–936
Xie JX (2012b) Study on the interactions between hepatitis B virus mutations and the polymorphisms of STAT3 in the occurrence of hepatocellular carcinoma. PhD Thesis. The Second Military Medical University
Xie JX, Yin JH, Zhang Q, Pu R, Zhang YW, Lu WY, Cao GW (2012) Association of genetic polymorphisms of key molecules in JAK/STAT signaling pathway with susceptibility of hepatocellular carcinoma. Zhonghua Liu Xing Bing Xue Za Zhi 33:215–219
Xie J, Zhang Y, Zhang Q, Han Y, Yin J, Pu R, Shen Q, Lu W, Du Y, Zhao J, Han X, Zhang H, Cao G (2013) Interaction of signal transducer and activator oftranscription 3 polymorphisms with hepatitis B virus mutations in hepatocellular carcinoma. Hepatology 57:2369–2377
Xu CX (2013)Polymorphisms in Inflammatory Pathway Genes and their Association with Colorectal Cancer Susceptibility. Master Thesis. Zhejiang University
Yang R (2013)The epidemiological study on the association of Single nucleotide polymorphisms within micro RNA binding sites in NF-κB and STAT3 inflammatory signaling pathways and environmental factors with the risk of lung cancer. Master Thesis. Fujian Medical University
Yu H, Jove R (2004) The STATs of cancer—new molecular targets come of age. Nat Rev Cancer 4:97–105
Yu H, Pardoll D, Jove R (2009) STATs in cancer inflammation and immunity: a leading role for STAT3. Nat Rev Cancer 9:798–809
Yuan K, Liu H, Huang L, Ren X, Liu J, Dong X, Tian W, Jia Y (2014) rs744166 polymorphism of the STAT3 gene is associated with risk of gastric cancer in a Chinese population. Biomed Res Int 2014:527918
Zaridze DG (2008) Molecular epidemiology of cancer. Biochemistry (Mosc) 73:532–542
Zhang T (2011) Association between Polymorphisms of Inflammation-related Genes of NF-KB1, COX-2, NOS2, STAT3 and Risk of Esophageal Squamous Cell Carcinoma. Master Thesis. Huazhong University of Science and Technology
Zhang LL (2013) Corelation between STAT3 C1697G polymorphisms and risks of gastric cancer. Acad J Guangzhou Med Coll 41:59–62
Zhao H, Wang Z, Wu H, Xiao Q, Yao W, Wang E, Liu Y, Wei M (2015) STAT3 geneticvariant, alone and in combination with STAT5b polymorphism, contributes to breastcancer risk and clinical outcomes. Med Oncol 32:375
Zhong Y, Wu J, Chen B, Ma R, Cao H, Wang Z, Cheng L, Ding J, Feng J (2012) Investigation and analysis of single nucleotide polymorphisms in Januskinase/signal transducer and activator of transcription genes with leukemia. LeukLymphoma 53:1216–1221
Zhou T, Chao L, Rong G, Wang C, Ma R, Wang X (2013) Down-regulation of GRIM-19 is associated with STAT3 overexpression in breast carcinomas. Hum Pathol 44:1773–1779
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Communicated by S. Hohmann.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yan, R., Lin, F., Hu, C. et al. Association between STAT3 polymorphisms and cancer risk: a meta-analysis. Mol Genet Genomics 290, 2261–2270 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00438-015-1074-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00438-015-1074-y