Abstract
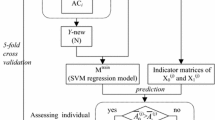
Carboxy-terminal α-amidation is a widespread post-translational modification of proteins found widely in vertebrates and invertebrates. The α-amide group is required for full biological activity, since it may render a peptide more hydrophobic and thus better be able to bind to other proteins, preventing ionization of the C-terminus. However, in particular, the C-terminal amidation is very difficult to detect because experimental methods are often labor-intensive, time-consuming and expensive. Therefore, in silico methods may complement due to their high efficiency. In this study, a computational method was developed to predict protein amidation sites, by incorporating the maximum relevance minimum redundancy method and the incremental feature selection method based on the nearest neighbor algorithm. From a total of 735 features, 41 optimal features were selected and were utilized to construct the final predictor. As a result, the predictor achieved an overall Matthews correlation coefficient of 0.8308. Feature analysis showed that PSSM conservation scores and amino acid factors played the most important roles in the α-amidation site prediction. Site-specific feature analyses showed that features derived from the amidation site itself and adjacent sites were most significant. This method presented could be used as an efficient tool to theoretically predict amidated peptides. And the selected features from our study could shed some light on the in-depth understanding of the mechanisms of the amidation modification, providing guidelines for experimental validation.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Altschul SF, Madden TL, Schaffer AA, Zhang J, Zhang Z, Miller W, Lipman DJ (1997) Gapped BLAST and PSI-BLAST: a new generation of protein database search programs. Nucleic Acids Res 25(17):3389–3402 [pii: gka562]
Apweiler R, Martin MJ, O’Donovan C, Magrane M, Alam-Faruque Y, Antunes R, Barrell D, Bely B, Bingley M, Binns D, Bower L, Browne P, Chan WM, Dimmer E, Eberhardt R, Fedotov A, Foulger R, Garavelli J, Huntley R, Jacobsen J, Kleen M, Laiho K, Leinonen R, Legge D, Lin Q, Liu WD, Luo J, Orchard S, Patient S, Poggioli D, Pruess M, Corbett M, di Martino G, Donnelly M, van Rensburg P, Bairoch A, Bougueleret L, Xenarios I, Altairac S, Auchincloss A, Argoud-Puy G, Axelsen K, Baratin D, Blatter MC, Boeckmann B, Bolleman J, Bollondi L, Boutet E, Quintaje SB, Breuza L, Bridge A, deCastro E, Ciapina L, Coral D, Coudert E, Cusin I, Delbard G, Doche M, Dornevil D, Roggli PD, Duvaud S, Estreicher A, Famiglietti L, Feuermann M, Gehant S, Farriol-Mathis N, Ferro S, Gasteiger E, Gateau A, Gerritsen V, Gos A, Gruaz-Gumowski N, Hinz U, Hulo C, Hulo N, James J, Jimenez S, Jungo F, Kappler T, Keller G, Lachaize C, Lane-Guermonprez L, Langendijk-Genevaux P, Lara V, Lemercier P, Lieberherr D, Lima TD, Mangold V, Martin X, Masson P, Moinat M, Morgat A, Mottaz A, Paesano S, Pedruzzi I, Pilbout S, Pillet V, Poux S, Pozzato M, Redaschi N, Rivoire C, Roechert B, Schneider M, Sigrist C, Sonesson K, Staehli S, Stanley E, Stutz A, Sundaram S, Tognolli M, Verbregue L, Veuthey AL, Yip LN, Zuletta L, Wu C, Arighi C, Arminski L, Barker W, Chen CM, Chen YX, Hu ZZ, Huang HZ, Mazumder R, McGarvey P, Natale DA, Nchoutmboube J, Petrova N, Subramanian N, Suzek BE, Ugochukwu U, Vasudevan S, Vinayaka CR, Yeh LS, Zhang J, Consortium U (2010) The Universal Protein Resource (UniProt) in 2010. Nucleic Acids Res 38:D142–D148. doi:10.1093/Nar/Gkp846
Atchley WR, Zhao J, Fernandes AD, Druke T (2005) Solving the protein sequence metric problem. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 102(18):6395–6400. doi:10.1073/pnas.0408677102
Bousquet-Moore D, Prohaska JR, Nillni EA, Czyzyk T, Wetsel WC, Mains RE, Eipper BA (2010) Interactions of peptide amidation and copper: novel biomarkers and mechanisms of neural dysfunction. Neurobiol Dis 37(1):130–140. doi:10.1016/j.nbd.2009.09.016
Cai Y, He J, Li X, Lu L, Yang X, Feng K, Lu W, Kong X (2009) A novel computational approach to predict transcription factor DNA binding preference. J Proteome Res 8(2):999–1003. doi:10.1021/pr800717y
Cheng J, Randall AZ, Sweredoski MJ, Baldi P (2005) SCRATCH: a protein structure and structural feature prediction server. Nucleic Acids Res 33:W72–W76. doi:10.1093/Nar/Gki396
Chufan EE, De M, Eipper BA, Mains RE, Amzel LM (2009) Amidation of bioactive peptides: the structure of the lyase domain of the amidating enzyme. Structure 17(7):965–973. doi:10.1016/j.str.2009.05.008
Crooks GE, Hon G, Chandonia JM, Brenner SE (2004) WebLogo: a sequence logo generator. Genome Res 14(6):1188–1190. doi:10.1101/gr.849004
De M, Bell J, Blackburn NJ, Mains RE, Eipper BA (2006) Role for an essential tyrosine in peptide amidation. J Biol Chem 281(30):20873–20882
Dennison SR, Phoenix DA (2011) Influence of C-terminal amidation on the efficacy of Modelin-5. Biochemistry 50:1514–1523
Dennison SR, Harris F, Bhatt T, Singh J, Phoenix DA (2009) The effect of C-terminal amidation on the efficacy and selectivity of antimicrobial and anticancer peptides. Mol Cell Biochem 332(1–2):43–50. doi:10.1007/s11010-009-0172-8
Driscoll WJ, Mueller SA, Eipper BA, Mueller GP (1999) Differential regulation of peptide α-amidation by dexamethasone and disulfiram. Mol Pharmacol 55:1067–1076
Eipper BA, Milgram SL, Husten EJ, Yun HY, Mains RE (1993) Peptidylglycine alpha-amidating monooxygenase: a multifunctional protein with catalytic, processing, and routing domains. Protein Sci 2(4):489–497
Eipper BA, Stoffers DA, Mains RE (1992) The biosynthesis of neuropeptides: peptide alpha-amidation. Annu Rev Neurosci 15:57–85. doi:10.1146/annurev.ne.15.030192.000421
Goldschmidt L, Teng PK, Riek R, Eisenberg D (2010) Identifying the amylome, proteins capable of forming amyloid-like fibrils. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 107(8):3487–3492. doi:10.1073/pnas.0915166107
Huang T, Cui W, Hu L, Feng K, Li YX, Cai YD (2009) Prediction of pharmacological and xenobiotic responses to drugs based on time course gene expression profiles. PLoS ONE 4(12):e8126. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0008126
Huang T, Shi XH, Wang P, He Z, Feng KY, Hu L, Kong X, Li YX, Cai YD, Chou KC (2010) Analysis and prediction of the metabolic stability of proteins based on their sequential features, subcellular locations and interaction networks. PLoS ONE 5(6):e10972. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0010972
Huang T, Tu K, Shyr Y, Wei CC, Xie L, Li YX (2008) The prediction of interferon treatment effects based on time series microarray gene expression profiles. J Transl Med 6:44. doi:10.1186/1479-5876-6-44
In Y, Ono H, Ishida T (2002) Structural studies on C-amidated amino acids and peptides: function of amide group in molecular association in crystal structures of Val-Gly-NH2, Ser-Phe-NH2, Gly-Tyr-NH2 and Pro-Tyr-NH2 hydrochloride salts. Chem Pharm Bull (Tokyo) 50(5):571–577
Jain E, Bairoch A, Duvaud S, Phan I, Redaschi N, Suzek BE, Martin MJ, McGarvey P, Gasteiger E (2009) Infrastructure for the life sciences: design and implementation of the UniProt website. BMC Bioinformatics 10:136. doi:10.1186/1471-2105-10-136
Jordan IK, Kondrashov FA, Adzhubei IA, Wolf YI, Koonin EV, Kondrashov AS, Sunyaev S (2005) A universal trend of amino acid gain and loss in protein evolution. Nature 433(7026):633–638. doi:10.1038/Nature03306
Kang TS, Vivekanandan S, Jois SDS, Kini RM (2005) Effect of C-terminal amidation on folding and disulfide-pairing of α-conotoxin ImI. Angew Chem Int Ed 44:6333–6337
Katopodis AG, Ping DS, Smith CE, May SW (1991) Functional and structural characterization of peptidylamidoglycolate lyase, the enzyme catalyzing the second step in peptide amidation. Biochemistry 30(25):6189–6194
Kawashima S, Kanehisa M (2000) AAindex: amino acid index database. Nucleic Acids Res 28(1):374. doi:gkd029
Kolhekar AS, Roberts MS, Jiang N, Johnson RC, Mains RE, Eipper BA, Taghert PH (1997) Neuropeptide amidation in Drosophila: separate genes encode the two enzymes catalyzing amidation. J Neurosci 17(4):1363–1376
Kuyama H, Nakajima C, Nakazawa T, Nishimura O, Tsunasawa S (2009) A new approach for detecting C-terminal amidation of proteins and peptides by mass spectrometry in conjunction with chemical derivatization. Proteomics 9(16):4063–4070. doi:10.1002/pmic.200900267
Liu J, Tan H, Rost B (2002) Loopy proteins appear conserved in evolution. J Mol Biol 322(1):53–64 [pii: S0022283602007362]
Liu MC, Yasuda S, Idell S (2007) Sulfation of nitrotyrosine: biochemistry and functional implications. IUBMB Life 59(10):622–627. doi:10.1080/15216540701589320
Ma BY, Elkayam T, Wolfson H, Nussinov R (2003) Protein–protein interactions: structurally conserved residues distinguish between binding sites and exposed protein surfaces. P Natl Acad Sci USA 100(10):5772–5777. doi:10.1073/pnas.1030237100
Mueller GP, Driscoll WJ (2008) alpha-Amidated peptides: approaches for analysis. Methods Mol Biol 446:67–84. doi:10.1007/978-1-60327-084-7_5
Peng H, Long F, Ding C (2005) Feature selection based on mutual information: criteria of max-dependency, max-relevance, and min-redundancy. IEEE Trans Pattern Anal Mach Intell 27(8):1226–1238. doi:10.1109/TPAMI.2005.159
Peng K, Radivojac P, Vucetic S, Dunker AK, Obradovic Z (2006) Length-dependent prediction of protein intrinsic disorder. BMC Bioinformatics 7:208. doi:10.1186/1471-2105-7-208
Plewczynski D, Tkacz A, Wyrwicz LS, Rychlewski L (2005) AutoMotif server: prediction of single residue post-translational modifications in proteins. Bioinformatics 21(10):2525–2527
Popelier PL, Aicken FM (2003) Atomic properties of selected biomolecules: quantum topological atom types of carbon occurring in natural amino acids and derived molecules. J Am Chem Soc 125(5):1284–1292. doi:10.1021/ja0284198
Priggea ST, Mainsb RE, Eipperb BA, Amzel LM (2000) New insights into copper monooxygenases and peptide amidation: structure, mechanism and function. CMLS Cell Mol Life Sci 57:1236–1259
Qian Z, Cai YD, Li Y (2006) A novel computational method to predict transcription factor DNA binding preference. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 348(3):1034–1037
Rocchi P, Boudouresque F, Zamora AJ, Muracciole X, Lechevallier E, Martin PM, Ouafik L (2001) Expression of adrenomedullin and peptide amidation activity in human prostate cancer and in human prostate cancer cell lines. Cancer Res 61(3):1196–1206
Schneider TD, Stephens RM (1990) Sequence logos: a new way to display consensus sequences. Nucleic Acids Res 18(20):6097–6100
Shimosawa T, Kanozawa K, Nagasawa R, Mitarai T, Isoda K, Takahashi K, Ando K, Tozawa Y, Nagase M, Sasaki N, Fujita M, Takano K, Iiri T, Fujita T (2000) Adrenomedullin amidation enzyme activities in hypertensive patients. Hypertens Res 23(2):167–171
Tompa P (2002) Intrinsically unstructured proteins. Trends Biochem Sci 27(10):527–533 [pii: S0968000402021692]
Trouillas P, Berges J, Houee-Levin C (2011) Toward understanding the protein oxidation processes: (OH)-O-center dot addition on tyrosine, phenylalanine, or methionine? Int J Quantum Chem 111(6):1143–1151. doi:10.1002/Qua.22556
Wilkins MR, Gasteiger E, Gooley AA, Herbert BR, Molloy MP, Binz PA, Ou K, Sanchez JC, Bairoch A, Williams KL, Hochstrasser DF (1999) High-throughput mass spectrometric discovery of protein post-translational modifications. J Mol Biol 289(3):645–657. doi:10.1006/jmbi.1999.2794
Wright PE, Dyson HJ (1999) Intrinsically unstructured proteins: re-assessing the protein structure-function paradigm. J Mol Biol 293(2):321–331. doi:10.1006/jmbi.1999.3110
Yamaguchi H, Sasaki K, Satomi Y, Shimbara T, Kageyama H, Mondal MS, Toshinai K, Date Y, Gonzalez LJ, Shioda S, Takao T, Nakazato M, Minamino N (2007) Peptidomic identification and biological validation of neuroendocrine regulatory peptide-1 and -2. J Biol Chem 282(36):26354–26360. doi:10.1074/jbc.M701665200
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by grants from National Basic Research Program of China (2011CB510102, 2011CB510101), National Science Foundation of China (81171342, 81201148), Innovation Program of Shanghai Municipal Education Commission (12ZZ087), Independent Innovation Foundation of Tianjin University (60302069, 60302064), The National Research Foundation for the Doctoral Program of Higher Education of China (20120032120073) and the grant of “The First-class Discipline of Universities in Shanghai”.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Additional information
Communicated by S. Hohmann.
W. Cui, S. Niu and L. Zheng contributed equally to this work.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Cui, W., Niu, S., Zheng, L. et al. Prediction of protein amidation sites by feature selection and analysis. Mol Genet Genomics 288, 391–400 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00438-013-0760-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00438-013-0760-x