Abstract
The integrase encoded by the lambdoid phage HK022 (Int-HK022) resembles its coliphage λ counterpart (Int-λ) in the roles of the cognate DNA arm binding sites and in controlling the direction of the reaction. We show here that within mammalian cells, Int-HK022 does not exhibit such a control. Rather, Int-HK022 recombined between all ten possible pairwise att site combinations, including attB × attB that was more effective than the conventional integrative attP × attB reaction. We further show that Int-HK022 depends on the accessory integration host factor (IHF) protein considerably less than Int-λ and exhibits stronger binding affinity to the att core. These differences explain why wild-type Int-HK022 is active in mammalian cells whereas Int-λ is active there only as an IHF-independent mutant.








Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- ApR :
-
Ampicillin resistance
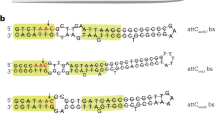
- att :
-
Attachment site
- bp:
-
Base pairs
- CMV:
-
Cytomegalovirus
- FACS:
-
Fluorescent-activated cell sorting
- FIS:
-
Factor for inversion specificity
- GFP:
-
Green fluorescent protein
- HygR :
-
Hygromycin resistance
- IHF:
-
Integration host factor
- Int:
-
Integrase
- KmR :
-
Kanamycin resistance
- LB:
-
Luria–Bertani broth
- MW:
-
Molecular weight markers
- NeoR :
-
Neomycin resistance
- wt:
-
Wild type
- X-gal:
-
5-bromo-4-chloro-3-indolyl-β-d-galactopyranoside
- Xis:
-
Excisionase
References
Anastassiadis K, Fu J, Patsch C, Hu S, Weidlich S, Duerschke K, Buchholz F, Edenhofer F, Stewart AF (2009) Dre recombinase, like Cre, is a highly efficient site-specific recombinase in E. coli, mammalian cells and mice. Dis Model Mech 2:508–515
Azaro MA, Landy A (2002) Integrase and the λ int family. In: Craig NL, Craigie R, Gellert M, Lambowitz A (eds) Mobile DNAII. American Society of Microbiology, Washington, DC, pp 118–148
Birling MC, Gofflot F, Warot X (2009) Site-specific recombinases for manipulation of the mouse genome. Methods Mol Biol 561:245–263
Bolusani S, Ma CH, Paek A, Konieczka JH, Jayaram M, Voziyanov Y (2006) Evolution of variants of yeast site-specific recombinase Flp that utilize native genomic sequences as recombination target sites. Nucl Acids Res 34:5259–5269
Branda CS, Dymecki SM (2004) Talking about a revolution: the impact of site-specific recombinases on genetic analyses in mice. Dev Cell 6:7–28
Christ N, Dröge P (2002) Genetic manipulation of mouse embryonic stem cells by mutant lambda integrase. Genesis 32:203–208
Christ N, Corona T, Dröge P (2002) Site-specific recombination in eukaryotic cells mediated by mutant lambda integrases: implications for synaptic complex formation and the reactivity of episomal DNA segments. J Mol Biol 319:305–314
Corona T, Bao QY, Christ N, Schwartz T, Li JM, Dröge P (2003) Activation of site-specific DNA integration in human cells by a single chain integration host factor. Nucl Acids Res 31:5140–5148
Craig NL (1988) The mechanism of conservative site-specific recombination. Annu Rev Genet 22:77–105
Dorgai L, Yagil E, Weisberg R (1995) Identifying determinants of recombination specificity: construction and characterization of mutant bacteriophage integrases. J Mol Biol 252:178–188
Giladi H, Koby S, Prag G, Engelhorn M, Geiselmann J, Oppenheim AB (1998) Participation of IHF and a distant UP element in the stimulation of the phage lambda PL promoter. Mol Microbiol 30:443–451
Glaser S, Anastassiadis K, Stewart AF (2005) Current issues in mouse genome engineering. Nat Genet 37:1187–1193
Gottfried P, Yagil E, Kolot M (2000) Core-binding specificity of bacteriophage integrase. Mol Gen Genet 263:619–624
Gottfried P, Kolot M, Yagil E (2001) The effect of mutations in the Xis-binding sites on site-specific recombination in coliphage HK022. Mol Genet Genomics 266:584–590
Harel-Levy G, Goltsman J, Tuby CNJH, Yagil E, Kolot M (2008) Human genomic site-specific recombination catalyzed by coliphge HK022 integrase. J Biotechnol 134:45–54
Hirt B (1967) Selective extraction of polyoma DNA from infected mouse cell cultures. J Mol Biol 26:365–369
Kolot M, Gottfried P, Yagil E (1996) A second site-specific recombination event in the lambdoid bacteriophage HK022. Mol Gen Genet 253:362–369
Kolot M, Silberstein N, Yagil E (1999) Site-specific recombination in mammalian cells expressing the Int recombinase of bacteriophage HK022. Mol Biol Rep 26:207–213
Kolot M, Meroz A, Yagil E (2003) Site-specific recombination in human cells catalyzed by the wild-type integrase protein of coliphage HK022. Biotechnol Bioeng 84:56–60
Lorbach E, Christ N, Schwikardi M, Dröge P (2000) Site-specific recombination in human cells catalyzed by phage lambda integrase mutants. J Mol Biol 296:1175–1181
Malchin N, Molotsky T, Yagil E, Kotlyar AB, Kolot M (2008) Molecular analysis of recombinase-mediated cassette exchange reactions catalyzed by integrase of coliphage HK022. Res in Microbiol 159:663–670
Malchin N, Goltsman J, Dabool L, Gorovits R, Bao Q, Dröge P, Yagil E, Kolot M (2009) Optimization of coliphage HK022 integrase activity in human cells. Gene 437:9–13
Nagaraja R, Weisberg RA (1990) Specificity determinants in the attachment sites of bacteriophages HK022 and lambda. J Bacteriol 172:6540–6550
Numrych TE, Gumport RI, Gardner JF (1990) A comparison of the effects of single-base and triple-base changes in the integrase arm-type binding sites on the site-specific recombination of bacteriophage lambda. Nucl Acids Res 18:3953–3959
Patsey RL, Bruist MF (1995) Characterization of the interaction between the lambda intasome and attB. J Mol Biol 252:47–58
Radman-Livaja M, Biswas T, Ellenberger T, Landy A, Aihara H (2006) DNA arms do the legwork to ensure the directionality of lambda site-specific recombination. Curr Opin Struct Biol 16:42–50
Sambrook J, Fritsch EF, Maniatis T (1989) Molecular cloning: a laboratory manual. Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory, Cold Spring Harbor
Sarkar D, Radman-Livaja M, Landy A (2001) The small DNA binding domain of lambda integrase is a context-sensitive modulator of recombinase functions. EMBO J 20:1203–1212
Sauer B (1993) Manipulation of transgenes by site-specific recombination: use of Cre recombinase. Methods Enzymol 225:890–900
Segall AM, Nash HA (1996) Architectural flexibility in lambda site-specific recombination: three alternate conformations channel the attL site into three distinct pathways. Genes Cells 1:453–463
Segall AM, Goodman SD, Nash HA (1994) Architectural elements in nucleoprotein complexes: interchangeability of specific and non-specific DNA binding proteins. EMBO J 13:4536–4548
Sorrell DA, Kolb AF (2005) Targeted modification of mammalian genomes. Biotechnol Adv 23:431–469
Summers DK, Sherratt DJ (1988) Resolution of ColE1 dimers requires a DNA sequence implicated in the 3-dimensional organization of the Cer site. EMBO J 7:851–858
Vieira J, Messing J (1991) New Puc-derived cloning vectors with different selectable markers and DNA-replication origins. Gene 100:189–194
Weisberg RA, Gottesmann ME, Hendrix RW, Little JW (1999) Family values in the age of genomics: comparative analyses of temperate bacteriophage HK022. Annu Rev Genet 33:565–602
Wirth D, Gama-Norton L, Riemer P, Sandhu U, Schucht R, Hauser H (2007) Road to precision: recombinase-based targeting technologies for genome engineering. Curr Opin Biotechnol 18:411–419
Yagil E, Dolev S, Oberto J, Kislev N, Ramaiah N, Weisberg RA (1989) Determinants of site-specific recombination in the lambdoid coliphage HK022. An evolutionary change in specificity. J Mol Biol 207:695–717
Yanisch-Perron C, Vieira J, Messing J (1985) Improved M13 phage cloning vectors and host strains: nucleotide sequence of the M13mp18 and pUC19 vectors. Gene 33:103–119
Acknowledgments
N.M. is supported by the Leon Reich Scholarship Fund. Gabi Kaufman assisted us with science and language. László Dorgai sent us plasmid pAG159. Research was supported by grant No. MB-8713-08 from BARD, the United States-Israel Binational Agricultural Research and Development Fund and grant No. 1062/2008 from G.I.F., the German Israeli Foundation for Scientific Research and Development to E.Y. and M.K.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Communicated by D. Andersson.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Malchin, N., Tuby, C.N., Yagil, E. et al. Arm site independence of coliphage HK022 integrase in human cells. Mol Genet Genomics 285, 403–413 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00438-011-0614-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00438-011-0614-3