Abstract
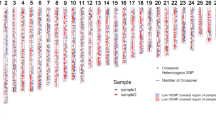
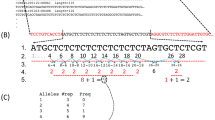
Microsatellite genotyping from trace DNA is now common in fields as diverse as medicine, forensics and wildlife genetics. Conversely, small-pool PCR (SP-PCR) has been used to investigate microsatellite mutation mechanisms in human DNA, but has had only limited application to non-human species. Trace DNA and SP-PCR studies share many challenges, including problems associated with allelic drop-out, false alleles and other PCR artefacts, and the need to reliably identify genuine alleles and/or mutations. We provide a framework for the validation of such studies without a multiple tube approach and demonstrate the utility of that approach with an analysis of microsatellite mutations in the tammar wallaby (Macropus eugenii). Specifically, we amplified three autosomal microsatellites from somatic DNA to characterise efficiency and reliability of PCR from low-template DNA. Reconstruction experiments determined our ability to discriminate mutations from parental alleles. We then developed rules to guide data interpretation. We estimated mutation rates in sperm DNA to range from 1.5 × 10−2 to 2.2 × 10−3 mutations per locus per generation. Large multi-step mutations were observed, providing evidence for complex mutation processes at microsatellites and potentially violating key assumptions in the stepwise mutation model. Our data demonstrate the necessity of actively searching for large mutation events when investigating microsatellite evolution and highlight the need for a thorough understanding of microsatellite amplification characteristics before embarking on SP-PCR or trace DNA studies.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bacon AL, Farrington SM, Dunlop MG (2000) Sequence interruptions confer differential stability at microsatellite alleles in mismatch repair-deficient cells. Hum Mol Genet 9:2707–2713
Bacon AL, Dunlop MG, Farrington SM (2001) Hypermutability at a poly(A/T) tract in the human germline. Nucleic Acids Res 29:4405–4413
Balloux F, Lugon-Moulin N (2002) The estimation of population differentiation with microsatellite markers. Mol Ecol 11:155–165
Brinkmann B, Klintschar M, Neuhuber F, Hühne J, Rolf B (1998) Mutation rate in human microsatellites: influence of the structure and length of the tandem repeat. Am J Hum Genet 62:1408–1415
Brohede J, Primmer CR, Møller A, Ellegren H (2002) Heterogeneity in the rate and pattern of germline mutation at individual microsatellite loci. Nucleic Acids Res 30:1997–2003
Brohede J, Arnheim N, Ellegren H (2004) Single-molecule analysis of the hypermutable tetranucleotide repeat locus D21S1245 through sperm genotyping: a heterogeneous pattern of mutation but no clear male age effect. Mol Biol Evol 21:58–64
Budowle B, Garofano P, Hellman A, Ketchum M, Kanthaswamy S, Parson W, van Haeringen W, Fain S, Broad T (2005) Recommendations for animal DNA forensic and identity testing. Int J Leg Med 119:295–302
Buschiazzo E, Gemmell NJ (2006) The rise, fall and renaissance of microsatellites in eukaryotic genomes. BioEssays 28:1040–1050
Caudron AK, Negro SS, Muller CG, Boren LJ, Gemmell NJ (2007) Hair sampling and genotyping from hair follicles: a minimally-invasive alternative for genetics studies in small, mobile pinnipeds and other mammals. Mar Mamm Sci 23:184–192
Coolbaugh-Murphy M, Maleki A, Ramagli L, Frazier M, Lichtiger B, Monckton D, Siciliano M, Brown B (2004) Estimating mutant microsatellite allele frequencies in somatic cells by small-pool PCR. Genomics 84:419–430
Crawford DC, Wilson B, Sherman SL (2000) Factors involved in the initial mutation of the fragile X CGG repeat as determined by sperm small pool PCR. Hum Mol Genet 9:2909–2918
Davison A, Chiba S (2003) Laboratory temperature variation is a previously unrecognized source of genotyping error during capillary electrophoresis. Mol Ecol Notes 3:321–323
De Biase I, Rasmussen A, Monticelli A, Al-Mahdawi S, Pook M, Cocozza S, Bidichandani SI (2007) Somatic instability of the expanded GAA triplet-repeat sequence in Friedreich ataxia progresses throughout life. Genomics 90:1–5
DeWoody J, Nason JD, Hipkins VD (2006) Mitigating scoring errors in microsatellite data from wild populations. Mol Ecol Notes 6:951–957
Di Rienzo A, Peterson AC, Garza JC, Valdes AM, Slatkin M, Freimer NB (1994) Mutational processes of simple-sequence repeat loci in human populations. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 91:3166–3170
Di Rienzo A, Donnelly P, Toomajian C, Sisk B, Hill A, Petzl-Erler ML, Haines GK, Barch DH (1998) Heterogeneity of microsatellite mutations within and between loci, and implications for human demographic histories. Genetics 148:1269–1284
Eisen J (1999) Mechanistic basis for microsatellite instability. In: Goldstein DB, Schlötterer C (eds) Microsatellites: evolution and applications. Oxford University Press, Oxford, pp 34–48
Ellegren H (2000) Microsatellite mutations in the germline: implications for evolutionary inference. Trends Genet 16:551–558
Ellegren H (2004) Microsatellites: simple sequences with complex evolution. Nat Rev Genet 5:435–445
Estoup A, Jarne P, Cornuet JM (2002) Homoplasy and mutation model at microsatellite loci and their consequences for population genetics analysis. Mol Ecol 11:1591–1604
Ewen KR, Bahlo M, Treloar SA, Levinson DF, Mowry B, Barlow JW, Foote SJ (2000) Identification and analysis of error types in high-throughput genotyping. Am J Hum Genet 67:727–736
Fernando P, Vidya TNC, Rajapakse C, Dangolla A, Melnick DJ (2003) Reliable noninvasive genotyping: fantasy or reality? J Hered 94:115–123
Fitzsimmons NN (1998) Single paternity of clutches and sperm storage in the promiscuous green turtle (Chelonia mydas). Mol Ecol 7:575–584
Foucault F, Praz F, Jaulin C, Amor-Gueret M (1996) Experimental limits of PCR analysis of (CA) n repeat alterations. Trends Genet 12:450
Gagneux P, Boesch C, Woodruff D (1997) Microsatellite scoring errors associated with noninvasive genotyping based on nuclear DNA amplified from shed hair. Mol Ecol 6:861–868
Gardner MG, Bull CM, Cooper SJB, Duffield GA (2000) Microsatellite mutations in litters of the Australian lizard Egernia stokesii. J Evol Biol 13:551–560
Goldstein DB, Pollock DD (1997) Launching microsatellites: a review of mutation processes and methods of phylogenetic inference. J Hered 88:335–342
Goldstein DB, Linares AR, Cavalli-Sforza LL, Feldman MW (1995) Genetic absolute dating based on microsatellites and the origin of modern humans. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 92:6723–6727
Goossens B, Waits LP, Taberlet P (1998) Plucked hair samples as a source of DNA: reliability of dinucleotide microsatellite genotyping. Mol Ecol 7:1237–1241
Gregory TR (2006) Animal Genome Size Database. http://www.genomesize.com
Gusmão L, Sanchez-Diz P, Calafell F, Martin P, Alonso CA, Alvarez-Fernandez F, Alves C, Borjas-Fajardo L, Bozzo WR, Bravo ML, Builes JJ, Capilla J, Carvalho M, Castillo C, Catanesi CI, Corach D, Di Lonardo AM, Espinheira R, Fagundes de Carva E, Farfan MJ, Figueiredo HP, Gomes I, Lojo MM, Marino M, Pinheiro MF, Pontes ML, Prieto V, Ramos-Luis E, Riancho JA, Souza Goes AC, Santapa OA, Sumita DR, Vallejo G, Vidal Rioja L, Vide MC, Vieira da Silva CI, Whittle MR, Zabala W, Zarrabeitia MT, Alonso A, Carracedo A, Amorim A (2005) Mutation rates at Y chromosome specific microsatellites. Hum Mutat 26:520–528
Haberl M, Tautz D (1999) Comparative allele sizing can produce inaccurate allele size differences for microsatellites. Mol Ecol 8:1347–1349
Hebsgaard MB, Phillips MJ, Willerslev E (2005) Geologically ancient DNA: fact or artefact? Trends Microbiol 13:212–220
Hoffman JI, Amos W (2005) Microsatellite genotyping errors: detection approaches, common sources and consequences for paternal exclusion. Mol Ecol 14:599–612
Holtkemper U, Rolf B, Hohoff C, Forster P, Brinkmannn B (2001) Mutation rates at two human Y-chromosomal microsatellite loci using small pool PCR techniques. Hum Mol Genet 10:629–633
Ionov Y, Peinado MA, Malkhosyan S, Shibata D, Perucho M (1993) Ubiquitous somatic mutations in simple repeated sequences reveal a new mechanism for colonic carcinogenesis. Nature 363:558–561
Jarne P, Lagoda PJL (1996) Microsatellites, from molecules to populations and back. Trends Ecol Evol 11:424–429
Jeffreys AJ, Tamaki K, MacLeod A, Monckton DG, Neil DL, Armour JA (1994) Complex gene conversion events in germline mutation at human minisatellites. Nat Genet 6:136–145
Jeffreys AJ, Bois P, Buard J, Collick A, Dubrova Y, Hollies CR, May CA, Murray J, Neil DL, Neumann R, Stead JD, Tamaki K, Yardley J (1997) Spontaneous and induced minisatellite instability. Electrophoresis 18:1501–1511
Jobling MA, Gill P (2004) Encoded evidence: DNA in forensic analysis. Nat Rev Genet 5:739–751
Kelkar YD, Tyekucheva S, Chiaromonte F, Makova KD (2008) The genome-wide determinants of human and chimpanzee microsatellite evolution. Genome Res 18:30–38
Kimura M, Ohta T (1978) Stepwise mutation model and distribution of allelic frequencies in a finite population. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 75:2868–2872
Kofler R, Schlotterer C, Luschutzky E, Lelley T (2008) Survey of microsatellite clustering in eight fully sequenced species sheds light on the origin of compound microsatellites. BMC Genomics 9:612
Kruglyak S, Durrett RT, Schug MD, Aquadro CF (1998) Equilibrium distributions of microsatellite repeat length resulting from a balance between slippage events and point mutations. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 95:10774–10778
Leonard JA, Shanks O, Hofreiter M, Kreuz E, Hodges L, Ream W, Wayne RK, Fleischer RC (2007) Animal DNA in PCR reagents plagues ancient DNA research. J Archaeol Sci 34:1361–1366
Leopoldino AM, Pena SDJ (2003) The mutational spectrum of human autosomal tetranucleotide microsatellites. Hum Mutat 21:71–79
Li H, Gyllensten UB, Cui X, Saiki RK, Erlich HA, Arnheim N (1988) Amplification and analysis of DNA sequences in single human sperm and diploid cells. Nature 335:414
Lian C, Oishi R, Miyashita N, Hogetsu T (2004) High somatic instability of a microsatellite locus in a clonal tree, Robinia pseudoacacia. Theor Appl Genet 108:836–841
Lopez-Giraldez F, Marmi J, Domingo-Roura X (2007) High incidence of nonslippage mechanisms generating variability and complexity in Eurasian badger microsatellites. J Hered 98:620–628
MacDonald AJ (2008) Sex chromosome microsatellite markers from an Australian marsupial: development, application and evolution. Dissertation, University of Canberra
MacDonald AJ, Sarre SD, FitzSimmons NN, Graves JAM (2007) Chromosome-specific microsatellites from the tammar wallaby X chromosome and chromosome 2. Mol Ecol Notes 7:1063–1066
Markert JA, Danley PD, Arnegard ME (2001) New markers for new species: microsatellite loci and the East African cichlids. Trends Ecol Evol 16:100–107
Martinez JG, Burke T (2003) Microsatellite typing of sperm trapped in the perivitelline layers of avian eggs: a cautionary note. J Avian Biol 34:20–24
Merkel A, Gemmell N (2008) Detecting short tandem repeats from genome data: opening the software black box. Brief Bioinform 9:355–366
Michalakis Y, Excoffier L (1996) A generic estimation of population subdivision using distances between alleles with special reference for microsatellite loci. Genetics 142:1061–1064
Miquel C, Bellemain E, Poillot C, Bessiere J, Durand A, Taberlet P (2006) Quality indexes to assess the reliability of genotypes in studies using noninvasive sampling and multiple-tube approach. Mol Ecol Notes 6:985–988
Morin PA, Chambers KE, Boesch C, Vigilant L (2001) Quantitative polymerase chain reaction analysis of DNA from noninvasive samples for accurate microsatellite genotyping of wild chimpanzees (Pan troglodytes verus). Mol Ecol 10:1835–1844
Mornet E, Chateau C, Hirst MC, Thepot F, Taillandier A, Cibois O, Serre JL (1996) Analysis of germline variation at the FMR1 CGG repeat shows variation in the normal-premutated borderline range. Hum Mol Genet 5:821–825
Nielsen R, Palsboll PJ (1999) Single-locus tests of microsatellite evolution: multi-step mutations and constraints on allele size. Mol Phylogenet Evol 11:477–484
Pääbo S, Poinar H, Serre D, Jaenicke-Despres V, Hebler J, Rohland N, Kuch M, Krause J, Vigilant L, Hofreiter M (2004) Genetic analyses from ancient DNA. Annu Rev Genet 38:645–679
Paetkau D (2003) An empirical exploration of data quality in DNA-based population inventories. Mol Ecol 12:1375–1387
Piggott MP, Taylor AC (2003) Remote collection of animal DNA and its applications in conservation management and understanding the population biology of rare and cryptic species. Wildl Res 30:1–13
Piggott MP, Bellemain E, Taberlet P, Taylor AC (2004) A multiplex pre-amplification method that significantly improves microsatellite amplification and error rates for faecal DNA in limiting conditions. Conserv Genet 5:417–420
Piñeiro E, Fernàndez-López L, Gamez J, Marcos R, Surrallés J, Velázquez A (2003) Mutagenic stress modulates the dynamics of CTG repeat instability associated with myotonic dystrophy type 1. Nucleic Acids Res 31:6733–6740
Pompanon F, Bonin A, Bellemain E, Taberlet P (2005) Genotyping errors: causes, consequences and solutions. Nat Rev Genet 6:847
Primmer CR, Saino N, Moller AP, Ellegren H (1998) Unravelling the processes of microsatellite evolution through analysis of germ line mutations in barn swallows Hirundo rustica. Mol Biol Evol 15:1047–1054
Rousset F (1996) Equilibrium values of measures of population subdivision for stepwise mutation processes. Genetics 142:1357–1362
Sambrook J, Russell D (2001) Molecular cloning: a laboratory manual, 3rd edn. Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press, Cold Spring Harbor
Schlötterer C (2000) Evolutionary dynamics of microsatellite DNA. Chromosoma 109:365–371
Schlötterer C (2004) The evolution of molecular markers—just a matter of fashion? Nat Rev Genet 5:63–69
Sharma R, Bhatti S, Gomez M, Clark RM, Murray C, Ashizawa T, Bidichandani SI (2002) The GAA triplet-repeat sequence in Friedreich ataxia shows a high level of somatic instability in vivo, with a significant predilection for large contractions. Hum Mol Genet 11:2175–2187
Slatkin M (1995) A measure of population subdivision based on microsatellite allele frequencies. Genetics 139:457–462
Stenman J, Orpana A (2001) Accuracy in amplification. Nat Biotechnol 19:1011–1012
Sunnucks P (2000) Efficient genetic markers for population biology. Trends Ecol Evol 15:199–203
Taberlet P, Griffin S, Goossens B, Questiau S, Manceau V, Escaravage N, Waits LP, Bouvet J (1996) Reliable genotyping of samples with very low DNA quantities using PCR. Nucleic Acids Res 24:3189–3194
Taberlet P, Waits LP, Luikart G (1999) Noninvasive genetic sampling: look before you leap. Trends Ecol Evol 14:323–327
Tvedebrink T, Eriksen PS, Mogensen HS, Morling N (2009) Estimating the probability of allelic drop-out of STR alleles in forensic genetics. Forensic Sci Int 3:222–226
Valdes AM, Slatkin M, Freimer NB (1993) Allele frequencies at microsatellite loci: the stepwise mutation model revisited. Genetics 133:737–749
van Oosterhout C, Hutchinson WF, Wills DPM, Shipley P (2004) Micro-checker: software for identifying and correcting genotyping errors in microsatellite data. Mol Ecol Notes 4:535–538
Wattier R, Engel CR, Saumitou-Laprade P, Valero M (1998) Short allele dominance as a source of heterozygote deficiency at microsatellite loci: experimental evidence at the dinucleotide locus Gv1CT in Gracilaria gracilis (Rhodophyta). Mol Ecol 7:1569–1573
Zenger KR (2001) Genetic linkage maps and population genetics of macropods. Dissertation, Macquarie University
Zhang L, Leeflang EP, Yu J, Arnheim N (1994) Studying human mutations by sperm typing: instability of CAG trinucleotide repeats in the human androgen receptor gene. Nat Genet 7:531–535
Acknowledgments
Thanks to Merrilee Harris for the donation of tammar wallaby sperm samples and to Marilyn Renfree for the donation of tissue samples from Kangaroo Island wallabies. Thanks to Dennis McNevin for the use of laboratory space for PCR setups and to David Pederson for advice on statistical analyses. This work was supported by the Australian Research Council (DP0211687 to S.S. and N.F.).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Communicated by S. Hohmann.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
MacDonald, A.J., Sarre, S.D., FitzSimmons, N.N. et al. Determining microsatellite genotyping reliability and mutation detection ability: an approach using small-pool PCR from sperm DNA. Mol Genet Genomics 285, 1–18 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00438-010-0577-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00438-010-0577-9