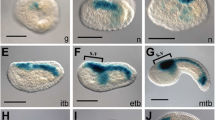
Abstract
Excretory renal organs are critical in animals for osmoregulation and the elimination of waste. Renal organs across a range of species exhibit cellular and molecular similarities. For example, class III POU-homeodomain transcription factors are expressed in the renal organs of many invertebrates and vertebrates. However, the functional role for these factors is not well characterized. To better understand the role of class III POU-homeodomain proteins in animal excretory systems, we have characterized a set of genes expressed in the Caenorhabditis elegans excretory cell, and determined their regulation by the POU-III transcription factor CEH-6. Our molecular and biochemical studies show that CEH-6 regulates a subset of genes expressed in the excretory cell. Additionally, we find that the CEH-6-dependent genes share two molecular features: they contain at least one octamer regulatory element and they encode for transport and channel proteins. This work suggests that a role for POU-III factors in renal organs is to coordinate the expression of a set of functionally related genes.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Altun ZF, Hall DH (2005) The excretory system. In: WormAtlas. http://www.wormatlas.org/ver1/handbook/excretory.htm
Aurora R, Herr W (1992) Segments of the POU domain influence one another’s DNA-binding specificity. Mol Cell Biol 12:455–467
Ben-Tabou de-Leon S, Davidson EH (2007) Gene regulation: gene control network in development. Annu Rev Biophys Biomol Struct 36:191–212
Brenner S (1974) The genetics of Caenorhabditis elegans. Genetics 77:71–94
Broitman-Maduro G, Lin KT, Hung WW, Maduro MF (2006) Specification of the C. elegans MS blastomere by the T-box factor TBX-35. Development 133:3097–3106
Buechner M, Hall DH, Bhatt H, Hedgecock EM (1999) Cystic canal mutants in Caenorhabditis elegans are defective in the apical membrane domain of the renal (excretory) cell. Dev Biol 214:227–241
Burglin TR, Ruvkun G (2001) Regulation of ectodermal and excretory function by the C. elegans POU homeobox gene ceh-6. Development 128:779–790
Certel K, Anderson M, Shrigley R, Johnson W (1996) Distinct variant DNA-binding sites determine cell-specific autoregulated expression of the Drosophila POU domain transcription factor drifter in midline glia or trachea. Mol Cell Biol 16:1813–1823
Chang S, Johnston RJ Jr, Hobert O (2003) A transcriptional regulatory cascade that controls left/right asymmetry in chemosensory neurons of C. elegans. Genes Dev 17:2123–2137
Chavez M, Landry C, Loret S, Muller M, Figueroa J, Peers B, Rentier-Delrue F, Rousseau GG, Krauskopf M, Martial JA (1999) APH-1, a POU homeobox gene expressed in the salt gland of the crustacean Artemia franciscana. Mech Dev 87:207–212
Davidson EH, Rast JP, Oliveri P, Ransick A, Calestani C, Yuh CH, Minokawa T, Amore G, Hinman V, Arenas-Mena C, Otim O, Brown CT, Livi CB, Lee PY, Revilla R, Rust AG, Pan Z, Schilstra MJ, Clarke PJ, Arnone MI, Rowen L, Cameron RA, McClay DR, Hood L, Bolouri H (2002) A genomic regulatory network for development. Science 295:1669–1678
Dawson SJ, Liu YZ, Rodel B, Moroy T, Latchman DS (1996) The ability of POU family transcription factors to activate or repress gene expression is dependent on the spacing and context of their specific response elements. Biochem J 314(Pt 2):439–443
Defrance M, Janky R, Sand O, van Helden J (2008) Using RSAT oligo-analysis and dyad-analysis tools to discover regulatory signals in nucleic sequences. Nat Protoc 3:1589–1603
Drummond I (2003) Making a zebrafish kidney: a tale of two tubes. Trends Cell Biol 13:357–365
Etchberger JF, Lorch A, Sleumer MC, Zapf R, Jones SJ, Marra MA, Holt RA, Moerman DG, Hobert O (2007) The molecular signature and cis-regulatory architecture of a C. elegans gustatory neuron. Genes Dev 21:1653–1674
Fei Y, Liu J, Inoue K, Zhuang L, Miyake K, Miyauchi S, Ganapathy V (2004) Relevance of NAC-2, an Na+-coupled citrate transporter, to life span, body size and fat content in Caenorhabditis elegans. Biochem J 379:191–198
Fire A, Xu S, Montgomery MK, Kostas SA, Driver SE, Mello CC (1998) Potent and specific genetic interference by double-stranded RNA in Caenorhabditis elegans. Nature 391:806–811
Futai M, Oka T, Sun-Wada G, Moriyama Y, Kanazawa H, Wada Y (2000) Luminal acidification of diverse organelles by V-ATPase in animal cells. J Exp Biol 203:107–116
Gaudet J, Mango SE (2002) Regulation of organogenesis by the Caenorhabditis elegans FoxA protein PHA-4. Science 295:821–825
Giannakou ME, Dow JA (2001) Characterization of the Drosophila melanogaster alkali-metal/proton exchanger (NHE) gene family. J Exp Biol 204:3703–3716
Good K, Ciosk R, Nance J, Neves A, Hill RJ, Priess JR (2004) The T-box transcription factors TBX-37 and TBX-38 link GLP-1/Notch signaling to mesoderm induction in C. elegans embryos. Development 131:1967–1978
Gruber TM, Gross CA (2003) Multiple sigma subunits and the partitioning of bacterial transcription space. Annu Rev Microbiol 57:441–466
Hahn-Windgassen A, Van Gilst MR (2009) The Caenorhabditis elegans HNF4a homolog, NHR-31, mediates excretory tube growth and function through coordinate regulation of the vaculolar ATPase. PLoS Genet 5:7
Harris TW, Chen N, Cunningham F, Tello-Ruiz M, Antoshechkin I, Bastiani C, Bieri T, Blasiar D, Bradnam K, Chan J et al (2004) WormBase: a multi-species resource for nematode biology and genomics. Nucleic Acids Res 32:D411–D417
Hobert O (2008) Regulatory logic of neuronal diversity: terminal selector genes and selector motifs. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 105:20067–20071
Igarashi P (2005) Overview: nonmammalian organisms for studies of kidney development and disease. J Am Soc Nephrol 16:296–298
Ishibashi K, Sasaki S, Fushimi K, Uchida S, Kuwahara M, Saito H, Furukawa T, Nakajima K, Yamaguchi Y, Gojobori T (1994) Molecular cloning and expression of a member of the aquaporin family with permeability to glycerol and urea in addition to water expressed at the basolateral membrane of kidney collecting duct cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 91:6269–6273
Josephson R, Muller T, Pickel J, Okabe S, Reynolds K, Turner PA, Zimmer A, McKay RD (1998) POU transcription factors control expression of CNS stem cell-specific genes. Development 125:3087–3100
Jung AC, Denholm B, Skaer H, Affolter M (2005) Renal tubule development in Drosophila: a closer look at the cellular level. J Am Soc Nephrol 16:322–328
Kennedy S, Wang D, Ruvkun G (2004) A conserved siRNA-degrading RNase negatively regulates RNA interference in C. elegans. Nature 427:645–649
Lan L, Liu M, Liu Y, Liu Y, Zhang W, Xue J, He R (2006) Expression of qBrn-1, a new member of the POU gene family, in the early developing nervous system and embryonic kidney. Dev Dyn 235:1107–1114
Ludwig MZ, Bergman C, Patel NH, Kreitman M (2000) Evidence for stabilizing selection in a eukaryotic enhancer element. Nature 403:564–567
Mah AK, Armstrong KR, Chew DS, Chu JS, Tu DK, Johnsen RC, Chamberlin HM, Baillie DL (2007) Transcriptional regulation of AQP-8 by CEH-6. J Biol Chem 282:28074–28086
Mann RS, Carroll SB (2002) Molecular mechanisms of selector gene function and evolution. Curr Opin Genet Dev 12:592–600
McGhee JD, Sleumer MC, Bilenky M, Wong K, McKay SJ, Goszczynski B, Tian H, Krich ND, Khattra J, Holt RA et al (2007) The ELT-2 GATA-factor and the global regulation of transcription in the C. elegans intestine. Dev Biol 302:627–645
McGhee JD, Fukushige T, Krause MW, Minnema SE, Goszczynski B, Gaudet J, Kohara Y, Bossinger O, Zhao Y, Khattra J, Hirst M, Jones SJ, Marra MA, Ruzanov P, Warner A, Zapf R, Moerman DG, Kalb JM (2009) ELT-2 is the predominant transcription factor controlling differentiation and function of the C. elegans intestine, from embryo to adult. Dev Biol 327:551–565
Mello CC, Kramer JM, Stinchcomb D, Ambros V (1991) Efficient gene transfer in C. elegans: extrachromosomal maintenance and integration of transforming sequences. EMBO J 10:3959–3970
Nelson FK, Riddle DL (1984) Functional study of the Caenorhabditis elegans secretory–excretory system using laser microsurgery. J Exp Zool 231:45–56
Nelson FK, Albert PS, Riddle DL (1983) Fine structure of the Caenorhabditis elegans secretory–excretory system. J Ultrastruct Res 82:156–171
Prakash K, Fang X, Engelberg D, Behal A, Parker CS (1992) DOct2, a Drosophila Oct transcription factor that functions in yeast. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 89:7080–7084
Quandt K, Frech K, Karas H, Wingender E, Werner T (1995) MatInd and MatInspector: new fast and versatile tools for detection of consensus matches in nucleotide sequence data. Nucleic Acids Res 23:4878–4884
Rowan S, Cepko CL (2005) A POU factor binding site Upstream of the Chx10 Homeobox Gene is Required for Chx10 Expression in Subsets of Retinal Progenitor Cells and Bipolar Cells. Dev. Biol. 281:240–255
Ryan AK, Rosenfeld MG (1997) POU domain family values: flexibility, partnerships, and developmental codes. Genes Dev 11:1207–1225
Schreiber J, Enderich J, Sock E, Schmidt C, Richter-Landsberg C, Wegner M (1997) Redundancy of class III POU proteins in the oligodendrocyte lineage. J Biol Chem 272:32286–32293
Schwarz EM, Antoshechkin I, Bastiani C, Bieri T, Blasiar D, Canaran P, Chan J, Chen N, Chen WJ, Davis P et al (2006) WormBase: better software, richer content. Nucleic Acids Res 34:D475–D478
Spaniol P, Bornmann C, Hauptmann G, Gerster T (1996) Class III POU genes of zebrafish are predominantly expressed in the central nervous system. Nucleic Acids Res 24:4874–4881
Stern DL, Orgogozo V (2009) Is genetic evolution predictable? Science 323:746–751
Swoboda P, Adler HT, Thomas JH (2000) The RFX-type transcription factor DAF-19 regulates sensory neuron cilium formation in C. elegans. Mol Cell 5:411–421
Torrie LS, Radford JC, Southall TD, Kean L, Dinsmore AJ, Davies SA, Dow JA (2004) Resolution of the insect ouabain paradox. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 101:13689–13693
Uchida O, Nakano H, Koga M, Ohshima Y (2003) The C. elegans che-1 gene encodes a zinc finger transcription factor required for specification of the ASE chemosensory neurons. Development 130:1215–1224
Wang X, Greenberg JF, Chamberlin HM (2004) Evolution of regulatory elements producing a conserved gene expression pattern in Caenorhabditis. Evol Dev 6:237–245
Whittle CM, Lazakovitch E, Gronostajski RM, Lieb JD (2009) DNA-binding specificity and in vivo targets of Caenorhabditis elegans nuclear factor I. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 106:12049–12054
Witta SE, Agarwal VR, Sato SM (1995) XIPOU 2, a noggin-inducible gene, has direct neuralizing activity. Development 121:721–730
Yanai I, Hunter CP (2009) Comparison of diverse developmental transcriptomes reveals that co-expression of gene neighbors is not evolutionarily conserved. Genome Res (in press). doi:10.1101/gr.093815.109
Zhao Z, Fang L, Chen N, Johnsen RC, Stein L, Baillie DL (2005) Distinct regulatory elements mediate similar expression patterns in the excretory cell of Caenorhabditis elegans. J Biol Chem 280:38787–38794
Acknowledgments
We thank the Burglin, Baillie, Nehrke, Salkoff, Hope, Futai, Ahnn, and Starich laboratories for providing materials, and Dr Kirk McHugh for critical reading of the manuscript. Some nematode strains were provided by the Caenorhabditis Genetics Center, which is funded by the NIH National Center for Research Resources (NCRR). This work was supported by the NSF (IOB-0516554).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Communicated by S. Hekimi.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Armstrong, K.R., Chamberlin, H.M. Coordinate regulation of gene expression in the C. elegans excretory cell by the POU domain protein CEH-6. Mol Genet Genomics 283, 73–87 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00438-009-0497-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00438-009-0497-8