Abstract
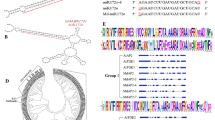
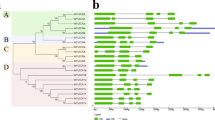
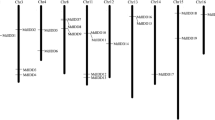
Fruit trees, such as apple (Malus × domestica Borkh.), are woody perennial plants with a long juvenile phase. The biological analysis for the regulation of flowering time provides insights into the reduction of juvenile phase and the acceleration of breeding in fruit trees. In Arabidopsis, LIKE HETEROCHROMATIN PROTEIN1 (LHP1) is involved in epigenetic silencing of the target genes such as flowering genes. We isolated and characterized twin apple LHP1 homolog genes, MdLHP1a and MdLHP1b. These genes may have been generated as a result of ancient genome duplication. Although the putative MdLHP1 proteins showed lower similarity to any other known plant LHP1 homologs, a chromo domain, a chromo shadow domain, and the nuclear localization signal motifs were highly conserved among them. RT-PCR analysis showed that MdLHP1a and MdLHP1b were expressed constantly in developing shoot apices of apple trees throughout the growing season. Constitutive expression of MdLHP1a or MdLHP1b could compensate for the pleiotropic phenotype of lhp1/tfl2 mutant, suggesting that apple LHP1 homolog genes are involved in the regulation of flowering time and whole-plant growth. Based on these results, LHP1 homolog genes might have rapidly evolved among plant species, but the protein functions were conserved, at least between Arabidopsis and apple.





Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- FBS:
-
Fruit-bearing shoot
- LD:
-
Long-day
- SD:
-
Short-day
- SS:
-
Succulent shoot
- VS:
-
Vegetative shoot
References
Adams KL, Wendel JF (2005) Polyploidy and genome evolution in plants. Curr Opin Plant Biol 8:135–141
Bechtold N, Ellis J, Pelletier G (1993) In planta Agrobacterium-mediated gene transfer by infiltration of adult Arabidopsis thaliana plants. C R Acad Sci III 316:1194–1199
Brasher SV, Smith BO, Fogh RH, Nietlispach D, Thiru A, Nielsen PR, Broadhurst RW, Ball LJ, Murzina NV, Laue ED (2000) The structure of mouse HP1 suggests a unique mode of single peptide recognition by the shadow chromo domain dimer. EMBO J 19:1587–1597
Cammas F, Herzog M, Lerouge T, Chambon P, Losson R (2004) Association of the transcriptional corepressor TIF1beta with heterochromatin protein 1 (HP1): an essential role for progression through differentiation. Genes Dev 18:2147–2160
Chanvivattana Y, Bishopp A, Schubert D, Stock C, Moon YH, Sung ZR, Goodrich J (2004) Interaction of Polycomb-group proteins controlling flowering in Arabidopsis. Development 131:5263–5276
Dennis F Jr (2003) Flowering, pollination and fruit set and development. In: Ferree DC, Warrington IJ (eds) Apples: botany, production and uses. CAB Intl, Oxon, Wallingford
Eissenberg JC (2001) Decisive factors: a transcription activator can overcome heterochromatin silencing. Bioessays 23:767–771
Esumi T, Tao R, Yonemori K (2005) Isolation of LEAFY and TERMINAL FLOWER 1 homologues from six fruit tree species in the subfamily Maloideae of the Rosaceae. Sex Plant Reprod 17:277–287
Evans RC, Campbell CS (2002) The origin of the apple subfamily (Maloideae; Rosaceae) is clarified by DNA sequence data from duplicated GBSSI genes. Am J Bot 89:1478–1484
Gallie DR, Walbot V (1992) Identification of the motifs within the tobacco mosaic virus 5′-leader responsible for enhancing translation. Nucleic Acids Res 20:4631–4638
Gaudin V, Libault M, Pouteau S, Juul T, Zhao G, Lefebvre D, Grandjean O (2001) Mutations in LIKE HETEROCHROMATIN PROTEIN 1 affect flowering time and plant architecture in Arabidopsis. Development 128:4847–4858
Germann S, Juul-Jensen T, Letarnec B, Gaudin V (2006) DamID, a new tool for studying plant chromatin profiling in vivo, and its use to identify putative LHP1 target loci. Plant J 48:153–163
Goodrich J, Puangsomlee P, Martin M, Long D, Meyerowitz EM, Coupland G (1997) A Polycomb-group gene regulates homeotic gene expression in Arabidopsis. Nature 386:44–51
Hackett WP (1985) Juvenility, maturation, and rejuvenility in woody plants. Hortic Rev 7:109–155
Hood EE, Helmer GL, Fraley RT, Chilton MD (1986) The hypervirulence of Agrobacterium tumefaciens A281 is encoded in a region of pTiBo542 outside of T-DNA. J Bacteriol 168:1291–1301
Hsieh TF, Hakim O, Ohad N, Fischer RL (2003) From flour to flower: how Polycomb group proteins influence multiple aspects of plant development. Trends Plant Sci 8:439–445
Jeanmougin F, Thompson JD, Gouy M, Higgins DG, Gibson TJ (1998) Multiple sequence alignment with Clustal X. Trends Biochem Sci 23:403–405
Kotake T, Takada S, Nakahigashi K, Ohto M, Goto K (2003) Arabidopsis TERMINAL FLOWER 2 gene encodes a heterochromatin protein 1 homolog and represses both FLOWERING LOCUS T to regulate flowering time and several floral homeotic genes. Plant Cell Physiol 44:555–564
Kotoda N, Iwanami H, Takahashi S, Abe K (2006) Antisense expression of MdTFL1, a TFL1-like gene, reduces the juvenile phase in apple. J Am Soc Hortic Sci 131:74–81
Kotoda N, Wada M (2005) MdTFL1, a TFL1-like gene of apple, retards the transition from the vegetative to reproductive phase in transgenic Arabidopsis. Plant Sci 168:95–104
Kotoda N, Wada M, Komori S, Kidou S, Abe K, Masuda T, Soejima J (2000) Expression pattern of homologues of floral meristem identity genes LFY and AP1 during flower development in apple. J Am Soc Hortic Sci 125:398–403
Kotoda N, Wada M, Kusaba S, Kano-Murakami Y, Masuda T, Soejima J (2002) Overexpression of MdMADS5, an APETALA1-like gene of apple, causes early flowering in transgenic Arabidopsis. Plant Sci 162:679–687
Larsson AS, Landberg K, Meeks-Wagner DR (1998) The TERMINAL FLOWER2 (TFL2) gene controls the reproductive transition and meristem identity in Arabidopsis thaliana. Genetics 149:597–605
Luby JJ (2003) Taxonomic classification and brief history. In: Ferree DC, Warrington IJ (eds) Apples: botany, production and uses. CAB Intl, Oxon, Wallingford
Maison C, Almouzni G (2004) HP1 and the dynamics of heterochromatin maintenance. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 5:296–304
Minc E, Courvalin JC, Buendia B (2000) HP1gamma associates with euchromatin and heterochromatin in mammalian nuclei and chromosomes. Cytogenet Cell Genet 90:279–284
Murashige T, Skoog F (1962) A revised medium for rapid growth and bioassays with tobacco tissue culture. Physiol Plant 15:473–497
Nakahigashi K, Jasencakova Z, Schubert I, Goto K (2005) The Arabidopsis HETEROCHROMATIN PROTEIN1 Homolog (TERMINAL FLOWER2) silences genes within the euchromatic region but not genes positioned in heterochromatin. Plant Cell Physiol 46:1747–1756
Nicholas KB, Nicholas HB Jr, Deerfield DW II (1997) GeneDoc: analysis and visualization of genetic variation, EMBnet News 4:1–4
Perrière G, Gouy M (1996) WWW-Query: an on-line retrieval system for biological sequence banks. Biochimie 78:364–369
Pires JC, Zhao JW, Schranz ME, Leon EJ, Quijada PA, Lukens LN, Osborn TC (2004) Flowering time divergence and genomic rearrangements in resynthesized Brassica polyploids (Brassicaceae). Biol J Linn Soc Lond 82:675–688
Sambrook J, Fritsch EF, Maniatis T (1989) Molecular cloning: a laboratory manual, 2nd edn. Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press, New York
Sax K (1933) The origin of the Pomoideae. Proc Am Soc Hortic Sci 30:147–150
Sung S, He Y, Eshoo TW, Tamada Y, Johnson L, Nakahigashi K, Goto K, Jacobsen SE, Amasino RM (2006) Epigenetic maintenance of the vernalized state in Arabidopsis thaliana requires LIKE HETEROCHROMATIN PROTEIN 1. Nat Genet 38:706–710
Takada S, Goto K (2003) TERMINAL FLOWER2, an Arabidopsis homolog of HETEROCHROMATIN PROTEIN1, counteracts the activation of FLOWERING LOCUS T by CONSTANS in the vascular tissues of leaves to regulate flowering time. Plant Cell 15:2856–2865
Wada M, Cao QF, Kotoda N, Soejima J, Masuda T (2002) Apple has two orthologues of FLORICAULA/LEAFY involved in flowering. Plant Mol Biol 49:567–577
Yao JL, Dong YH, Kvarnheden A, Morris B (1999) Seven MADS-box genes in apple are expressed in different parts of the fruit. J Am Soc Hortic Sci 124:8–13
Yoshida N, Yanai Y, Chen L, Kato Y, Hiratsuka J, Miwa T, Sung ZR, Takahashi S (2001) EMBRYONIC FLOWER2, a novel Polycomb group protein homolog, mediates shoot development and flowering in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell 13:2471–2481
Zemach A, Li Y, Ben-Meir H, Oliva M, Mosquna A, Kiss V, Avivi Y, Ohad N, Grafi G (2006) Different domains control the localization and mobility of LIKE HETEROCHROMATIN PROTEIN1 in Arabidopsis nuclei. Plant Cell 18:133–145
Acknowledgments
We thank Dr. H. Ichikawa, National Institute of Agrobiological Sciences (Tsukuba, Japan), for kindly providing the binary vectors, pSMAK312Blue and pSMAK193E. We also thank Dr. E.E. Hood, Texas A&M University College Station, for kindly providing Agrobacterium tumefaciens EHA101. A. thaliana tfl2-2 seeds were kindly provided by the Arabidopsis Biological Resource Center at Ohio State University. This work was supported by the “PROBRAIN (Program for Promotion of Basic Research Activities for Innovative Biosciences)” from the Bio-Oriented Technology Research Advancement Institution (BRAIN). This publication constitutes the contribution number 1445 of the National Institute of Fruit Tree Science.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Communicated by S. Hohmann.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
438_2007_250_MOESM1_ESM.pdf
S1. Restriction fragments of PCR products of the MdLHP1a gene PCR products of the MdLHP1a gene corresponding to the probe region used in Southern blot analysis were digested with EcoRI, PstI, BamHI, or EcoRV. The molecular size marker is shown in kbp on the left. (PDF 69.6 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mimida, N., Kidou, Si. & Kotoda, N. Constitutive expression of two apple (Malus × domestica Borkh.) homolog genes of LIKE HETEROCHROMATIN PROTEIN1 affects flowering time and whole-plant growth in transgenic Arabidopsis . Mol Genet Genomics 278, 295–305 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00438-007-0250-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00438-007-0250-0