Abstract
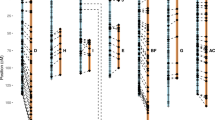
Comparative genome analysis has been performed between alfalfa ( Medicago sativa) and pea ( Pisum sativum), species which represent two closely related tribes of the subfamily Papilionoideae with different basic chromosome numbers. The positions of genes on the most recent linkage map of diploid alfalfa were compared to those of homologous loci on the combined genetic map of pea to analyze the degree of co-linearity between their linkage groups. In addition to using unique genes, analysis of the map positions of multicopy (homologous) genes identified syntenic homologs (characterized by similar positions on the maps) and pinpointed the positions of non-syntenic homologs. The comparison revealed extensive conservation of gene order between alfalfa and pea. However, genetic rearrangements (due to breakage and reunion) were localized which can account for the difference in chromosome number (8 for alfalfa and 7 for pea). Based on these genetic events and our increasing knowledge of the genomic structure of pea, it was concluded that the difference in genome size between the two species (the pea genome is 5- to 10-fold larger than that of alfalfa) is not a consequence of genome duplication in pea. The high degree of synteny observed between pea and Medicago loci makes further map-based cloning of pea genes based on the genome resources now available for M. truncatula a promising strategy.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Acarkan A, Rossberg M, Koch M, Schmidt R (2000) Comparative genome analysis reveals extensive conservation of genome organisation for Arabidopsis thaliana and Capsella rubella. Plant J 23:55–62
Ahn S, Tanksley SD (1993) Comparative linkage maps of rice and maize genomes. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 90:7980–7984
Arumuganathan K, Earle ED (1991) Nuclear DNA content of some important plant species. Plant Mol Biol Rep 9:208–218
Bassam BJ, Caetano-Anolles G (1993) Silver staining of DNA in polyacryamide gels. Appl Biochem and Biotech 42:181–188
Bennetzen JL, SanMiguel P, Chen M, Tikhonov A, Francki M, Avramova Z (1998) Grass genomes. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 95:1975–1978
Boivin K, Acarkan A, Mbulu RS, Clarenz O, Schmidt R (2004) The Arabidopsis genome sequence as a tool for the genome analysis in Brassicaceae. A comparison of the Arabidopsis and the Capsella rubella genomes. Plant Phys 135:735–744
Bonierbale MW, Plaisted RL Tanksley SD (1988) RFLP maps based on a common set of clones reveal modes of chromosomal evolution in potato and tomato. Genetics 120:1095–1103
Boutin SR, Young ND, Olsen TC, Yu ZH, Shoemaker RC, Vallejos CE (1995) Genome conservation among three legume genera detected with DNA markers. Genome 38:928–937
Brouwer DJ, Osborn TC (1999) A molecular marker linkage map of tetraploid alfalfa ( Medicago sativa L.). Theor Appl Genet 99:1194–1200
Brummer EC, Kochert G, Bouton JH (1991) RFLP variation in diploid and tetraploid alfalfa. Theor Appl Genet 83:89–96
Brummer EC, Bouton JH, Kochert G (1993) Development of an RFLP map in diploid alfalfa. Theor Appl Genet 86:329–332
Chang MM, Culley DE, Hadwiger LA (1993) Nucleotide sequence of a pea Pisum sativum L. beta-1,3-glucanase gene. Plant Phys 101:1121–1122
Choi HK, Kim D, Uhm T, Limpens E, Lim H, Mun J, Kalo P, Penmetsa RV, Seres A, Kulikova O, Roe BA, Bisseling T, Kiss GB, Cook DR (2004a) A sequence-based genetic map of Medicago truncatula and comparison of marker co-linearity with Medicago sativa. Genetics 166:1463–1502
Choi HK, Kim D, Zhu H, Mun J, Baek J, Roe BA, Ellis THN, Young ND, Doyle J, Kiss GB, Cook DR (2004b) Conserved gene order between crop and model legume species. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA (in press)
Devos KM, Gale MD (1997) Comparative genetics in the grasses. Plant Mol Biol 35:3–15
Echt CS, Kidwell KK, Knapp SJ, Osborn TC, McCoy TJ (1994) Linkage mapping in diploid alfalfa ( Medicago sativa). Genome 37:61–71
Ehrlich J, Sankoff D, Nadeau JH (1997) Synteny conservation and chromosome rearrangements during mammalian evolution. Genetics 147:289–296
Ellis THN, Poyser SJ (2002) An integrated and comparative view of pea genetic and cytogenetic maps. New Phytologist 153:17–25
Ellis THN, Turner L, Hellens RP, Lee D, Harker CL, Enard C, Domoney C, Davies DR (1992) Linkage maps in pea. Genetics 130:649–663
Endre G, Kaló P, Kevei Z, Kiss P, Mihacea S, Szakál B, Kereszt A, Kiss GB (2002a) Genetic mapping of the non-nodulation phenotype of the mutant MN-1008 in tetraploid alfalfa Medicago sativa Mol Gen Genet 266:1012–1019
Endre G, Kereszt A, Kevei Z, Mihacea S, Kaló P, Kiss GB (2002b) A receptor kinase gene regulating symbiotic nodule development. Nature 417:962–966
Gale MD, Devos KM (1998) Comparative genetics in the grasses. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 95:1971–1974
Gebhardt C, Ritter E, Barone A, Debener T, Walkemeier B, Schachtschabel U, Kaufmann H, Thompson RD, Bonierbale MW, Ganal MW, Tanksley SD (1991) RFLP maps of potato and their alignment with the homologous tomato genome. Theor Appl Genet 83:49–57
Gilpin BJ, McCallum JA, Frew TJ, Timmerman-Vaughan GM (1997) A linkage map of the pea Pisum sativum L. genome containing cloned sequences of known function and expressed tags ESTs. Theor Appl Genet 95:1289–1299
Gowri G, Paiva NL, Dixon RA (1991) Stress responses in alfalfa Medicago sativa L. 12. Sequence analyses of phenylalanine ammonia-lyase PAL cDNA clones and appearance of PAL transcripts in elicitor-treated cell cultures and developing plants. Plant Mol Biol 17:415–429
Györgyey J, Gartner A, Nemeth K, Magyar Z, Hirt H, Heberle-Bors E, Dudits D (1991) Alfalfa heat shock genes are differentially expressed during somatic embryogenesis. Plant Mol Biol 16:999–1007
Hall KJ, Parker JS, Ellis THN, Turner L, Knox MR, Hofer JMI, Lu J, Ferrandiz C, Hunter PJ, Taylor JD, Baird K (1997) The relationship between genetic and cytogenetic maps of pea. II. Physical maps of linkage mapping populations. Genome 40:755–769
Harker CL, Ellis THN, Coen ES (1990) Identification and genetic regulation of the chalcone synthase multigene family in pea. Plant Cell 2:185–194
Hofer JMI, Turner L, Hellens R, Ambrose M, Matthews P, Michael A, Ellis THN (1997) UNIFOLIATA regulates leaf and flower morphogenesis in pea. Curr Biol 7:581–587
Humphry ME, Konduri V, Lambrides CJ, Magner T, McIntyre CL, Aitken EAB, Liu CJ (2002) Development of a mungbean ( Vigna radiata) RFLP linkage map and its comparison with lablab ( Lablab purpureus) reveals a high level of colinearity between the two genomes. Theor Appl Genet 105:160–166
Irzykowska L, Wolko B, Swiecicki WK (2001) The genetic linkage map of pea Pisum sativum L. based on molecular, biochemical and morphological markers. Pisum Genet 33:13–18
Kaló P, Endre G, Zimányi L, Csanádi G, Kiss GB (2000) Construction of an improved linkage map diploid alfalfa Medicago sativa. Theor Appl Genet 100:641–657
Kaló P, Felföldi K, Seres A, Endre G, Kiss GB (2003) Genetic mapping of seed and nodule protein markers in diploid alfalfa ( Medicago sativa), In: Nagata, Tabata (eds) Biotechnology in agriculture and forestry: Brassicas and Legumes. Springer-Verlag Berlin, Heidelberg. Vol. 52 pp. 228–244
Keller B, Feuillet C (2000) Colinearity and gene density in grass genomes. Trends Plant Sci 5:246–251
Kiss GB, Csanádi G, Kálmán K, Kaló P, Ökrész L (1993) Construction of a basic genetic map for alfalfa using RFLP, RAPD, isozyme and morphological markers. Mol Gen Genet 238:129–137
Kiss GB, Kereszt A, Kiss P, Endre G (1998) Colormapping:a non-mathematical procedure for genetic mapping. Acta Biol Hun 49:125–142
Kopriva S, Turner SR, Rawsthorne S, Bauwe H (1995) T-protein of the glycine decarboxylase multienzyme complex:evidence for partial similarity to formyltetrahydrofolate synthetase. Plant Mol Biol 27:1215–1220
Kulikova O, Gualtieri G, Geurts R, Kim DJ, Cook D, Huguet T, de Jong JH, Fransz PF, Bisseling T (2001) Integration of the FISH pachytene and genetic maps of Medicago truncatula. Plant J 27:49–58
Lagercrantz U (1998) Comparative mapping between Arabidopsis thaliana and Brassica nigra indicates that Brassica genomes have evolved through extensive genome replication accompanied by chromosome fusions and frequent rearrangements. Genetics 150:1217–1228
Lagercrantz U, Lydiate DJ (1996) Comparative genome mapping in Brassica. Genetics 144:1903–1910
Livingstone KD, Lackney VK, Blauth JR, van Wijk R, Jahn MK (1999) Genome mapping in Capsicum and the evolution of genome structure in the Solanaceae. Genetics 152:1183–1202
Llewellyn DJ, Finnegan EJ, Ellis JG, Dennis ES, Peacock WJ (1987) Structure and expression of an alcohol dehydrogenase 1 gene from Pisum sativum (cv. “Greenfeast”). J Mol Biol 195:115–123
Lukens L, Zou F, Lydiate D, Parkin I, Osborn T (2003) Comparison of a Brassica oleracea genetic map with the genome of Arabidopsis thaliana. Genetics 164:359–372
Macherel D, Bourguignon J, Douce R (1992) Cloning of the gene gdcH encoding H-protein, a component of the glycine decarboxylase complex of pea Pisum sativum L. Biochem J 286:627–630
Maniatis T, Fritsch EF, Sambrook J (1982) Molecular cloning: a laboratory manual. Cold Spring Laboratory Press, Cold Spring Harbor, N.Y.
Menancio-Hautea D, Fatokun CA, Kumar L, Danesh D, Young ND (1993) Comparative genome analysis of mungbean ( Vigna radiata (L.) Wilczek) and cowpea ( V. unguiculata (L.) Walpers) using RFLP mapping data. Theor Appl Genet 86:797–810
Navratilova A, Neumann P, Macas J (2003) Karyotype analysis of four Vicia species using in situ hybridization with repetitive sequences. Ann Botany 91:921–926
Orita M, Iwahana H, Kanazawa H, Hayashi K, Sekiya T (1989) Detection of polymorphisms of human DNA by gel electrophoresis as single-strand conformation polymorphisms. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 86:2766–2770
Osborn TC, Kole C, Parkin IAP, Sharpe AG, Kruiper M, Lydiate DJ, Trick M (1997) Comparison of flowering genes in Brassica rapa, Brassica napus and Arabidopsis thaliana. Genetics 146:1123–1129
Paterson AH, Bowers JE, Burow MD, Draye X, Elsik CG, Jiang CX, Katsar CS, Lan TH, Lin YR, Ming R, Wright RJ (2000) Comparative genomics of plant chromosomes. Plant Cell 12:1523–1539
Sankoff D (2001) Gene and genome duplication. Curr Op Genet Dev 11:681–684
Schneider A, Walker SA, Poyser S, Sagan M, Ellis THN, Downie JA (1999) Genetic mapping and functional analysis of a nodulation defective mutant sym19 of pea Pisum sativum L. Mol Gen Genet 262:1–11
Simon CJ, FJ Muehlbauer (1997) Construction of a chickpea linkage map and its comparison with maps of pea and lentil. J Hered 88:115–119
Sorefan K, Booker J, Haurogné K, Goussot M, Foo E Chatfield S, Ward S, Beveridge C, Rameau C, Leyser O (2003) MAX4 and RMS1 are orthologous dioxygenases-like genes that regulate shoot branching in Arabidopsis and pea. Genes and Dev 17:1469–1474
Taketa S, Harrison GE, Heslop-Harrison JS (1999) Comparative physical mapping of the 5S and 18s-25S rDNA in nine wild Hordeum species and cytotypes. Theor Appl Genet 98:1–9
Tanksley SD, Bernatzky R, Lapitan NL, Prince JP (1988) Conservation of gene repertoire but not gene order in pepper and tomato. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 85:6419–6423
Tanksley SD, Ganal MW, Prince JP, de Vicente MC, Bonierbale MW, Broun P, Fulton TM, Giovannoni JJ, Grandillo S, Martin GB, Messeguer R, Miller JC, Miller L, Paterson AH, Pined O, Röder MS, Wing RA, Wu W, Young ND (1992) High density molecular map linkage maps of the tomato and potato genomes. Genetics 132:1141–1160
Taylor SA, Hofer JMI, Murfet IC, Sollinger JD, Singer SR, Knox MR, Ellis THN (2002 PROLIFERATING INFLORESCENCE MERISTEM, a MADS-Box gene that regulates floral meristem identity in pea. Plant Phys 129:1150–1159
Turner SR, Ireland R, Rawsthorne S (1992a) Purification and primary amino-acid sequence of the L subunit of glycine decarboxylase. J Biol Chem 267:7745–7750
Turner SR, Ireland R, Rawsthorne S (1992b) Cloning and characterization of the P subunit of the glycine decarboxylase from pea Pisum sativum. J Biol Chem 267:5355–5360
Turner L, Hellens RP, Lee D, Ellis THN (1993) Genetic aspects of the organization of legumin genes in pea. Plant Mol Biol 22:101–112
Vavilov NI (1922) The law of homologous series in variation. J Genetics 12:47–88
Vershinin AV, Allnutt TR, Knox MR, Ambrose MJ, Ellis THN (2003) Transposable elements reveal the impact of introgression, rather than transposition, in Pisum diversity, evolution and domestication. Mol Biol Evol 20:2067–2075
Vincent JL, MR Knox, THN Ellis, P Kaló, GB Kiss, Brewin NJ (2000) Nodule-expressed Cyp15a cysteine protease genes map to syntenic genome regions in Pisum and Medicago spp. Mol Plant Microbe Int 13:715–723
Weeden NF, Marx GA (1987) Further genetic analysis and linkage relationships of isozyme loci in the pea. J Hered 78:153–159
Weeden NF, Muehlbauer FJ, Ladizinsky G (1992) Extensive conservation of linkage relationships between pea and lentil genetic maps. J Hered 83:123–129
Weeden NF, Ellis THN, Timmerman-Vaughan GM, Skwiecicki WK, Rozov SM, Berdnikov VA (1998) A consensus linkage map for Pisum sativum. Pisum Genet 30:1–4
Weeden NF, Tonguc M, Boone WE (1999) Mapping coding sequences in pea by PCR. Pisum Genet 31:30–32
Acknowledgements
We would like to thank K. Karchesz, C. Ernhoffer, P. Somkúti, S. Jenei, Z. Liptay for skillful technical assistance; P. Kiss for help in mapping EuDicot gene-specific loci ( GAPDH, HSP70 , RPL17 , RPL32 , RPS9 , RPSA40 and UCE), Á. Dalmadi and S. Stranczinger for their help during the mapping of Uni, and PscDNA clones in alfalfa. The authors thank Michel Delseny for useful discussions. This work was supported by the ABC Gödöllő, the BRC Szeged, and the Bástyai-Holczer Foundation, and by grants from the EU EuDicotMap (Grant No. BIO 4CT97-2170; EU), and MEDICAGO (Grant No. QLG2-CT-2000-30676; EU), and by the Hungarian National Grants OMFB EU-97-D8-063 (National Committee for Technical Development), NKFP Medicago Genomics (Grant No. 4/023/2001-Ministry of Education) and Biotechnology 2001 (Grant No. OMFD-00229/2002), OTKA (Grant No.T038211). P. Kaló, A. Kereszt and G. Endre were supported by János Bolyai postdoctoral fellowships
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Communicated by W. R. McCombie
Electronic Supplementary Material
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kaló, P., Seres, A., Taylor, S.A. et al. Comparative mapping between Medicago sativa and Pisum sativum. Mol Genet Genomics 272, 235–246 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00438-004-1055-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00438-004-1055-z