Abstract
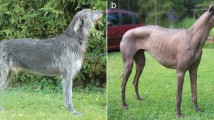
We describe here a spontaneous, autosomal recessive mutant mouse suffering from skin and hair defects, which arose in the outbred Kunming strain. By haplotype analysis and direct sequencing of PCR products, we show that this mutation is a new allele of the asebia locus with a naturally occurring mutation in the Scd1 gene (a CCC insertion at nucleotide position 835 in exon 5), which codes for stearoyl-CoA desaturase 1. This mutation introduces an extra proline residue at position 279 in the Scd1 protein. The mutant mice, originally designated km/km but now assigned the name Scd1 ab-Xyk (hereafter abbreviated as ab Xyk/ ab Xyk), have a similar gross and histological phenotype to that reported for previously characterized allelic asebia mutations ( Scd1 ab, Scd1 abJ, Scd1 ab2J, and Scd1 tm1Ntam). Histological analysis showed they were also characterized by hypoplasic sebaceous glands and abnormal hair follicles. In a cross between Kunming- ab Xyk/ ab Xyk and ABJ/Le- ab J/ ab Jmice, all the progeny showed the same phenotype, indicating that the two mutations were non-complementing and therefore allelic. Comparisons with the other four allelic mutants indicate that the Scd1 ab-Xyk mutation causes the mildest change in Scd1 function. This new mouse mutant is a good model not only for the study of scarring alopecias in humans, which are characterized by hypoplasic sebaceous glands, but also for studying the structure and function of the Scd1 protein.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Cohen P, Miyazaki M, Socci ND, Greenberg AH, Liedtke W, Soukas AA, Sharma R, Hudgins LC, Ntambi JM, Friedman JM (2002) Role for stearoyl-CoA desaturase-1 in leptin-mediated weight loss. Science 297:240–243
Falvella FS, Pascale RM, Gariboldi M, Manenti G, De Miglio MR, Simile MM, Dragani TA, Feo F (2002) Stearoyl-CoA desaturase 1 ( Scd1) gene overexpression is associated with genetic predisposition to hepatocarcinogenesis in mice and rats. Carcinogenesis 23:1933–1936
Gates AH, Karasek M (1965) Hereditary absence of sebaceous glands in the mouse. Science 148:1471–1473
Herron BJ, Bryda EC, Heverly SA, Collins DN, Flaherty L (1999) scraggly, a new hair loss mutation on mouse chromosome 19. Mamm Genome 10:864–869
Josefowicz WJ, Hardy MH (1978a) The expression of the gene asebia in the laboratory mouse, 1. Epidermis and dermis. Genet Res 31:53–65
Josefowicz WJ, Hardy MH (1978b) The expression of the gene asebia in the laboratory mouse. 2. Hair follicles. Genet Res 31:145–155
Josefowicz WJ, Hardy MH (1978c) The expression of the gene asebia in the laboratory mouse. 3. Sebaceous glands. Genet Res 31:157–166
Kaestner KH, Christy RJ, McLenithan JC, Braiterman LT, Cornelius P, Pekala PH, Lane MD (1989) Sequence, tissue distribution, and differential expression of mRNA for a putative insulin-responsive glucose transporter in mouse 3T3-L1 adipocytes. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 86:3150–3154
Miyazaki M, Kim YC, Ntambi JM (2001a) A lipogenic diet in mice with a disruption of the stearoyl-CoA desaturase 1 gene reveals a stringent requirement of endogenous monounsaturated fatty acids for triglyceride synthesis. J Lipid Res 42:1018–1024
Miyazaki M, Man WC, Ntambi JM (2001b) Targeted disruption of stearoyl-CoA desaturase1 gene in mice causes atrophy of sebaceous and meibomian glands and depletion of wax esters in the eyelid. J Nutr 131:2260–2268
Miyazaki M, Jacobson MJ, Man WC, Cohen P, Asilmaz E, Friedman JM, Ntambi JM (2003) Identification and characterization of murine SCD4, a novel heart-specific stearoyl-CoA desaturase isoform regulated by leptin and dietary factors. J Biol Chem 278:33904–33911
Nakamura Y, Fukami K, Yu H, Takenaka K, Kataoka Y, Shirakata Y, Nishikawa S, Hashimoto K, Yoshida N, Takenawa T (2003) Phospholipase Cdelta1 is required for skin stem cell lineage commitment. EMBO J 22:2981–2991
Ntambi JM, Buhrow SA, Kaestner KH, Christy RJ, Sibley E, Kelly TJ Jr, Lane MD (1988) Differentiation-induced gene expression in 3T3-L1 preadipocytes. J Biol Chem 263:17291–17300
Ntambi JM, Miyazaki M, Stoehr JP, Lan H, Kendziorski CM, Yandell BS, Song Y, Cohen P, Friedman JM, Attie AD (2002) Loss of stearoyl-CoA desaturase-1 function protects mice against adiposity. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 99:11482–11486
Rahman SM, Dobrzyn A, Dobrzyn P, Lee SH, Miyazaki M, Ntambi JM (2003) Stearoyl-CoA desaturase 1 deficiency elevates insulin-signaling components and down-regulates protein-tyrosine phosphatase 1B in muscle. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 100:11110–11115
Sun Y, Hao M, Luo Y, Liang CP, Silver DL, Cheng C, Maxfield FR, Tall AR (2003) Stearoyl-CoA desaturase inhibits ATP-binding cassette transporter A1-mediated cholesterol efflux and modulates membrane domain structure. J Biol Chem 278:5813–5820
Sundberg JP (1994) Handbook of mouse mutations with skin and hair abnormalities. CRC Press, Boca Raton
Sundberg JP, Boggess D, Sundberg BA, Eilertsen K, Parimoo S, Filippi M, Stenn K (2000) Asebia-2J ( Scd1 ab2J): a new allele and a model for scarring alopecia. Am J Pathol 156:2067–2075
Zhang L, Lan GE, Parimoo S, Stenn K, Prouty SM (1999) Human stearoyl-CoA desaturase: alternative transcripts generated from a single gene by usage of tandem polyadenylation sites. Biochem J 340:255–264
Zheng Y, Eilertsen KJ, Ge L, Zhang L, Sundberg JP, Prouty SM, Stenn KS, Parimoo S (1999) Scd1 is expressed in sebaceous glands and is disrupted in the asebia mouse. Nat Genet 23:268–270
Zheng Y, Prouty SM, Harmon A, Sundberg JP, Stenn KS, Parimoo S (2001) Scd3 —a novel gene of the stearoyl-coA desaturase family with restricted expression in skin. Genomics 71:182–191
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the National High Technology “863” Programs of China (Grant No. 2001AA221091 to XYK) and the Distinguished Young Scholars’ Fund of the National Natural Science Foundation (Grant No. 301250281 to XYK). It was also supported in part by grants from the National Institutes of Health (CA34196 and RR173 to JPS) of the USA. We would like to thank Xiaokun Teng for help in the histological analysis. We are grateful to Bin Cui, Heng Xu and Qing-Lian Xie for their technical assistance. We appreciate John P. Sundberg for helping to edit the manuscript
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Communicated by G. Reuter
The first two authors contribute equally to this work
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lu, Y., Bu, L., Zhou, S. et al. Scd1 ab-Xyk: a new asebia allele characterized by a CCC trinucleotide insertion in exon 5 of the stearoyl-CoA desaturase 1 gene in mouse. Mol Genet Genomics 272, 129–137 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00438-004-1043-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00438-004-1043-3