Abstract
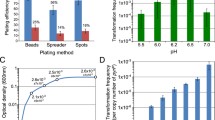
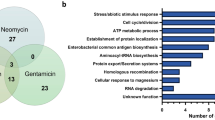
In up to 100% of all bacteria grown in the presence of initially inhibitory concentrations of five diverse inhibitors, an extra copy of the resident insertion element IS31831 was found in specific chromosomal regions, the sites of which apparently depended on the inhibitor used. Thus, in nine out of nine independently isolated cyanide-associated transpositions, the acquired copy was located within an ORF encoding a protein related to the hypothetical but conserved protein YeiH of Escherichia coli. A putative Sox box upstream of the yeiH gene implicates superoxide as a potential regulator of the gene, a possibility further supported by the finding that superoxide dismutase (SodA) is overexpressed in cells cultured in cyanide-containing medium. Neither the cyanide-associated nor any of the other transposition mutations appeared to confer any discernible phenotypic advantage upon cells grown in the presence or absence of the inhibitors, as revealed most stringently by mixed-cell experiments. An alternative, albeit heterodox, explanation for the emergence of the mutants postulates a very high rate of transpositional activity in the presence of inhibitors. The initial emergence of the mutants was found to depend crucially upon the cell density. Thus, when growth medium was supplemented with 50 mM fluoropyruvate and inoculated to a density of 2×107 cfu/ml, single colonies with heterogeneous restriction fragment length polymorphisms (RFLPs) were routinely isolated at a frequency of 6 to 16% after 1–2 days of incubation. After 3 days, 10–36% of the colonies showed RFLPs, but the type was now dominated by the fluoropyruvate-specific RFLP, which, at higher resolution, invariably proved to be heterogeneous. This heterogeneity proved that these specific mutants were of multiple origin, indicating that clonal enrichment was irrelevant to their emergence. It is suggested that the presence of the inhibitor induces the development of hyper-transpositional activity, which is regulated by a soluble bacterial product.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Arakawa H, Maeda M, Tsuji A (1991) Chemiluminescent assay of various enzymes using indoxyl derivatives as substrate and its applications to enzyme immunoassay and DNA probe assay. Anal Biochem 199:238–242
Arber W (2000) Genetic variation: molecular mechanisms and impact on microbial evolution. FEMS Microbiol Rev 4:1–7
Bisswanger H (1981) Substrate specificity of the pyruvate dehydrogenase complex from Escherichia coli. J Biol Chem 256:815–822
De Boer AS, Borgdorff MW, de Haas PE, Nagelkerke NJ, van Embden JD, van Soolingen D (1999) Analysis of rate of change of IS6110 RFLP patterns of Mycobacterium tuberculosis based on serial patient isolates. J Infect Dis 180:1238–1244
Cairns J (1981) The origin of human cancers. Nature 289:353–357
Chalmers R, Blot M (1999) Insertion sequences and transposons. In: Charlebois RL (ed) Organization of the prokaryotic genome. ASM Press, Washington DC, pp 151–169
Fawcett WP, Wolf RE Jr (1994) Purification of a MalE-SoxS fusion protein and identification of the control sites of Escherichia coli superoxide-inducible genes. Mol Microbiol 14:669–79
Garbe TR, Yukawa H (2001) Common solvent toxicity: autoxidation of respiratory redox-cyclers enforced by membrane derangement. Z Naturforsch 56c:483–491
Garbe TR, Hibler NS, Deretic V (1999) Response to reactive nitrogen intermediates in Mycobacterium tuberculosis: induction of the 16-kilodalton α-crystallin homolog by exposure to nitric oxide donors. Infect Immun 67:460–465
Garbe TR, Kobayashi M, Yukawa H (2000) Indole-inducible proteins in bacteria suggest membrane and oxidant toxicity. Arch Microbiol 173:78–82
Ghanekar K, McBride A, Dellagostin O, Thorne S, Mooney R, McFadden (1999) Stimulation of transposition of the Mycobacterium tuberculosis insertion sequence IS6110 by exposure to a microaerobic environment. Mol Microbiol 33:982–993
Gould SJ (2002) The structure of evolutionary theory. Belknap Harvard
Gould SJ, Eldredge N (1993) Punctuated equilibrium comes of age. Nature 366:223–227
Gould SJ, Lewontin RC (1979) The spandrels of San Marco and the Panglossian paradigm: a critique of the adaptationist programme. Proc R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 205:581–98
Iida H (1988) Multistress resistance of Saccharomyces cerevisiae is generated by insertion of retrotransposon Ty into the 5′ coding region of the adenylate cyclase gene. Mol Cell Biol 8:5555–5560
Kamendulis LM, Zhang H, Wang Y, Klaunig JE (2002) Morphological transformation and oxidative stress induced by cyanide in Syrian hamster embryo (SHE) cells. Toxicol Sci 68:437–443
Knowles CJ (1976) Microorganisms and cyanide. Bacteriol Rev 40:652–680
Kurusu Y, Kainuma M, Inui M, Satoh Y, Yukawa H (1990) Electroporation-transformation system for corynebacteria by auxotrophic complementation. Agric Biol Chem 54:443–447
Lambert JL, Ramasamy J, Paukstells JV (1975) Stable reagents for the colorimetric determination of cyanide by modified König reactions. Anal Chem 47:916–918
Mahillon J, Chandler M (1998) Insertion sequences. Microbiol Mol Biol Rev 62:725–774
Matsushita K, Yamamoto T, Toyama H, Adacj O (1998) NADPH oxidase system as a superoxide-generating cyanide-resistant pathway in the respiratory chain of Corynebacterium glutamicum. Biosci Biochem 62:1968–1977
Merkamm M, Guyonvarch A (2001) Cloning of the sodA gene from Corynebacterium melassecola and role of superoxide dismutase in cellular viability. J Bacteriol 183:1284–1295
Messner KR, Imlay JA (1999) The identification of primary sites of superoxide and hydrogen peroxide formation in the aerobic respiratory chain and sulfite reductase complex of Escherichia coli. J Biol Chem 274:10119–10128
Naas T, Blot M, Fitch WM, Arber W (1994) Insertion sequence-related genetic variation in resting Escherichia coli K-12. Genetics 136:721–730
Nakagawa S, Mizoguchi H, Ando S, Hayashi M, Ochiai K, Yokoi H, Tateishi N, Senoh A, Ikeda M, Ozaki A (2001) Novel polynucleotides. Patent No. EP1108790-A/1
Osgood C, Sterling D (1991) Dichloroacetonitrile, a by-product of water chlorination, induces aneuploidy in Drosophila. Mutat Res 261:85–91
Papadopoulos D, Schneider D, Meier-Eiss J, Arber W, Lenski RE, Blot M (1999) Genomic evolution during a 10,000-generation experiment with bacteria. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 96:3807–3812
Skowronski B, Strobel GA (1969) Cyanide resistance and cyanide utilization by a strain of Bacillus pumilus. Can J Microbiol 15:93–98
Takami H, Han CG, Takaki Y, Ohtsubo E (2001) Identification and distribution of new insertion sequences in the genome of alkaliphilic Bacillus halodurans C-125. J Bacteriol 183:4345–4356
Van Dijck P, Ma P, Versele M, Gorwa MF, Colombo S, Lemaire K, Bossi D, Loiez A, Thevelein JM (2000) A baker’s yeast mutant ( fil1) with a specific, partially inactivating mutation in adenylate cyclase maintains a high stress resistance during active fermentation and growth. J Mol Microbiol Biotechnol 2:521–530
Vertès AA, Inui M, Kobayashi M, Kurusu Y, Yukawa H (1993) Presence of mrr - and mcr -like restriction systems in coryneform bacteria. Res Microbiol 144:181–185
Vertès AA, Inui M, Kobayashi M, Kurusu Y, Yukawa H (1994a) Isolation and characterization of IS31831, a transposable element from Corynebacterium glutamicum. Mol Microbiol 11:739–746
Vertès AA, Asai Y, Inui M, Kobayashi M, Kurusu Y, Yukawa H (1994b) Transposon mutagenesis of coryneform bacteria. Mol Gen Genet 245:397–405
Acknowledgements
The highly appreciated assistance of Kana Ninomiya and Shoko Shimokawa is gratefully acknowledged. The mixed-cell experiments were kindly suggested by Prof. David Thaler of the Rockefeller University in New York. The presence of a putative Sox box in the upstream region of yeiH was suggested by an anonymous reviewer.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Communicated by W. Arber
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Garbe, T.R., Suzuki, N., Inui, M. et al. Inhibitor-associated transposition events in Corynebacterium glutamicum . Mol Genet Genomics 271, 729–741 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00438-004-1026-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00438-004-1026-4