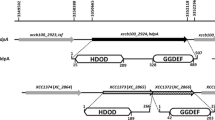
Abstract
Extracellularly targeted proteins are crucial for virulence of gram-negative phytopathogenic bacteria. Erwinia carotovora subsp. carotovora employs the so-called type II (GSP) pathway to secrete a number of pectinases and cellulases, which cause the typical tissue maceration symptoms of soft-rot disease. The type III ( hrp) pathway is the major virulence determinant in the genera Pseudomonas, Ralstonia and Xanthomonas, and in non-macerating species of Erwinia. The hrp cluster was recently partially characterized from E. carotovora sp. carotovora, and shown to affect virulence during early stages of infection. Here we have isolated and characterized 15 hrp genes comprising the remaining part of the cluster. The genes hrpL, hrpXY and hrpS were deduced to be transcribed as separate units, whereas the 11 remaining genes from hrpJ to hrcU form a single large operon. The hrpX gene, which codes for the sensory kinase of the two-component regulatory locus hrpXY was insertionally inactivated by placing a transposon (entranceposon) in the gene. The resulting mutant bacterium expresses the hrp genes at high basal level even in a non-inducing medium. This relative overexpression was shown to be due to the hrpX::entranceposon insertion causing enhanced transcription of the downstream hrpY gene. The hrpX - -hrpY C mutant bacterium exhibited a slower growth rate and the appearance of disease symptoms in infected Arabidopsis plants was delayed, as compared to the wild-type strain. The need for hrp gene expression for virulence has been documented in both non-macerating plant pathogens and in soft-rotting Erwinia sp. but this is the first demonstration that high basal-level expression of hrp -regulated genes may actually have a negative impact on disease progress in a susceptible host plant.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alfano J, Collmer A (1997) The type III (Hrp) secretion pathway of plant pathogenic bacteria: trafficking harpins, Avr proteins, and death. J Bacteriol 179:5655–5662
Barras F, van Gijsegem F, Chatterjee AK (1994) Extracellular enzymes and pathogenesis of soft-rot Erwinia. Annu Rev Phytopathol 32:201–234
Bauer DW, Beer SV (1991) Further characterization of an hrp gene cluster of Erwinia amylovora. Mol Plant-Microbe Interact 4:493–499
Bauer DW, Wei Z-M, Beer SV, Collmer A (1995) Erwinia chrysanthemi harpinEch: an elicitor of the hypersensitive response that contributes to soft-rot pathogenesis. Mol Plant-Microbe Interact 8:484–491
Bell KS, Avrova AO, Holeva MC, Cardle L, Morris W, De Jong W, Toth IK, Waugh R, Bryan GJ, Birch PR (2002) Sample sequencing of a selected region of the genome of Erwinia carotovora subsp. atroseptica reveals candidate phytopathogenicity genes and allows comparison with Escherichia coli. Microbiology 148:1367–1378
Bogdanove AJ, Wei Z-M, Zhao L, Beer SV (1996) Erwinia amylovora secretes harpin via a type III pathway and contains a homolog of yopN of Yersinia spp. J Bacteriol 178:1720–1730
Bonas U (1994) hrp genes of phytopathogenic bacteria. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol 192:79–98
Chatterjee A, Cui Y, Chatterjee AK (2002a) Regulation of Erwinia carotovora hrpL (Ecc) (sigma-L(Ecc)), which encodes an extracytoplasmic function subfamily of sigma factor required for expression of the HRP regulon. Mol Plant Microbe Interact 15:971–980
Chatterjee A, Cui Y, Chaudhuri S, Chatterjee AK (2002b) Identification of Erwinia carotovora ssp. carotovora and characterization of HrpLEcc (SigmaLEcc), an alternative sigma factor. Mol Plant Pathol 3:359–370
Cui Y, Madi L, Mukherjee A, Dumenyo CK, Chatterjee AK (1996) The RsmA- mutants of Erwinia carotovora subsp. carotovora strain Ecc71 overexpresses hrpN Ecc and elicit a hypersensitive reaction-like response in tobacco leaves. Mol Plant-Microbe Interact 9:565–573
Delepelaire P, Wandersman C (1989) Protease secretion by Erwinia chrysanthemi. Proteases B and C are secreted as zymogens without a signal peptide. J Biol Chem 264:9083–9089
Deng W-L, Preston G, Collmer A, Chang C-J, Huang H-C (1998) Characterization of the hrpC and hrpRS operons of Pseudomonas syringae pathovar syringae, tomato, and glycinea and analysis of the ability of hrpF, hrpG, hrpT, and hrpV mutants to elicit the hypersensitive response and disease in plants. J Bacteriol 10:4523–4531
Fouts DE, (2002) Genomewide identification of Pseudomonas syringae pv. tomato DC3000 promoters controlled by the HrpL alternative sigma factor. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 99:2275–2280
Galán JE, Collmer A (1999) Type III secretion machines: bacterial devices for protein delivery into host cells. Science 284:1322–1328
Genin S, Gough CL, Zischek C, Boucher CA (1992) Evidence that the hrpB gene encodes a positive regulator of pathogenicity genes from Pseudomonas solanacearum. Mol Microbiol 6:3065–3076
Gil D, Bouché J-P (1991) ColE1-type vectors with fully repressible replication. Gene 105:17–22
Gopalan S, Bauer DW, Alfano JR, Loniello AO, He SY, Collmer A (1996) Expression of the Pseudomonas syringae avirulence protein AvrB in plant cells alleviates its dependence on the hypersensitive response and pathogenicity (Hrp) secretion system in eliciting genotype-specific hypersensitive cell death. Plant Cell 8:1095–1105
Haapa S, Taira S, Heikkinen E, Savilahti H (1999) An efficient and accurate integration of mini-Mu transposons in vitro: a general methodology for a functional genetic analysis and molecular biology applications. Nucleic Acids Res 27:2777–2784
Haapalainen M, Karp M, Metzler MC (1996) Isolation of strong promoters from Clavibacter xyli subsp. cynodontis using a promoter probe plasmid. Biochim Biophys Acta 1305:130–134
Hobbs M, Mattick JK (1993) Common components in the assembly of type 4 fimbriae, DNA transfer systems, filamentous phage and protein-secretion apparatus: a general system for the formation of surface-associated protein complexes. Mol Microbiol 10:233–243
Huang H-C, Lin R-H, Chang, C-J, Collmer A, Deng WL (1995) The complete hrp gene cluster of Pseudomonas syringae pv. syringae 61 includes two blocks of genes required for harpinPss secretion that are arranged colinearly with Yersinia ysc homologs. Mol Plant-Microbe Interact 8:733–746
Hueck CJ (1998) Type III protein secretion systems in bacterial pathogens of animals and plants. Microbiol Mol Biol Rev 62:379–433
Huynh TV, Dahlbeck D, Staskawicz BJ (1989) Bacterial blight of soybean: regulation of a pathogen gene determining host cultivar specificity. Science 245:1374–1377
Kim JF, Wei Z-M, Beer S (1997) The hrpA and hrpC operons of Erwinia amylovora encode components of a type III pathway that secretes harpin. J Bacteriol 179:1690–1697
Kim JF, Ham JH, Bauer DW, Collmer A, Beer SV (1998) The hrpC and hrpN operons of Erwinia chrysanthemi EC16 are flanked by plcA and homologs of hemolysin/adhesin genes and accompanying activator/transporter genes. Mol Plant-Microbe Interact 5:412–419
Kim S-B, Shin B-S, Choi S-K, Kim C-K, Park SH (2001) Involvement of acetyl phosphate in the in vivo activation of the response regulator ComA in Bacillus subtilis. FEMS Microbiol Lett 195:179–183
Li C-M, Brown I, Mansfield J, Romantschuk M, Taira S (2002) The Hrp pilus of Pseudomonas syringae elongates from its tip and acts as a conduit for translocation of the effector protein HrpZ. EMBO J 21:1909–1915
Lindgren PB, Peet RC, Panopoulos NJ (1986) Gene cluster of Pseudomonas syringae pv. “ phaseolicola” controls pathogenicity of bean plants and hypersensitivity on nonhost plants. J Bacteriol 168:512–522
Marits R, Koiv V, Laasik E, Mäe A (1999) Isolation of an extracellular protease gene of Erwinia carotovora subsp. carotovora strain SCC3193 by transposon mutagenesis and the role of protease in phytopathogenicity. Microbiology 145:1959–1966
Mäe A, Montesano M, Koiv V, Palva ET (2001) Transgenic plants producing the bacterial pheromone N -acyl-homoserine lactone exhibit enhanced resistance to the bacterial phytopathogen Erwinia carotovora. Mol Plant-Microbe Interact 14:1035–1042
McCleary WR, Stock JB (1994) Acetyl phosphate and the activation of two-component response regulators. J Biol Chem 269:31567–31572
Miller J (1972) Experiments in molecular genetics. Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press, Cold Spring Harbor, N.Y.
Mukherjee A, Cui Y, Liu Y, Chatterjee AK (1997) Molecular characterization and expression of the Erwinia carotovora hrpN Ecc gene, which encodes an elicitor of the hypersensitive reaction. Mol Plant-Microbe Interact 10:462–471
Nizan-Koren R, Manulis S, Mor H, Iraki NM, Barash I (2003) The regulatory cascade that activates the Hrp regulon in Erwinia herbicola pv. gypsophilae. Mol Plant Microbe Interact. 16:249–260
Oku T, Alvarez AM, Kado CI (1995) Conservation of the hypersensitivity-pathogenicity regulatory gene hrpX of Xanthomonas campestris and X. oryzae. DNA sequence 5:245–249
Palomäki T, Saarilahti HT (1995) The extreme C-terminus is required for secretion of both the native polygalacturonase (PehA) and PehA-Bla hybrid proteins in Erwinia carotovora subsp. carotovora. Mol Microbiol 17:449–459
Palomäki T, Pickersgill R, Riekki R, Romantschuk M, Saarilahti HT (2002) A putative three-dimensional targeting motif of polygalacturonase (PehA), a protein secreted through the type II (GSP) pathway in Erwinia carotovora. Mol Microbiol 43:585–596
Pirhonen M, Flego D, Heikinheimo R, Palva ET (1993) A small diffusible signal molecule is responsible for the global control of virulence and exoenzyme production in the plant pathogen Erwinia carotovora. EMBO J 12:2467–2476
Pugsley AP, Poquet I, Kornacker MG (1991) Two distinct steps in pullulanase secretion by Escherichia coli K-12. Mol Microbiol 5:865–873
Py B, Chippaux M, Barras F (1993) Mutagenesis of cellulase EGZ for studying the general protein secretory pathway in Erwinia chrysanthemi. Mol Microbiol 7:785–793
Rantakari A, Virtaharju O, Vähämiko S, Taira S, Palva ET, Saarilahti HT, Romantschuk M (2001) Type III secretion contributes to the pathogenesis of the soft-rot pathogen Erwinia carotovora: partial characterization of the hrp gene cluster. Mol Plant-Microbe Interact 14:962–968
Roine E, Wei W, Yuan J, Nurmiaho-Lassila E-L, Kalkkinen N, Romantschuk M, He SY (1997) Hrp pilus: an hrp -dependent bacterial surface appendage product by Pseudomonas syringae pv. tomato DC3000. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 94:3459–3464
Saarilahti HT, Palva ET (1986) Major outer membrane proteins in the phytopathogenic bacteria Erwinia carotovora subsp. carotovora and subsp. atroseptica. FEMS Microbiol Lett 35:267–270
Sambrook J, Russell DW (2001) Molecular cloning: a laboratory manual (3rd edn). Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press, Cold Spring Harbor, N.Y.
Summers WC (1970) A simple method for extraction of RNA from E. coli utilizing diethylpyrocarbonate. Anal Biochem 33:459–463
Van den Ackerveken G, Marois E, Bonas U (1996) Recognition of the bacterial avirulence protein AvrBs3 occurs inside the host plant cell. Cell 87:1307–1316
Wei Z-M, Beer SV (1995) hrpL activates Erwinia amylovora hrp gene transcription and is a member of the ECF subfamily of sigma factors. J Bacteriol 177:6201–6210
Wei Z-M, Sneath BJ, Beer SV (1992a) Expression of Erwinia amylovora hrp genes in response to environmental stimuli. J Bacteriol 174:1875–1882
Wei Z-M, Laby RJ, Zumoff CH, Bauer DW, He SY, Collmer A, Beer SV (1992b) Harpin, elicitor of the hypersensitive response produced by the plant pathogen Erwinia amylovora. Science 257:85–88
Wei Z-M, Kim JF, Beer SV (2000) Regulation of hrp genes and type III protein secretion in Erwinia amylovora by HrpX/HrpY a novel two-component system, and HrpS. Mol Plant-Microbe Interact 13:1251–1262
Xiao Y, Hutcheson SW (1994) A single promoter sequence recognized by a newly identified alternate sigma factor directs expression of pathogenicity and host range determinants in Pseudomonas syringae. J Bacteriol 176:3089–3091
Yang CH, Gavilanes-Ruiz M, Okinaka Y, Vedel R, Berthuy I, Boccara M, Chen JW, Perna NT, Keen NT (2002) hrp genes of Erwinia chrysanthemi 3937 are important virulence factors. Mol Plant Microbe Interact 15:472–480
Acknowledgements
Ms. Arja Ikävalko is acknowledged for technical assistance. This study was supported by the Academy of Finland and the Viikki Graduate School of Helsinki University Biocenter
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Communicated by K. Isono
A. R. and J. R. made equal contributions to this study
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lehtimäki, S., Rantakari, A., Routtu, J. et al. Characterization of the hrp pathogenicity cluster of Erwinia carotovora subsp. carotovora: high basal level expression in a mutant is associated with reduced virulence. Mol Genet Genomics 270, 263–272 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00438-003-0905-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00438-003-0905-4