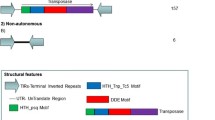
Abstract
The phytopathogenic basidiomycete Ustilago maydis has become a model system for the analysis of plant-pathogen interactions. The genome sequence of this organism will soon be available, increasing the need for techniques to analyse gene function on a broad basis. We describe a heterologous transposition system for U. maydis that is based on the Caenorhabditis transposon Tc1, which is known to function independently of host factors and to be active in evolutionarily distant species. We have established a nitrate reductase based two-component counterselection system to screen for Tc1 transposition. The element was shown to be functional and transposed to several different locations in the genome of U. maydis. The insertion pattern observed was consistent with the proposed general mechanism of Tc1/mariner integration and constitutes a proof of principle for the first heterologous transposition system in a basidiomycete species. By mapping the insertion site context to known genomic sequences, Tc1 insertion events were shown to occur on different chromosomes, but exhibit a preference for non-coding regions. Only 20% of the insertions were found in putative open reading frames. The establishment of this system will permit efficient gene tagging in U. maydis and possibly also in other fungi.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Altmann T, Felix G, Jessop A, Kauschmann A, Uwer U, Pena-Cortes H, Willmitzer L (1995) Ac /Ds transposon mutagenesis in Arabidopsis thaliana: mutant spectrum and frequency of Ds insertion mutants. Mol Gen Genet 247:646–652
Banks GR, Shelton PA, Kanuga N, Holden DW, Spanos A (1993) The Ustilago maydis nar1 gene encoding nitrate reductase activity: sequence and transcriptional regulation. Gene 131:69–78
Banuett F, Herskowitz I (1989) Different a alleles of Ustilago maydis are necessary for maintenance of filamentous growth but not for meiosis. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 86:5878–5882
Banuett F, Herskowitz I (1994) Identification of fuz 7, a Ustilago maydis MEK/MAPKK homolog required for a -locus-dependent and -independent steps in the fungal life cycle. Genes Dev 8:1367–1378
Bhatt AM, Page T, Lawson EJ, Lister C, Dean C (1996) Use of Ac as an insertional mutagen in Arabidopsis. Plant J 9:935–945
Bohlmann R, Schauwecker F, Basse C, Kahmann R (1994) Genetic regulation of mating and dimorphism in Ustilago maydis. Adv Mol Genet Plant-Microbe Interact 3:239–245
Bölker M, Böhnert HU, Braun KH, Görl J, Kahmann R (1995) Tagging pathogenicity genes in Ustilago maydis by restriction enzyme mediated integration (REMI). Mol Gen Genet 248:547–552
Bottin A, Kämper J, Kahmann R (1996) Isolation of a carbon source-regulated gene from Ustilago maydis. Mol Gen Genet 253:342–352
Brachmann A, Weinzierl G, Kämper J, Kahmann R (2001) Identification of genes in the bW/bE regulatory cascade in Ustilago maydis. Mol Microbiol 42:1047–1063
Broomfield PL, Hargreaves JA (1992) A single amino-acid change in the iron-sulphur protein subunit of succinate dehydrogenase confers resistance to carboxin in Ustilago maydis. Curr Genet 22:117–121
Cooley L, Kelley R, Spradling A (1988) Insertional mutagenesis of the Drosophila genome with single P elements. Science 239:1121–1128
Cove DJ (1976) Chlorate toxicity in Aspergillus nidulans. Studies of mutants altered in nitrate assimilation. Mol Gen Genet 146:147–159
Crawford NM, Arst HNJ (1993) The molecular genetics of nitrate assimilation in fungi and plants. Annu Rev Genet 27:115–146
Daboussi MJ, Langin T (1994) Transposable elements in the fungal plant pathogen Fusarium oxysporum. Genetica 93:49–59
Daboussi MJ, Langin T, Brygoo Y (1992) Fot1, a new family of fungal transposable elements. Mol Gen Genet 232:12–16
Fadool JM, Hartl DL, Dowling JE (1998) Transposition of the mariner element from Drosophila mauritiana in zebrafish. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 95:5182–5186
Fischer SE, Wienholds E, Plasterk RH (2001) Regulated transposition of a fish transposon in the mouse germ line. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 98:6759–6764
Fotheringham S, Holloman WK (1989) Cloning and disruption of Ustilago maydis genes. Mol Cell Biol 9:4052–4055
Garrido E, Perez-Martin J (2003) The crk1 gene encodes an Ime2-related protein that is required for morphogenesis in the plant pathogen Ustilago maydis. Mol Microbiol 47:729–743
Glayzer DC, Roberts IN, Archer DB, Oliver RP (1995) The isolation of Ant1, a transposable element from Aspergillus niger. Mol Gen Genet 249:432–438
Gold SE, Bakkeren G, Davies JE, Kronstad JW (1994) Three selectable markers for transformation of Ustilago maydis.Gene 142:225–230
Gold SE, Brogdon SM, Mayorga ME, Kronstad JW (1997) The Ustilago maydis regulatory subunit of a cAMP-dependent protein kinase is required for gall formation in maize. Plant Cell 9:1585–1594
Gómez-Gómez E, Anaya N, Roncero MIG, Hera C (1999) Folyt1, a new member of the hAT family, is active in the genome of the plant pathogen Fusarium oxysporum. Fungal Genet Biol 27:67–76
Gritz L, Davies J (1983) Plasmid-encoded hygromycin B resistance: the sequence of the hygromycin B phosphotransferase gene and its expression in Escherichia coli and Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Gene 25:179–188
Gueiros Filho FJ, Beverley SM (1997) Trans-kingdom transposition of the Drosophila element mariner within the protozoan Leishmania. Science 276:1716–1719
Hartmann HA, Kahmann R, Bölker M (1996) The pheromone response factor coordinates filamentous growth and pathogenicity in Ustilago maydis. EMBO J 15:1632–1641
Hehl R, Baker B (1989) Induced transposition of Ds by a stable Ac in crosses of transgenic tobacco plants. Mol Gen Genet 217:53–59
Hoffman CS, Winston F (1987) A ten-minute DNA preparation from yeast efficiently releases autonomous plasmids for transformation of E. coli. Gene 57:267–272
Holliday R (1974) Ustilago maydis. In: King RC (ed.) Handbook of genetics, vol 1. Plenum Press, New York, pp 575–595
Hua-Van A, Pamphile JA, Langin T, Daboussi MJ (2001) Transposition of autonomous and engineered impala transposons in Fusarium oxysporum and a related species. Mol Gen Genet 264:724–731
Ivics Z, Hackett PB, Plasterk RH, Izsvak Z (1997) Molecular reconstruction of Sleeping Beauty, a Tc1-like transposon from fish, and its transposition in human cells. Cell 91:501–510
Izsvak Z, Ivics Z, Plasterk RH (2000) Sleeping Beauty, a wide host-range transposon vector for genetic transformation in vertebrates. J Mol Biol 302:93–102
Kahmann R, Basse C (1999) REMI (Restriction Enzyme Mediated Integration) and its impact on the isolation of pathogenicity genes in fungi attacking plants. Eur J Plant Pathol 105:221–229
Keon JP, Broomfield PL, White GA, Hargreaves JA (1994) A mutant form of the succinate dehydrogenase iron-sulphur protein subunit confers resistance to carboxin in the maize smut pathogen Ustilago maydis. Biochem Soc Trans 22:234–237
Ketting RF, Fischer SEJ, Plasterk RH (1997) Target choice determinants of the Tc1 transposon of Caenorhabditis elegans. Nucleic Acids Res 25:4041–4047
Kronstad J, De Maria AD, Funnell D, Laidlaw RD, Lee N, de Sa MM, Ramesh M (1998) Signaling via cAMP in fungi: interconnections with mitogen-activated protein kinase pathways. Arch Microbiol 170:395–404
Langin T, Capy P, Daboussi MJ (1995) The transposable element impala, a fungal member of the Tc1-mariner superfamily. Mol Gen Genet 246:19–28
Levis C, Fortini D, Brygoo Y (1997) Flipper, a mobile Fot1-like transposable element in Botrytis cinerea. Mol Gen Genet 254:674–680
Lewis CM, Fincham JR (1970) Regulation of nitrate reductase in the basidiomycete Ustilago maydis. J Bacteriol 103:55–61
Li Destri Nicosia MG, Brocard-Masson C, Demais S, Hua Van A, Daboussi MJ, Scazzocchio C (2001) Heterologous transposition in Aspergillus nidulans. Mol Microbiol 39:1330–1344
Li ZH, Liu DP, Wang J, Guo ZC, Yin WX, Liang CC (1998) Inversion and transposition of Tc1 transposon of C. elegans in mammalian cells. Somat Cell Mol Genet 24:363–369
Long D, Martin M, Sundberg E, Swinburne J, Puangsomlee P, Coupland G (1993) The maize transposable element system Ac/Ds as a mutagen in Arabidopsis: identification of an albino mutation induced by Ds insertion. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 90:10370–10374
Loubradou G, Brachmann A, Feldbrügge M, Kahmann R (2001) A homologue of the transcriptional repressor Ssn6p antagonizes cAMP signalling in Ustilago maydis. Mol Microbiol 40:719–730
Lu S, Lyngholm L, Yang G, Bronson C, Yoder OC, Turgeon BG (1994) Tagged mutations at the Tox1 locus of Cochliobolus heterostrophus by restriction enzyme-mediated integration. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 91:12649–12653
Marzluf GA (1997) Genetic regulation of nitrogen metabolism in the fungi. Microbiol Mol Biol Rev 61:17–32
Maurer P, Rejasse A, Capy P, Langin T, Riba G (1997) Isolation of the transposable element hupfer from the entomopathogenic fungus Beauveria bassiana by insertion mutagenesis of the nitrate reductase structural gene. Mol Gen Genet 256:195–202
Mayorga ME, Gold SE (1999) A MAP kinase encoded by the ubc3 gene of Ustilago maydis is required for filamentous growth and full virulence. Mol Microbiol 34:485–497
Migheli Q, Laugé R, Davière JM, Gerlinger C, Kaper F, Langin T, Daboussi MJ (1999) Transposition of the autonomous Fot1 element in the filamentous fungus Fusarium oxysporum. Genetics 151:1005–1013
Müller P, Aichinger C, Feldbrügge M, Kahmann R (1999) The MAP kinase Kpp2 regulates mating and pathogenic development in Ustilago maydis. Mol Microbiol 34:1007–1017
Nyyssönen E, Amutan M, Enfield L, Stubbs J, Dunn Coleman NS (1996) The transposable element Tan1 of Aspergillus niger var. awamori, a new member of the Fot1 family. Mol Gen Genet 253:50–56
Plasterk RH, Izsvak Z, Ivics Z (1999) Resident aliens: the Tc1/mariner superfamily of transposable elements. Trends Genet 15:326–332
Raz E, van Luenen HG, Schaerringer B, Plasterk RHA, Driever W (1998) Transposition of the nematode Caenorhabditis elegans Tc3 element in the zebrafish Danio rerio. Curr Biol 8:82–8
Rehm EJ (2001) Inverse PCR and cycle sequencing of P element Insertions for STS generation. Berkeley Drosophila Genome Project, Berkeley, pp 1–13 (http://www.fruitfly.org/about/methods/inverse.pcr.html)
Robertson HM (2002) Molecular evolution of DNA transposons. In: Craig NL, Craigie R, Gellert M, Lambowitz AM (eds) Mobile DNA II. ASM Press, Washington, DC, pp 1093–1110
Sambrook J, Frisch EF, and Maniatis T (1989) Molecular cloning: a laboratory manual. Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press, Cold Spring Harbor, N.Y.
Sanchez O, Navarro RE, Aguirre J (1998) Increased transformation frequency and tagging of developmental genes in Aspergillus nidulans by restriction enzyme-mediated integration (REMI). Mol Gen Genet 258:89–94
Schiestl RH, Petes TD (1991) Integration of DNA fragments by illegitimate recombination in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 88:7585–7589
Schouten GJ, van Luenen HG, Verra N, Valerio D, Plasterk R (1998) Transposon Tc1 of the nematode Caenorhabditis elegans jumps in human cells. Nucleic Acids Res 26:3013–3017
Schulz B, Banuett F, Dahl M, Schlesinger R, Schäfer W, Martin T, Herskowitz I, Kahmann R (1990) The b alleles of U. maydis, whose combinations program pathogenic development, code for polypeptides containing a homeodomain-related motif. Cell 60:295–306
Sheen J, Hwang S, Niwa Y, Kobayashi H, Galbraith DW (1995) Green-fluorescent protein as a new vital marker in plant cells. Plant J 8:777–784
Spellig T, Bottin A, Kahmann R (1996) Green fluorescent protein (GFP) as a new vital marker in the phytopathogenic fungus Ustilago maydis. Mol Gen Genet 252:503–509
Steinberg G, Schliwa M, Lehmler C, Bölker M, Kahmann R, McIntosh JR (1998) Kinesin from the plant pathogenic fungus Ustilago maydis is involved in vacuole formation and cytoplasmic migration. J Cell Sci 111:2235–2246
Steinberg G, Wedlich-Söldner R, Brill M, Schulz I (2001) Microtubules in the fungal pathogen Ustilago maydis are highly dynamic and determine cell polarity. J Cell Sci 114:609–622
Straube A, Enard W, Berner A, Wedlich-Söldner R, Kahmann R, Steinberg G (2001) A split motor domain in a cytoplasmic dynein. EMBO J 20:5091–5100
Talbot NJ (1995) Having a blast: exploring the pathogenicity of Magnaporthe grisea. Trends Microbiol 3:9–16
Tsukuda T, Carleton S, Fotheringham S, Holloman WK (1988) Isolation and characterization of an autonomously replicating sequence from Ustilago maydis. Mol Cell Biol 8:3703–3709
Van Luenen HG, Plasterk RH (1994) Target site choice of the related transposable elements Tc1 and Tc3 of Caenorhabditis elegans. Nucleic Acids Res 22:262–269
Vigdal TJ, Kaufman C, Izsvak Z, Voytas D, Ivics Z (2002) Common physical properties of DNA affecting target site selection of Sleeping Beauty and other Tc1/mariner transposable elements. J Mol Biol 323:441–452
Villalba F, Lebrun MH, Hua-Van A, Daboussi MJ, Grosjean-Cournoyer MC (2001) Transposon impala, a novel tool for gene tagging in the rice blast fungus Magnaporthe grisea. Mol Plant Microbe Interact 14:308–315
Vos JC, van Luenen HG, Plasterk RH (1993) Characterization of the Caenorhabditis elegans Tc1 transposase in vivo and in vitro. Genes Dev 7:1244–1253
Vos JC, De Baere I, Plasterk RH (1996) Transposase is the only nematode protein required for in vitro transposition of Tc1. Genes Dev 10:755–761
Wang J, Holden DW, Leong SA (1988) Gene transfer system for the phytopathogenic fungus Ustilago maydis. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 85:865–869
Wedlich-Söldner R, Straube A, Friedrich MW, Steinberg G (2002) A balance of KIF1A-like kinesin and dynein organizes early endosomes in the fungus Ustilago maydis. EMBO J 21:2946–2957
Weil CF, Kunze R (2000) Transposition of maize Ac/Ds transposable elements in the yeast Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Nat Genet 26:187-190
Yant SR, Meuse L, Chiu W, Ivics Z, Izsvak Z, Kay MA (2000) Somatic integration and long-term transgene expression in normal and haemophilic mice using a DNA transposon system. Nat Genet 25:35–41
Yant SR, Ehrhardt A, Mikkelsen JG, Meuse L, Pham T, Kay MA (2002) Transposition from a gutless adeno-transposon vector stabilizes transgene expression in vivo. Nat Biotechnol 20:999–1005
Zwaal RR, Broeks A, van Meurs J, Groenen JT, Plasterk RH (1993) Target-selected gene inactivation in Caenorhabditis elegans by using a frozen transposon insertion mutant bank. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 90:7431–7435
Acknowledgements
We are most grateful to Bayer CropScience AG for providing genomic sequence information for transposon insertion sites and for financial support. We would like to thank R. Plasterk and H. van Luenen for transposon and transposase expression clones, R. Kahmann and A. Jamnischek for critically reading the manuscript, K. Zarnack and M. Feldbrügge for stimulating discussion and S. Lindow for excellent technical assistance.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Communicated by G. Jürgens
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ladendorf, O., Brachmann, A. & Kämper, J. Heterologous transposition in Ustilago maydis . Mol Gen Genomics 269, 395–405 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00438-003-0848-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00438-003-0848-9