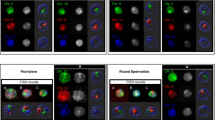
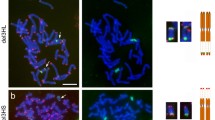
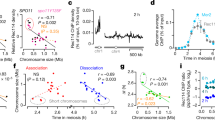
Abstract
During meiosis, the alignment of homologous chromosomes facilitates their subsequent migration away from one another to opposite spindle poles at anaphase I. Recombination is part of the mechanism by which chromosomes identify their homologous partners, and serves to link the homologs in a way that, in some organisms, has been shown to promote proper attachment to the meiotic spindle. We have built a diploid strain that contains a pair of homeologous chromosomes V': one is derived from Saccharomyces cerevisiae and one originates from S. carlsbergensis. Sequence analysis reveals that these chromosomes share 71% sequence identity. The homeologs experience high levels of meiotic double-stranded breaks. Despite their relatedness and their competence to initiate recombination, the meiotic segregation behavior of the homeologous chromosomes suggests that, in most meioses, they are partitioned by a meiotic segregation system that has been shown previously to partition non-exchange chromosomes and pairs with no homology. Though the homeologous chromosomes show a degree of meiotic segregation fidelity similar to that of other non-exchange pairs, our data provide evidence that their limited sequence homology may provide some bias in meiotic partner choice.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alani E, Padmore R, Kleckner N (1990) Analysis of wild-type and rad50 mutants of yeast suggests an intimate relationship between meiotic chromosome synapsis and recombination. Cell 61:419–436
Ausubel FM, Brent R, Kingston RE, Moore DD, Seidman JG (1989) Current protocols in molecular biology. Wiley, New York
Bascom-Slack CA, Ross LO, Dawson DD (1997) Chiasmata, crossovers, and meiotic chromosome segregation. Adv Genet 35:253–284
Borts RH, Haber JE (1987) Meiotic recombination in yeast: alteration by simple heterozygosities. Science 237:1459–1463
Borts RH, Chambers SR, Abdullah MF (2000) The many faces of mismatch repair in meiosis. Mutat Res 451:129–150
Burke D, Dawson D, Stearns T (2000) Methods in yeast genetics: a Cold Spring Harbor laboratory course manual. Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press, Cold Spring Harbor, N.Y.
Carle GF, Olson MV (1985) An electrophoretic karyotype for yeast. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 82:3756–3760
Chambers SR, Hunter N, Louis EJ, Borts RH (1996) The mismatch repair system reduces meiotic homeologous recombination and stimulates recombination-dependent chromosome loss. Mol Cell Biol 16:6110–6120
Chen W, Jinks-Robertson S (1999) The role of the mismatch repair machinery in regulating mitotic and meiotic recombination between diverged sequences in yeast. Genetics 151:1299–1313
Datta A, Adjiri A, New L, Crouse G, Jinks-Robertson S (1996) Mitotic crossovers between diverged sequences are regulated by mismatch repair proteins in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Mol Cell Biol 16:1085–1093
Dawson D, Murray AW, Szostak JW (1986) An alternate pathway for meiotic chromosome segregation in yeast. Science 234:713–717
De Massy B, Baudat F, Nicolas A (1994) Initiation of recombination in Saccharomyces cerevisiae haploid meiosis. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 91:11929–11933
Dernburg AF, Sedat JW, Hawley RS (1996) Direct evidence of a role for heterochromatin in meiotic chromosome segregation. Cell 86:135–146
Earley MC, Crouse GF (1998) The role of mismatch repair in the prevention of base pair mutations in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 95:15487–15491
Evans E, Sugawara N, Haber JE, Alani E (2000) The Saccharomyces cerevisiae Msh2 mismatch repair protein localizes to recombination intermediates in vivo. Mol Cell 5:789–799
Gilbertson LA, Stahl FW (1994) Initiation of meiotic recombination is independent of interhomologue interactions. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 91:11934–11937
Goldman AS, Lichten M (2000) Restriction of ectopic recombination by interhomolog interactions during Saccharomyces cerevisiae meiosis. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 97:9537–9542
Guacci V, Kaback DB (1991) Distributive disjunction of authentic chromosomes in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Genetics 127:475–488
Guacci V, Koshland D, Strunnikov A (1997) A direct link between sister chromatid cohesion and chromosome condensation revealed through the analysis of MCD1 in S. cerevisiae. Cell 91:47–57
Hawley RS, Arbel T (1993) Yeast genetics and the fall of the classical view of meiosis. Cell 72:301–303
Hawley SR, Theurkauf WE (1993) Requiem for distributive segregation: achiasmate segregation in Drosophila females. Trends Genet 9 310–317
Herman PK, Rine J (1997) Yeast spore germination: a requirement for Ras protein activity during re-entry into the cell cycle. EMBO J 16:6171–6181
Hunter N, Chambers SR, Louis EJ, Borts RH (1996) The mismatch repair system contributes to meiotic sterility in an interspecific yeast hybrid. EMBO 15:1726–1733
Johnson RE, Kovvali GK, Prakash L, Prakash S (1996) Requirement of the yeast MSH3 and MSH6 genes for MSH2 -dependent genomic stability. J Biol Chem 271:7285–7288
Karpen GH, Le MH, Le H (1996) Centric heterochromatin and the efficiency of achiasmate disjunction in Drosophila female meiosis. Science 273 118–122
Loidl J, Scherthan H, Kaback DB (1994) Physical association between nonhomologous chromosomes precedes distributive disjunction in yeast. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 91:331–334
Mann C, Davis RW (1986) Meiotic disjunction of circular minichromosomes in yeast does not require DNA homology. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 83:6017–6019
Marsischky GT, Filosi N, Kane MF, Kolodner R (1996) Redundancy of Saccharomyces cerevisiae M SH3 and MSH6 in MSH2 -dependent mismatch repair. Genes Dev 10:407–420
Nicholson A, Hendrix M, Jinks-Robertson S, Crouse GF (2000) Regulation of mitotic homeologous recombination in yeast. Functions of mismatch repair and nucleotide excision repair genes. Genetics 154:133–146
Nicolas A, Treco D, Schultes NP, Szostak JW (1989) An initiation site for meiotic gene conversion in the yeast Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Nature 338:35–39
Nilsson-Tillgren T, Gjermansen C, Kielland-Brandt NC, Litske Peterson JG, Holmberg S (1981) Genetic differences between Saccharomyces carlsbergensis and S. cerevisiae. Analysis of chromosome III by single chromosome transfer. Carlsberg Res Comm. 46:65–76
Nilsson-Tillgren T, Gjermansen C, Holmberg S, Litske Peterson JG, Kielland-Brandt MC (1986) Analysis of chromosome V and the ILV1 gene from Saccharomyces carlsbergensis. Carlsberg Res Comm 51:309–326
Radman M (1989) Mismatch repair and the fidelity of genetic recombination. Genome 31:68–73
Resnick MA, Zgaga Z, Hieter P, Westmoreland J, Fogel S (1992) Recombinant repair of diverged DNAs: a study of homoeologous chromosomes and mammalian YACs in yeast. Mol Gen Genet 234:65–73
Ross LO, Treco D, Nicolas A, Szostak JW, Dawson D (1992) Meiotic recombination on artificial chromosomes in yeast. Genetics 131:541–550
Ross LO, Maxfield R, Dawson D (1996a) Exchanges are not equally able to enhance meiotic chromosome segregation in yeast. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 93:4979–4983
Ross LO, Rankin S, Flatters M, Dawson D (1996b) Effects of homology, size and exchange on the meiotic segregation of model chromosomes in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Genetics 142:79–89
Ross LO, Zenvirth D, Jardim AR, Dawson D (2000) Double-strand breaks on artificial chromosomes in yeast. Chromosoma 109:226–234
Rothstein RJ (1983) One-step gene disruption in yeast. Methods Enzymol 101:202–211
Sandler L, Novitski E (1956) Evidence for genetic homology between chromosomes I and IV in Drosophila melanogaster, with a proposed explanation for the crowding effect of triploids. Genetics 41:189–193
Sears DS, Hegemann JH, Hieter P (1992) Meiotic recombination and segregation of human-derived artificial chromosomes in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 89:5296–5300
Selva EM, New L, Crouse GF, Lahue RS (1995) Mismatch correction acts as a barrier to homeologous recombination in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Genetics 139:1175–1188
Shubochkina EA, Nielsen T, Nilsson-Tillgren T (2001) Meiotic crossing-over in the regions of homology between homeologous chromosomes V. Yeast 18:1173–1183
Southern EM (1975) Detection of specific sequences among DNA fragments separated by gel electrophoresis. J Mol Biol 98:503–517
Winey M, Mamay CL, O'Toole ET, Mastronarde DN, Giddings TH Jr, McDonald KL, McIntosh JR (1995) Three dimensional ultrastructural analysis of the Saccharomyces cerevisiae mitotic spindle. J Cell Biol 129:1601–1615
Wolf KW (1994) How meiotic chromosomes deal with non-exchange chromosomes. Bioessays 16:107–114
Zenvirth D, Arbel T, Sherman A, Goldway M, Klein S, Simchen G (1992) Multiple sites for double-strand breaks in whole meiotic chromsomes of Saccharomyces cerevisiae. EMBO J 11:3441–3447
Acknowledgements
We thank Janette Garrido for help in constructing the S. carlsbergensis chromosome V plasmids, Aaron Straight and Andrew Murray for reagents for GFP-tagging of chromosomes in yeast, and Robert Lahue for MSH2 and MSH3 disruption plasmids. David Kaback, Michael Lichten, Rhona Borts and members of the Dawson lab provided helpful comments on the project. The project was supported by NSF grant MCB-0078138. Experiments were carried out in compliance with US guidelines for genetic experimentation
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Communicated by E. Cerdá-Olmedo
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Maxfield Boumil, R., Kemp, B., Angelichio, M. et al. Meiotic segregation of a homeologous chromosome pair. Mol Gen Genomics 268, 750–760 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00438-002-0796-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00438-002-0796-9