Abstract
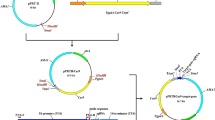
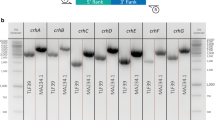
Blaster cassettes are of significant value in functional genomics, as they represent tools with which to inactivate duplicated or homologous genes in an individual organism. We have constructed a novel blaster module which allows repeated gene deletion in the filamentous fungus Aspergillus nidulans. Because bacterial resistance marker cassettes are employed as flanking repeats in direct orientation, the blaster cassette is suited for recombinogenic engineering by ET cloning in Escherichia coli. The functionality of the blaster module was demonstrated by deleting the chorismate mutase-encoding gene aroC of A. nidulans, followed by marker rescue based on mitotic recombination. The resulting aroCΔ strains are auxotrophic for phenylalanine but not tyrosine, and display a limited capacity for fruit body formation and ascosporogenesis, which depends on the phenylalanine/tyrosine supply. The data support the notion that amino acid status has a strong impact on cleistothecium development in A. nidulans.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alani E, Cao L, Kleckner N (1987) A method for gene disruption that allows repeated use of URA3 selection in the construction of multiply disrupted yeast strains. Genetics 116:541–545
Andrews PR, Smith GD, Young IG (1973) Transition-state stabilization and enzymic catalysis. Kinetic and molecular orbital studies of the rearrangement of chorismate to prephenate. Biochemistry 12:3492–3498
Boeke JD, Lacroute F, Fink GR (1984) A positive selection for mutants lacking orotidine-5′-phosphate decarboxylase activity in yeast: 5-fluoro-orotic acid resistance. Mol Gen Genet 197:345–346
Bradford MM (1976) A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem 72:248–254
Braus GH (1991) Aromatic amino acid biosynthesis in the yeast Saccharomyces cerevisiae: a model system for the regulation of a eukaryotic biosynthetic pathway. Microbiol Rev 55:349–370
Braus GH, Krappmann S, Eckert SE (2002) Sexual development in Ascomycetes: fruit body formation of Aspergillus nidulans. In: Osiewacz HD (ed) Molecular biology of fungal development. Marcel Dekker, New York-Basel, pp 215–244
Busch S, Hoffmann B, Valerius O, Starke K, Düvel K, Braus GH (2001) Regulation of the Aspergillus nidulans hisB gene by histidine starvation. Curr Genet 38:314–322
Champe SP, Nagle DL, Yager LN (1994) Sexual sporulation. Prog Ind Microbiol 29:429–454
Chaveroche MK, Ghigo JM, d'Enfert C (2000) A rapid method for efficient gene replacement in the filamentous fungus Aspergillus nidulans. Nucleic Acids Res 28:e97
d'Enfert C (1996) Selection of multiple disruption events in Aspergillus fumigatus using the orotidine-5′-decarboxylase gene, pyrG, as a unique transformation marker. Curr Genet 30:76–82
de Hoogt R, Luyten WH, Contreras R, De Backer MD (2000) PCR- and ligation-mediated synthesis of split-marker cassettes with long flanking homology regions for gene disruption in Candida albicans. Biotechniques 28:1112–1116
Delneri D, Tomlin GC, Wixon JL, Hutter A, Sefton M, Louis EJ, Oliver SG (2000) Exploring redundancy in the yeast genome: an improved strategy for use of the cre-loxP system. Gene 252:127–135
Denning DW, Anderson MJ, Turner G, Latge JP, Bennett JW (2002) Sequencing the Aspergillus fumigatus genome. Lancet Infect Dis 2:251–253
Dower WJ, Miller JF, Ragsdale CW (1988) High efficiency transformation of E. coli by high voltage electroporation. Nucleic Acids Res 16:6127–6145
Eckert SE, Hoffmann B, Wanke C, Braus GH (1999) Sexual development of Aspergillus nidulans in tryptophan auxotrophic strains. Arch Microbiol 172:157–166
Eckert SE, Kübler E, Hoffmann B, Braus GH (2000) The tryptophan synthase-encoding trpB gene of Aspergillus nidulans is regulated by the cross-pathway control system. Mol Gen Genet 263:867–876
Feinberg AP, Vogelstein B (1983) A technique for radiolabeling DNA restriction endonuclease fragments to high specific activity. Anal Biochem 132:6–13
Ganem B (1996) The mechanism of the Claisen rearrangement: déjà vu all over again. Angew Chem Int Ed Engl 35:936–945
Gow NAR, Robbins PW, Lester JW, Brown AJP, Fonzi WA, Chapman T, Kinsman OS (1994) A hyphal-specific chitin synthase gene ( CHS2) is not essential for growth, dimorphism, or virulence of Candida albicans. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 91:6216–6220
Güldener U, Heck S, Fielder T, Beinhauer J, Hegemann JH (1996) A new efficient gene disruption cassette for repeated use in budding yeast. Nucleic Acids Res 24:2519–2524
Güldener U, Heinisch J, Köhler GJ, Voss D, Hegemann JH (2002) A second set of loxP marker cassettes for Cre-mediated multiple gene knockouts in budding yeast. Nucleic Acids Res 30:e23
Han DM, Han YJ, Lee YH, Jahng KY, Jahng SH, Chae KS (1990) Inhibitory conditions of asexual development and their application for the screening of mutants defective in sexual development. Kor J Mycol 18:225–232
Hanahan D, Jessee J, Bloom FR (1991) Plasmid transformation of Escherichia coli and other bacteria. Methods Enzymol 204:63–113
Heiner CR, Hunkapiller KL, Chen SM, Glass JI, Chen EY (1998) Sequencing multimegabase-template DNA with BigDye terminator chemistry. Genome Res 8:557–561
Helmstaedt K, Krappmann S, Braus GH (2001) Allosteric regulation of catalytic activity: Escherichia coli aspartate transcarbamoylase versus yeast chorismate mutase. Microbiol Mol Biol Rev 65:404–421
Hieter P, Boguski M (1997) Functional genomics: it's all how you read it. Science 278:601–602
Hoffmann B, Wanke C, LaPaglia SK, Braus GH (2000) c-Jun and RACK1 homologues regulate a control point for sexual development in Aspergillus nidulans. Mol Microbiol 37:28–41
Käfer E (1977) Meiotic and mitotic recombination in Aspergillus and its chromosomal aberrations. Adv Genet 19:33–131
Kast P, Asif-Ullah M, Jiang N, Hilvert D (1996) Exploring the active site of chorismate mutase by combinatorial mutagenesis and selection: the importance of electrostatic catalysis. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 93:5043–5048
Kolar M, Punt PJ, van den Hondel CA, Schwab H (1988) Transformation of Penicillium chrysogenum using dominant selection markers and expression of an Escherichia coli lacZ fusion gene. Gene 62:127–134
Krappmann S, Helmstaedt K, Gerstberger T, Eckert S, Hoffmann B, Hoppert M, Schnappauf G, Braus GH (1999) The aroC gene of Aspergillus nidulans codes for a monofunctional, allosterically regulated chorismate mutase. J Biol Chem 274:22275–22282
Krappmann S, Pries R, Gellissen G, Hiller M, Braus GH (2000) HARO7 encodes chorismate mutase of the methylotrophic yeast Hansenula polymorpha and is derepressed upon methanol utilization. J Bacteriol 182:4188–4197
Kupfer DM, Reece CA, Clifton SW, Roe BA, Prade RA (1997) Multicellular ascomycetous fungal genomes contain more than 8000 genes. Fungal Genet Biol 21:364–372
Mooney JL, Yager LN (1990) Light is required for conidiation in Aspergillus nidulans. Genes Dev 4:1473–1482
Muyrers JP, Zhang Y, Stewart AF (2000) ET-cloning: think recombination first. Genet Eng (NY) 22:77–98
Muyrers JP, Zhang Y, Stewart AF (2001) Recombinogenic engineering: new options for cloning and manipulating DNA. Trends Biochem Sci 26:325–331
Prade RA, Ayoubi P, Krishnan S, Macwana S, Russell H (2001) Accumulation of stress and inducer-dependent plant-cell-wall-degrading enzymes during asexual development in Aspergillus nidulans. Genetics 157:957–967
Punt PJ, van den Hondel CA (1992) Transformation of filamentous fungi based on hygromycin B and phleomycin resistance markers. Methods Enzymol 216:447–457
Roberts CF (1969) Isolation of multiple aromatic amino acid mutants in Aspergillus nidulans. Aspergillus Newslett 10:19–21
Romero RM, Roberts MF, Phillipson JD (1995) Chorismate mutase in microorganisms and plants. Phytochemistry 40:1015–1025
Saiki RK, Bugawan TL, Horn GT, Mullis KB, Erlich HA (1986) Analysis of enzymatically amplified beta-globin and HLA-DQ alpha DNA with allele-specific oligonucleotide probes. Nature 324:163–166
Sambrook J, Fritsch EF, Maniatis T (1989) Molecular cloning: a laboratory manual. Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press, Cold Spring Harbor, N.Y.
Sauer B (1987) Functional expression of the cre-lox site-specific recombination system in the yeast Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Mol Cell Biol 7:2087–2096
Schneider BL, Steiner B, Seufert W, Futcher AB (1996) pMPY-ZAP: a reusable polymerase chain reaction-directed gene disruption cassette for Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Yeast 12:129–134
Southern EM (1975) Detection of specific sequences among DNA fragments separated by gel electrophoresis. J Mol Biol 98:503–517
Swart K, van Heemst D, Slakhorst M, Debets F, Heyting C (2001) Isolation and characterization of sexual sporulation mutants of Aspergillus nidulans. Fungal Genet Biol 33:25–35
Wieczorke R, Krampe S, Weierstall T, Freidel K, Hollenberg CP, Boles E (1999) Concurrent knock-out of at least 20 transporter genes is required to block uptake of hexoses in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. FEBS Lett 464:123–128
Woodcock DM, Crowther PJ, Doherty J, Jefferson S, DeCruz E, Noyer-Weidner M, Smith SS, Michael MZ, Graham MW (1989) Quantitative evaluation of Escherichia coli host strains for tolerance to cytosine methylation in plasmid and phage recombinants. Nucleic Acids Res 17:3469–3478
Zaudy G (1969) The location of some multiple aromatic mutants in Aspergillus nidulans. Aspergillus Newslett 10:22
Acknowledgements
We are highly indebted to Verena Große for excellent technical assistance and to Christophe d'Enfert (Institut Pasteur, Paris, France) for providing the ET recombination system, as well as to all members of the department for fruitful discussions. Funding was received from the Deutsche Forschungsgemeinschaft, the Volkswagen Stiftung, and the Fonds der Chemischen Industrie
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Communicated by C. A. M. J. J. van den Hondel
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Krappmann, S., Braus, G.H. Deletion of Aspergillus nidulans aroC using a novel blaster module that combines ET cloning and marker rescue. Mol Gen Genomics 268, 675–683 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00438-002-0789-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00438-002-0789-8