Abstract.
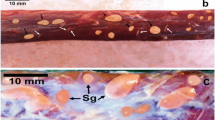
The prevalence of Sarcocystis infection among skinks, Scincus mitranus, was studied for the first time. Grossly macroscopic sarcocysts were found to infect the skeletal muscles of the skink (infection rate: 4.16%). Fecal examination for the presence of sporocysts was negative in this study. Sarcocysts were studied using light and transmission electron microscopes. Mature sarcocysts measuring 0.05–0.3×0.5–1.8 mm (mean 0.15×1.2 mm) were observed. The characteristic primary cyst wall, with long, finger-like, non-branched and non-stalked protrusions, is described. The ground substance gives rise to numerous thick septa dividing the interior of the cyst into chamber-like compartments. Zoites, including metrocytes and merozoites, were found to have the main architecture of Apicomplexa. Peculiarities of these elements and the importance of the primary cyst-wall ultrastructure for identification and specification of Sarcocystis are discussed. Secondary cyst wall was completely absent. Alterations in the infected host cell were observed.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Electronic Publication
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Abdel-Ghaffar, F., Al-Johany, A. A light and electron microscope study of Sarcocystis mitrani (sp. nov.) infecting the skink Scincus mitranus in the central region of Saudi Arabia. Parasitol Res 88, 102–106 (2002). https://doi.org/10.1007/s004360100506
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s004360100506