Abstract
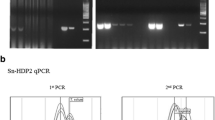
Parasites of the phylum Apicomplexa (Sporozoa) cause diseases such as malaria, toxoplasmosis, or intestinal coccidiosis. Invasive stages possess typical apical organelles such as dense granules that harbor a broad range of polypeptides that are believed to take part in the parasite-host cell interaction. In previous studies a 26-kDa polypeptide of dense granules from Sarcocystis muris cyst merozoites (bradyzoites) was characterized as a thiol (cysteine) proteinase. In this paper a method is demonstrated to amplify DNA fragments from genomic DNA of S. muris cyst merozoites by polymerase chain reaction, which probably code for the 26-kDa antigen.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Received: 12 December 1997 / Accepted: 17 January 1998
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hansner, T., Freyer, B., Mehlhorn, H. et al. Amplification of genomic DNA fragments of Sarcocystis muris (Apicomplexa) cyst merozoites encoding a thiol (cysteine) proteinase. Parasitol Res 84, 578–582 (1998). https://doi.org/10.1007/s004360050452
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s004360050452