Abstract
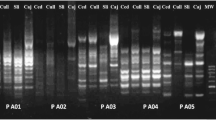
The taxonomic classification within the genus Tritrichomonas is a subject of controversy, and, potentially, separation of the tritrichomonads from cattle and swine on the species level is not valid. To tackle this hypothesis we comparatively assessed several isolates of protozoan parasites from the three Tritrichomonas species T. foetus, T. suis, and T. mobilensis by the RAPD (random amplified polymorphic DNA) technique. In this method with 20 different primers, all T. foetus and T. suis isolates resulted in identical genomic fingerprints, thus yielding additional evidence for the genetic identity of T. foetus and T. suis. In contrast, it turned out that the species T. mobilensis isolated from the squirrel monkey is genetically distinct and can clearly be discriminated from the other tritrichomonads. Consequently, the results obtained in this study support a possible future revision of the taxonomic classification of the genus Tritrichomonas.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Received: 6 July 1997 / Accepted: 19 August 1997
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Felleisen, R. Comparative genetic analysis of tritrichomonadid protozoa by the random amplified polymorphic DNA technique. Parasitol Res 84, 153–156 (1997). https://doi.org/10.1007/s004360050374
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s004360050374