Abstract
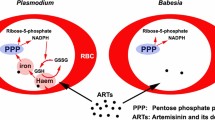
Catalase and glutathione peroxidase (Gpx), two enzymes destroying hydrogen peroxide, were reported in two Babesia species: B. divergens cultivated in vitro and B.hylomysci obtained in vivo. On the use of specific substrate and inhibitor, we confirmed that the Gpx activity detected was selenium-dependent. Moreover, the two Babesia species contain glutamate dehydrogenase activity. This enzyme is capable of providing to the cell the reduced nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate (NADPH) necessary for regeneration of the reduced glutathione. Gpx activity is weaker in B. divergens than in B. hylomysci and seems to be compensated by higher levels of catalase activity. Such a balance between the two enzymes may depend on the selenium concentration available for the parasite.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Received: 7 August 1996 / Accepted: 18 October 1996
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Clarebout, G., Gamain, B., Precigout, E. et al. Babesia hylomysci and B. divergens: presence of antioxidant enzymes destroying hydrogen peroxide. Parasitol Res 84, 75–77 (1997). https://doi.org/10.1007/s004360050360
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s004360050360