Abstract
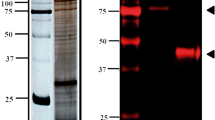
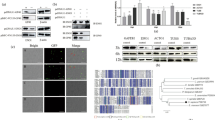
Cryptosporidium parvum is an important apicomplexan parasite causing severe diarrhea in both humans and animals. Calmodulin (CaM), a multifunctional and universal calcium-binding protein, contributes to the growth and development of apicomplexan parasites, but the role of CaM in C. parvum remains unknown. In this study, the CaM of C. parvum encoded by the cgd2_810 gene was expressed in Escherichia coli, and the biological functions of CpCaM were preliminarily investigated. The transcriptional level of the cgd2_810 gene peaked at 36 h post infection (pi), and the CpCaM protein was mainly located around the nucleus of the whole oocysts, in the middle of sporozoites and around the nucleus of merozoites. Anti-CpCaM antibody reduced the invasion of C. parvum sporozoites by 30.69%. The present study indicates that CpCaM is potentially involved in the growth of C. parvum. Results of the study expand our knowledge on the interaction between host and Cryptosporidium.





Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
All data and materials of the study are included in the manuscript.
References
Alves M, Xiao L, Sulaiman I, Lal AA, Matos O, Antunes F (2003) Subgenotype analysis of Cryptosporidium isolates from humans, cattle, and zoo ruminants in Portugal. J Clin Microbiol 41:2744–2747. https://doi.org/10.1128/JCM.41.6.2744-2747.2003
Andrews C, Xu Y, Kirberger M, Yang JJ (2020) Structural aspects and prediction of calmodulin-binding proteins. Int J Mol Sci 22:308. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms22010308
Billker O, Lourido S, Sibley LD (2009) Calcium-dependent signaling and kinases in apicomplexan parasites. Cell Host Microbe 5:612–622. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chom.2009.05.017
Chazin WJ (2011) Relating form and function of EF-hand calcium binding proteins. Acc Chem Res 44:171–179. https://doi.org/10.1021/ar100110d
Checkley W, White AC Jr, Jaganath D, Arrowood MJ, Chalmers RM, Chen XM, Fayer R, Griffiths JK, Guerrant RL, Hedstrom L, Huston CD, Kotloff KL, Kang G, Mead JR, Miller M, Petri WA Jr, Priest JW, Roos DS, Striepen B, Thompson RC, Ward HD, Van Voorhis WA, Xiao L, Zhu G, Houpt ER (2015) A review of the global burden, novel diagnostics, therapeutics, and vaccine targets for Cryptosporidium. Lancet Infect Dis 15:85–94. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1473-3099(14)70772-8
Choudhary HH, Nava MG, Gartlan BE, Rose S, Vinayak S (2020) A conditional protein degradation system to study essential gene function in Cryptosporidium parvum. mBio 11(4):01231–20. https://doi.org/10.1128/mBio.01231-20
Foroutan M, Ghaffarifar F (2018) Calcium-dependent protein kinases are potential targets for Toxoplasma gondii vaccine. Clin Exp Vaccine Res 7:24–36. https://doi.org/10.7774/cevr.2018.7.1.24
Geary TG, Divo AA, Jensen JB (1986) Effect of calmodulin inhibitors on viability and mitochondrial potential of Plasmodium falciparum in culture. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 30:785–788. https://doi.org/10.1128/AAC.30.5.785
Ghartey-Kwansah G, Yin Q, Li Z, Gumpper K, Sun Y, Yang R, Wang D, Jones O, Zhou X, Wang L, Bryant J, Ma J, Boampong JN, Xu X (2020) Calcium-dependent protein kinases in Malaria parasite development and infection. Cell Transplant 29:963689719884888. https://doi.org/10.1177/0963689719884888
Hoeflich KP, Ikura M (2002) Calmodulin in action: diversity in target recognition and activation mechanisms. Cell 108:739–742. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0092-8674(02)00682-7
Khalil IA, Troeger C, Rao PC, Blacker BF, Brown A, Brewer TG, Colombara DV, De Hostos EL, Engmann C, Guerrant RL, Haque R, Houpt ER, Kang G, Korpe PS, Kotloff KL, Lima AAM, Petri WA Jr, Platts-Mills JA, Shoultz DA, Forouzanfar MH, Hay SI, Reiner RC Jr, Mokdad AH (2018) Morbidity, mortality, and long-term consequences associated with diarrhoea from Cryptosporidium infection in children younger than 5 years: a meta-analyses study. Lancet Glob Health 6:e758–e768. https://doi.org/10.1016/S2214-109X(18)30283-3
Kieschnick H, Wakefield T, Narducci CA, Beckers C (2001) Toxoplasma gondii attachment to host cells is regulated by a calmodulin-like domain protein kinase. J Biol Chem 276:12369–12377. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M011045200
Kotloff KL, Nasrin D, Blackwelder WC, Wu Y, Farag T, Panchalingham S, Sow SO, Sur D, Zaidi AKM, Faruque ASG, Saha D, Alonso PL, Tamboura B, Sanogo D, Onwuchekwa U, Manna B, Ramamurthy T, Kanungo S, Ahmed S, Qureshi S, Quadri F, Hossain A, Das SK, Antonio M, Hossain MJ, Mandomando I, Acácio S, Biswas K, Tennant SM, Verweij JJ, Sommerfelt H, Nataro JP, Robins-Browne RM, Levine MM (2019) The incidence, aetiology, and adverse clinical consequences of less severe diarrhoeal episodes among infants and children residing in low-income and middle-income countries: a 12-month case-control study as a follow-on to the Global Enteric Multicenter Study (GEMS). Lancet Glob Health 7:e568–e584. https://doi.org/10.1016/S2214-109X(19)30076-2
Mauzy MJ, Enomoto S, Lancto CA, Abrahamsen MS, Rutherford MS (2012) The Cryptosporidium parvum transcriptome during in vitro development. PLoS One 7:e31715. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0031715
McCowin S, Marie C, Petri WA Jr (2021) Parasite protein pirates host cytoskeletal modulator during invasion. Trends Parasitol 37:937–939. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pt.2021.09.004
Moreno SN, Ayong L, Pace DA (2011) Calcium storage and function in apicomplexan parasites. Essays Biochem 51:97–110. https://doi.org/10.1042/bse0510097
O’Connor RM, Shaffie R, Kang G, Ward HD (2011) Cryptosporidiosis in patients with HIV/AIDS. AIDS 25:549–560. https://doi.org/10.1097/QAD.0b013e3283437e88
Pezzella-D’Alessandro N, Le Moal H, Bonhomme A, Valere A, Klein C, Gomez-Marin J, Pinon JM (2001) Calmodulin distribution and the actomyosin cytoskeleton in Toxoplasma gondii. J Histochem Cytochem 49:445–454. https://doi.org/10.1177/002215540104900404
Ryan U, Zahedi A, Paparini A (2016) Cryptosporidium in humans and animals-a one health approach to prophylaxis. Parasite Immunol 38:535–547. https://doi.org/10.1111/pim.12350
Tamura K, Stecher G, Peterson D, Filipski A, Kumar S (2013) MEGA6: molecular evolutionary genetics analysis version 6.0. Mol Biol Evol 30:2725–2729. https://doi.org/10.1093/molbev/mst197
Tandel J, English ED, Sateriale A, Gullicksrud JA, Beiting DP, Sullivan MC, Pinkston B, Striepen B (2019) Life cycle progression and sexual development of the apicomplexan parasite Cryptosporidium parvum. Nat Microbiol 4:2226–2236. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41564-019-0539-x
Tidow H, Nissen P (2013) Structural diversity of calmodulin binding to its target sites. FEBS J 280:5551–5565. https://doi.org/10.1111/febs.12296
Vaid A, Thomas DC, Sharma P (2008) Role of Ca2+/calmodulin-PfPKB signaling pathway in erythrocyte invasion by Plasmodium falciparum. J Biol Chem 283:5589–5597. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M708465200
Villalobo A (2018) The multifunctional role of phospho-calmodulin in pathophysiological processes. Biochem J 475:4011–4023. https://doi.org/10.1042/BCJ20180755
Villalobo A, Ishida H, Vogel HJ, Berchtold MW (2018) Calmodulin as a protein linker and a regulator of adaptor/scaffold proteins. Biochim Biophys Acta Mol Cell Res 1865:507–521. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbamcr.2017.12.004
Xiao L, Escalante L, Yang C, Sulaiman I, Escalante AA, Montali RJ, Fayer R, Lal AA (1999) Phylogenetic analysis of Cryptosporidium parasites based on the small-subunit rRNA gene locus. Appl Environ Microbiol 65:1578–1583. https://doi.org/10.1128/AEM.65.4.1578-1583.1999
Xu R, Lai C, Yang F, Zhang Q, Li N, Guo Y, Xiao L, Feng Y (2021) Preliminary characterization of two small insulinase-like proteases in Cryptosporidium parvum. Front Microbiol 12:651512. https://doi.org/10.3389/fmicb.2021.651512
Yamniuk AP, Rainaldi M, Vogel HJ (2007) Calmodulin has the potential to function as a Ca-dependent adaptor protein. Plant Signal Behav 2:354–357. https://doi.org/10.4161/psb.2.5.4155
Yang X, Guo Y, Xiao L, Feng Y (2021) Molecular epidemiology of human cryptosporidiosis in low- and middle-income countries. Clin Microbiol Rev 34:e00087-e119. https://doi.org/10.1128/CMR.00087-19
Ye Y, Lee HW, Yang W, Shealy S, Yang JJ (2005) Probing site-specific calmodulin calcium and lanthanide affinity by grafting. J Am Chem Soc 127:3743–3750. https://doi.org/10.1021/ja042786x
Zhang Q, Guo Y, Li N, Li Y, Su J, Xu R, Zhang Z, Feng Y, Xiao L (2020a) Characterization of calcium-dependent protein kinases 3, a protein involved in growth of Cryptosporidium parvum. Front Microbiol 11:907. https://doi.org/10.3389/fmicb.2020.00907
Zhang Q, Shao Q, Guo Y, Li N, Li Y, Su J, Xu R, Zhang Z, Xiao L, Feng Y (2020) Characterization of three calcium-dependent protein kinases of Cryptosporidium parvum. Front Microbiol 11:622203. https://doi.org/10.3389/fmicb.2020.622203
Funding
This work was funded by the grants from the National Natural Science Foundation of China (32072890, 32202838) and the Innovation Support Plan of Shaanxi Province (2021TD‑31).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Peng Lai, Xin Yang, Yun-Hui Li: conceptualization, methodology, investigation, data analysis, writing. Jun-Ke Song, Guang-Hui Zhao: conceptualization, methodology, supervision, reviewing. Yan-Ling Yin, Qian Yao, Shuang Huang, Ying-Ying Fan: data analysis, reviewing, editing.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval
This study was approved by the Research Ethics Committee of Northwest A&F University (Permit Number DY2021007).
Consent to participate
The authors declare that they have participated in this work.
Consent for publication
The authors declare that they know the content of this manuscript and agree to submit it to Parasitology Research.
Competing interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Section Editor: Lihua Xiao
Publisher's note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Lai, P., Yang, X., Li, YH. et al. Characterization of CpCaM, a protein potentially involved in the growth of Cryptosporidium parvum. Parasitol Res 122, 989–996 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00436-023-07803-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00436-023-07803-9