Abstract
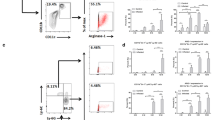
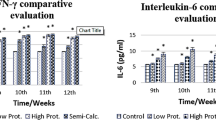
To investigate the phenotypic changes of the expression level of regulatory B cells and related molecules during the continuous infection of Echinococcus granulosus (E. granulosus) in mice and its relationship with E. granulosus infection and its immune effect. Experimental group mice were inoculated with protoscoleces suspension via intraperitoneally injection to prepare a mouse model of E. granulosus infection. Flow cytometry was used to detect the expression of regulatory B cells CD1dhiCD5+CD19hi cells and CD1dhiCD5+CD19hi IL-10+ cells in spleen and peripheral blood of mice. The expressions of IL-10 and TGF-β1 in mouse serum were detected via ELISA. The liver pathological changes in mice were observed by H&E staining; Moreover, the expressions and distribution of IL-10 and TGF-β1 in mice liver were measured through immunohistochemistry. The ELISA test results showed no significant changes in serum IL-10 and TGF-β1 levels in early infected mice. However, at the middle and late stages of infection, the levels of IL-10 and TGF-β1 in the serum of mice increased significantly (P < 0.05). The proportion of CD1dhiCD5+CD19hiBreg cells and the proportion of CD1dhiCD5+CD19hiIL-10+Breg cells in the spleen of mice infected with E. granulosus were increased at 90 days after infection, which indicating that Breg cells proliferated in the late stage of infection. CD1dhiCD5+CD19hi regulatory B cells may be one of the causes of immunosuppression of E. granulosus infection. It is speculated that Bregs inhibitory effect may play a role by regulating the expression of cytokines and inducing the secretion of inhibitory cytokines IL-10 and TGF-β1.















Similar content being viewed by others
References
Afifi MA, Jiman-Fatani AA, El Saadany S, Fouad MA (2015) Parasites-allergy paradox: disease mediators or therapeutic modulators. J Microsc Ultrastruct 3:53–61. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmau.2015.03.002
Bendtzen K (1994) Cytokines and natural regulators of cytokines. Immunol Lett 43:111–123. https://doi.org/10.1016/0165-2478(94)00153-7
Boer MC, Joosten SA, Ottenhoff THM (2015) Regulatory T-cells at the interface between human host and pathogens in infectious diseases and vaccination. Front Immunol 6. https://doi.org/10.3389/fimmu.2015.00217
Cai X, Li X, Lin X et al (2015) Expression of regulatory B cells in peripheral blood of patients with systemic lupus erythematosus. Natl Med J China 95:1310–1313. https://doi.org/10.3760/cma.j.issn.0376-2491.2015.17.007
Candando KM, Lykken JM, Tedder TF (2014) B10 cell regulation of health and disease. Immunol Rev 259:259–272. https://doi.org/10.1111/imr.12176
Cantaert T, Doorenspleet ME, Francosalinas G et al (2012) Increased numbers of CD5+ B lymphocytes with a regulatory phenotype in spondylarthritis. Arthritis Rheum 64:1859–1868. https://doi.org/10.1002/art.34364
Dalwadi H, Wei B, Schrage M, Spicher K, Su TT, Birnbaumer L, Rawlings DJ, Braun J (2004) B cell developmental requirement for the Gαi2 gene. J Immunol 173:695. https://doi.org/10.4049/jimmunol.173.1.695-a
Dilillo DJ, Matsushita T, Tedder TF (2010) B10 cells and regulatory B cells balance immune responses during inflammation, autoimmunity, and cancer. Ann N Y Acad Sci 1183:38–57. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1749-6632.2009.05137.x
Eckert J, Deplazes P (2004) Biological, epidemiological, and clinical aspects of Echinococcosis, a zoonosis of increasing concern. Clin Microbiol Rev 17:107–135. https://doi.org/10.1128/CMR.17.1.107-135.2004
Flores-Borja F, Bosma A, Ng D et al (2013) CD19+CD24hiCD38hi B cells maintain regulatory T cells while limiting TH1 and TH17 differentiation. Sci Transl Med 5:173ra23. https://doi.org/10.1126/scitranslmed.3005407
Gillan V, Lawrence RA, Devaney E (2005) B cells play a regulatory role in mice infected with the L3 of Brugia pahangi. Int Immunol 17:373–382. https://doi.org/10.1093/intimm/dxh217
Gray M, Miles K, Salter D, Gray D, Savill J (2007) Apoptotic cells protect mice from autoimmune inflammation by the induction of regulatory B cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 104:14080–14085. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.0700326104
Han X, Yang J, Zhang Y, et al (2018) Potential role for regulatory B cells as a major source of interleukin-10 in spleen from Plasmodium chabaudi-infected mice. Infect Immun 86. https://doi.org/10.1128/IAI.00016-18
Harris DP, Haynes L, Sayles PC, Duso DK, Eaton SM, Lepak NM, Johnson LL, Swain SL, Lund FE (2000) Reciprocal regulation of polarized cytokine production by effector B and T cells. Nat Immunol 1:475–482. https://doi.org/10.1038/82717
Kessel A, Haj T, Peri R, Snir A, Melamed D, Sabo E, Toubi E (2012) Human CD19+CD25high B regulatory cells suppress proliferation of CD4+ T cells and enhance Foxp3 and CTLA-4 expression in T-regulatory cells. Autoimmun Rev 11:670–677. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.autrev.2011.11.018
Liu Y, Cheng LS, Di Wu S et al (2016) IL-10-producing regulatory B-cells suppressed effector T-cells but enhanced regulatory T-cells in chronic HBV infection. Clin Sci 130:907–919. https://doi.org/10.1042/CS20160069
Mangan NE, Fallon RE, Smith P, van Rooijen N, McKenzie AN, Fallon PG (2004) Helminth infection protects mice from anaphylaxis via IL-10-producing B cells. J Immunol 173:6346–6356. https://doi.org/10.4049/jimmunol.173.10.6346
Matsumura Y, Byrne SN, Nghiem DX, Miyahara Y, Ullrich SE (2006) A role for inflammatory mediators in the induction of immunoregulatory B cells. J Immunol 177:4810–4817. https://doi.org/10.4049/jimmunol.177.7.4810
Mizoguchi A, Bhan AK (2006) A case for regulatory B cells. J Immunol 176:705–710. https://doi.org/10.4049/jimmunol.176.2.705
Unterberger C, Staples KJ, Smallie T, Williams L, Foxwell B, Schaefer A, Kempkes B, Hofer TPJ, Koeppel M, Lohrum M, Stunnenberg H, Frankenberger M, Ziegler-Heitbrock L (2008) Role of STAT3 in glucocorticoid-induced expression of the human IL-10 gene. Mol Immunol 45:3230–3237. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molimm.2008.02.020
Wang T, Li Z, Li X, Chen L, Zhao H, Jiang C, Song L (2017) Expression of CD19+CD24highCD38high B cells, IL-10 and IL-10R in peripheral blood from patients with systemic lupus erythematosus. Mol Med Rep 16:6326–6333. https://doi.org/10.3892/mmr.2017.7381
Yanaba K, Bouaziz JD, Haas KM, Poe JC, Fujimoto M, Tedder TF (2008) A regulatory B cell subset with a unique CD1dhiCD5+ phenotype controls T cell-dependent inflammatory responses. Immunity 28:639–650. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.immuni.2008.03.017
Zhu HQ, Xu RC, Chen YY, Yuan HJ, Cao H, Zhao XQ, Zheng J, Wang Y, Pan M (2015) Impaired function of CD19+CD24hiCD38hi regulatory B cells in patients with pemphigus. Br J Dermatol 172:101–110. https://doi.org/10.1111/bjd.13192
Funding
This work was supported by Scientific Research Project of Science Department of Xinjiang Autonomous Region (2017D01C313; 2020E0277) and the National Natural Science Foundation (81760372; 82060372).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Additional information
Section Editor: Bruno Gottstein
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Qi, X., Shan, J., Liu, X. et al. The role of regulatory B cells in Echinococcus granulosus-infected mice. Parasitol Res 120, 1389–1404 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00436-020-07025-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00436-020-07025-3