Abstract
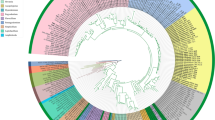
The evolutionary history of Acanthamoeba has been substantially resolved by the 18S rDNA phylogeny which made it possible to delimit the main lines associated with some classical species. Some of them have proven to be polyphyletic, but the inappropriate use of treating under the same names unrelated strains persists. In this study, phylogenies based on the complete genes of nuclear and mitochondrial rDNA were compared, in order to verify the congruence of the different lines. Various groups can thus be identified, some of which associated with the type strains of given species. Recognizing them only by their species names would significantly reduce the current confusion, in addition to logically following basic taxonomic rules. In this manner, the well-known polyphyletic taxa A. castellanii and A. polyphaga, are restricted to the two lines specified by their type strains, while other widely used strains like Neff and Linc-AP1 that are often confused with the previous ones, can be assigned to their own lines. New species are potentially present in other groups and additional efforts are needed to delimit them.


Similar content being viewed by others
Change history
09 March 2021
A Correction to this paper has been published: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00436-021-07102-1
References
Albuquerque P, Nicola AM, Magnabosco DAG, Derengowski LS, Crisóstomo LS, Xavier LCG et al (2019) A hidden battle in the dirt: Soil amoebae interactions with Paracoccidioides spp. PLoS Negl Trop Dis 13(10):e0007742. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pntd.0007742
Amaral-Zettler LA, Zettler ER, Theroux SM, Palacios C, Aguilera A, Amils R (2011) Microbial community structure across the tree of life in the extreme Rio Tinto. ISME J 5(1):42–50. https://doi.org/10.1038/ismej.2010.101
Barbeau J, Buhler T (2001) Biofilms augment the number of free-living amoebae in dental unit waterlines. Res Microbiol 152(8):753–760. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0923-2508(01)01256-6
Bowers B, Korn ED (1968) The fine structure of Acanthamoeba castellanii: I. The trophozoite. J Cell Biol 39(1):95–111. https://doi.org/10.1083/jcb.39.1.95
Bowers B, Korn ED (1969) The fine structure of Acanthamoeba castellanii (Neff strain): II. Encystment. J Cell Biol 41(3):786–805. https://doi.org/10.1083/jcb.41.3.786
Burger G, Plante I, Lonergan KM, Gray MW (1995) The mitochondrial DNA of the amoeboid protozoon, Acanthamoeba castellanii: complete sequence, gene content and genome organization. J Mol Biol 245(5):522–537. https://doi.org/10.1006/jmbi.1994.0043
Byers TJ, Hugo ER, Stewart VJ (1990) Genes of Acanthamoeba: DNA, RNA and protein sequences (a review). J Protozool 37(4):17S–25S. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1550-7408.1990.tb01141.x
Castellani A (1930) An amoeba found in culture of a yeast: preliminary note. J Trop Med Hyg 33:160
Chelkha N, Levasseur A, Pontarotti P, Raoult D, La Scola B, Colson P (2018) A phylogenomic study of Acanthamoeba polyphaga draft genome sequences suggests genetic exchanges with giant viruses. Front Microbiol 9:2098. https://doi.org/10.3389/fmicb.2018.02098
Chelkha N, Jardot P, Moussaoui I, Levasseur A, La Scola B, Colson P (2020) Core gene-based molecular detection and identification of Acanthamoeba species. Sci Rep 10(1):1583. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-020-57998-5
Corsaro D, Venditti D (2010) Phylogenetic evidence for a new genotype of Acanthamoeba (Amoebozoa, Acanthamoebida). Parasitol Res 107(1):233–238. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00436-010-1870-6
Corsaro D, Venditti D (2018a) An apparent Acanthamoeba genotype is the product of a chimeric 18S rDNA artefact. Parasitol Res 117(2):571–577. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00436-017-5690-9
Corsaro D, Venditti D (2018b) Nuclear group I introns with homing endonuclease genes in Acanthamoeba genotype T4. Eur J Protistol 66(4):26–35. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejop.2018.07.002
Corsaro D, Walochnik J, Köhsler M, Rott MB (2015) Acanthamoeba misidentification and multiple labels: redefining genotypes T16, T19 and T20, and proposal for Acanthamoeba micheli sp. nov. (genotype T19). Parasitol Res 114(7):2481–2490. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00436-015-4445-8
Corsaro D, Köhsler M, Montalbano Di Filippo M, Venditti D, Monno R, Di Cave D, Berrilli F, Walochnik J (2017) Update on Acanthamoeba jacobsi genotype T15, including full-length 18S rDNA molecular phylogeny. Parasitol Res 116(4):1273–1284. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00436-017-5406-1
Corsaro D, Köhsler M, Venditti D, Rott MR, Walochnik J (2019) Recovery of an Acanthamoeba strain with two group I introns in the nuclear 18S rRNA gene. Eur J Protistol 68(2):88–98. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejop.2019.01.007
Derr-Harf C, Molet B, Schreiber J, Kremer M (1978) Épidémiologie des amibes libres dans les eaux de Strasbourg. Ann Parasitol Hum Comp 53(5):467–477. https://doi.org/10.1051/parasite/1978535467
Dobell C (1914) Cytological studies on three species of Amoeba—A. lacertae Hartmann, A. fluvialis n. sp., A. glebae n. sp. Arch Protistenkd 34(2):139–189
Douglas M (1930) Notes on the classification of the amoeba found by Castellani in cultures of a yeast-like fungus. J Trop Med Hyg 33:258–259
Fallon RJ, Rowbotham TJ (1990) Microbiological investigations into an outbreak of Pontiac fever due to Legionella micdadei associated with use of a whirlpool. J Clin Pathol 43(6):479–483. https://doi.org/10.1136/jcp.43.6.479
Fuerst PA (2014) Insights from the DNA databases: approaches to the phylogenetic structure of Acanthamoeba. Exp Parasitol 145:S39–S45. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.exppara.2014.06.020
Fuerst PA, Booton GC, Crary M (2015) Phylogenetic analysis and the evolution of the 18S rRNA gene typing system of Acanthamoeba. J Eukaryot Microbiol 62(1):69–84. https://doi.org/10.1111/jeu.12186
Gast RJ (2001) Development of an Acanthamoeba-specific reverse dot-blot and the discovery of a new ribotype. J Eukaryot Microbiol 48(6):609–615. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1550-7408.2001.tb00199.x
Gast RJ, Ledee DR, Fuerst PA, Byers TJ (1996) Subgenus systematics of Acanthamoeba: four nuclear 18S rDNA sequence types. J Eukaryot Microbiol 43(6):498–504. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1550-7408.1996.tb04510.x
González-Robles A, Salazar-Villatoro L, Omaña-Molina M, Lorenzo-Morales J, Martínez-Palomo A (2013) Acanthamoeba royreba: morphological features and in vitro cytopathic effect. Exp Parasitol 133(4):369–375. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.exppara.2013.01.011
Gunderson JH, Sogin ML (1986) Length variation in eukaryotic rRNAs: small subunit rRNAs from the protists Acanthamoeba castellanii and Euglena gracilis. Gene 44(1):63–70. https://doi.org/10.1016/0378-1119(86)90043-0
Hasni I, Andréani J, Colson P, La Scola B (2020) Description of virulent factors and horizontal gene transfers of keratitis-associated amoeba Acanthamoeba triangularis by genome analysis. Pathogens 9(3):217. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens9030217
Hewett MK, Robinson BS, Monis PT, Saint CP (2003) Identification of a new Acanthamoeba 18S rRNA gene sequence type, corresponding to the species Acanthamoeba jacobsi Sawyer, Nerad and Visvesvara, 1992 (Lobosea: Acanthamoebidae). Acta Protozool 42(4):325–329
Hoffmann R, Michel R (2001) Distribution of free-living amoebae (FLA) during preparation and supply of drinking water. Int J Hyg Environ Health 203(3):215–219. https://doi.org/10.1078/S1438-4639(04)70031-0
Horn M, Fritsche TR, Gautom RK, Schleifer KH, Wagner M (1999) Novel bacterial endosymbionts of Acanthamoeba spp. related to the Paramecium caudatum symbiont Caedibacter caryophilus. Environ Microbiol 1(4):357–367. https://doi.org/10.1046/j.1462-2920.1999.00045.x
Im KI, Shin HJ (2003) Acanthamoeba sohi, n. sp., a pathogenic Korean isolate YM-4 from a freshwater fish. Korean J Parasitol 41(4):181–188. https://doi.org/10.3347/kjp.2003.41.4.181
Kang S, Tice AK, Spiegel FW, Silberman JD, Pánek T, Čepička I, Kostka M, Kosakyan A, Alcântara DMC, Roger AJ, Shadwick LL, Smirnov A, Kudryavtsev A, Lahr DJG, Brown MW (2017) Between a pod and a hard test: the deep evolution of amoebae. Mol Biol Evol 34(9):2258–2270. https://doi.org/10.1093/molbev/msx162
Karlyshev AV (2019) Remarkable features of mitochondrial DNA of Acanthamoeba polyphaga Linc Ap-1, revealed by whole-genome sequencing. Microbiol Resour Announc 8(25):e00430–e00419. https://doi.org/10.1128/MRA.00430-19
Khan NA, Tareen NK (2003) Genotypic, phenotypic, biochemical, physiological and pathogenicity-based categorisation of Acanthamoeba strains. Folia Parasitol 50(2):97–104. https://doi.org/10.14411/fp.2003.017
Kliescikova J, Kulda J, Nohynkova E (2011) Stress-induced pseudocyst formation-a newly identified mechanism of protection against organic solvents in Acanthamoebae of the T4 genotype. Protist 162(1):58–69. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.protis.2010.03.006
Korehi H, Blöthe M, Sitnikova MA, Dold B, Schippers A (2013) Metal mobilization by iron- and sulfur-oxidizing bacteria in a multiple extreme mine tailings in the Atacama Desert, Chile. Environ Sci Technol 47(5):2189–2196. https://doi.org/10.1021/es304056n
Kudryavtsev A, Wylezich C, Schlegel M, Walochnik J, Michel R (2009) Ultrastructure, SSU rRNA gene sequences and phylogenetic relationships of Flamella Schaeffer, 1926 (Amoebozoa), with description of three new species. Protist 160(1):21–40. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.protis.2008.09.004
Landell MS, Salton J, Caumo K, Broetto L, Rott MB (2013) Isolation and genotyping of free-living environmental isolates of Acanthamoeba spp. from bromeliads in Southern Brazil. Exp Parasitol 134(3):290–294. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.exppara.2013.03.028
Ledee DR, Booton GC, Awwad MH, Sharma S, Aggarwal RK, Niszl IA, Markus MB, Fuerst PA, Byers TJ (2003) Advantages of using mitochondrial 16S rDNA sequences to classify clinical isolates of Acanthamoeba. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci 44(3):1142–1149. https://doi.org/10.1167/iovs.02-0485
Lewis EJ, Sawyer TK (1979) Acanthamoeba tubisahi n. sp., a new species of fresh water amoebida (Acanthamoebidae). Trans Amer Microbiol Soc 98:543–549
Liu H, Moon EK, Yu HS, Jeong HJ, Hong YC, Kong HH, Chung DI (2005) Evaluation of taxonomic validity of four species of Acanthamoeba: A. divionensis, A. paradivionensis, A. mauritaniensis, and A. rhysodes, inferred from molecular analyses. Korean J Parasitol. 43(1):7–13. https://doi.org/10.3347/kjp.2005.43.1.7
Liu H, Ha YR, Lee ST, Hong YC, Kong HH, Chung DI (2006) Genetic diversity of Acanthamoeba isolates from ocean sediments. Korean J Parasitol 44(2):117–125. https://doi.org/10.3347/kjp.2006.44.2.117
Lorenzo-Morales J, Ortega-Rivas A, Martínez E, Khoubbane M, Artigas P, Periago MV, Foronda P, Abreu-Acosta N, Valladares B, Mas-Coma S (2006) Acanthamoeba isolates belonging to T1, T2, T3, T4 and T7 genotypes from environmental freshwater samples in the Nile Delta region, Egypt. Acta Trop 100(1-2):63–69. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actatropica.2006.09.008
Magistrado-Coxen P, Aqeel Y, Lopez A, Haserick JR, Urbanowicz BR, Costello CE, Samuelson J (2019) The most abundant cyst wall proteins of Acanthamoeba castellanii are lectins that bind cellulose and localize to distinct structures in developing and mature cyst walls. PLoS Negl Trop Dis 13(5):e0007352. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pntd.0007352
Magnet A, Henriques-Gil N, Galván-Diaz AL, Izquiedo F, Fenoy S, Del Aguila C (2014) Novel Acanthamoeba 18S rRNA gene sequence type from an environmental isolate. Parasitol Res 113(8):2845–2850. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00436-014-3945-2
Malavin S, Shmakova L (2020) Isolates from ancient permafrost help to elucidate species boundaries in Acanthamoeba castellanii complex (Amoebozoa: Discosea). Eur J Protistol 73:125671. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejop.2020.125671
Marciano-Cabral F, Cabral G (2003) Acanthamoeba spp. as agents of disease in humans. Clin Microbiol Rev 16(2):273–307. https://doi.org/10.1128/cmr.16.2.273-307.2003
Molet B, Ermolieff-Braun G (1976) Description d’une amibe d’eau douce: Acanthamoeba lenticulata, Sp. Nov. (Amoebida). Protistologica 12:571–576
Moura H, Wallace S, Visvesvara GS (1992) Acanthamoeba healyi n. sp. and the isozyme and immunoblot profiles of Acanthamoeba spp. groups 1 and 3. J Protozool 39(5):573–583. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1550-7408.1992.tb04853.x
Neff RJ (1957) Purification, axenic cultivation, and description of a soil amoeba, Acanthamoeba sp. J Protozool 4(3):176–182. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1550-7408.1957.tb02505.x
Nerad TA, Sawyer TK, Lewis EJ, McLaughlin SM (1995) Acanthamoeba pearcei N. Sp. (Protozoa: Amoebida) from sewage contaminated sediments. J Eukaryot Microbiol 42(6):702–705. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1550-7408.1995.tb01619.x
Nuprasert W, Putaporntip C, Pariyakanok L, Jongwutiwes S (2010) Identification of a novel T17 genotype of acanthamoeba from environmental isolates and T10 genotype causing keratitis in Thailand. J Clin Microbiol 48(12):4636–4640. https://doi.org/10.1128/JCM.01090-10
Obaseki DE, Forae GD, Iyawe DU, Akinwale D, Obahiagbon I (2016) A first reportable case of fatal granulomatous amoebic encephalitis in an immunocompetent Nigerian confirmed by molecular studies-polymerase chain reaction (PCR). J Med Public Health 6(3):148–150. https://doi.org/10.5530/ijmedph.2016.3.11
Page FC (1967) Re-definition of the genus Acanthamoeba with description of three species. J Protozool 14(4):709–724. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1550-7408.1967.tb02066.x
Page FC (1981) A light- and electron-microscopical study of Protacanthamoeba caledonica n. sp., type-species of Protacanthamoeba n. g. (Amoebida, Acanthamoebidae). J Protozool 28(1):70–78. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1550-7408.1981.tb02807.x
Page FC (1988) A new key to freshwater and soil Gymnamoebae. Freshwater Biological Association, Ambleside, Cumbria, pp 92–97
Pernin P, Pussard M (1979) Etude en microscopie photonique et électronique d’une amibe voisine du genre Acanthamoeba: Comandonia operculata n. gen., n. sp. Protistologica 15(1):87–102
Petry F, Torzewski M, Bohl J, Wilhelm-Schwenkmezger T, Scheid P, Walochnik J, Michel R, Zöller L, Werhahn KJ, Bhakdi S, Lackner KJ (2006) Early diagnosis of Acanthamoeba infection during routine cytological examination of cerebrospinal fluid. J Clin Microbiol 44(5):1903–1904. https://doi.org/10.1128/JCM.44.5.1903-1904.2006
Pussard M (1964a) Cytologie d’une amibe terricola: Acanthamoeba terricola n. sp. Ann Sci Nat Zool 6:565–600
Pussard M (1964b) Acanthamoeba comandoni n. sp., comparaison avec A. terricola. Rev Ecol Biol Sol 1:587–610
Pussard M, Pons R (1977) Morphologie de la paroi kystique et taxonomie du genre Acanthamoeba (Protozoa, Amoebida). Protistologica 13(4):557–598
Qvarnstrom Y, Nerad TA, Visvesvara GS (2013) Characterization of a new pathogenic Acanthamoeba species, A. byersi n. sp., isolated from a human with fatal amoebic encephalitis. J Eukaryot Microbiol 60(6):626–633. https://doi.org/10.1111/jeu.12069
Rahman MM, Yagita K, Kobayashi A, Oikawa Y, Hussein AIA, Matsumura T, Tokoro M (2013) Genetic characterization of clinical Acanthamoeba isolates from Japan using nuclear and mitochondrial small subunit ribosomal RNA. Korean J Parasitol 51(4):401–411. https://doi.org/10.3347/kjp.2013.51.4.401
Ray DL, Hayes RE (1954) Hartmannella astronyxis: a new species of free-living ameba. J Morph 95:159–187
Reich M (1935) Studien uber die bodenprotozoen Palastinas. Arch Protistenk 79:76–98
Rowbotham TJ (1980) Preliminary report on the pathogenicity of Legionella pneumophila for freshwater and soil amoebae. J Clin Pathol 33(12):1179–1183. https://doi.org/10.1136/jcp.33.12.1179
Sawyer TK (1970) The influence of seawater media on growth and encystment of Acanthamoeba polyphaga. Proc Helminthol Soc Wash 37(2):182–188
Sawyer TK (1971) Acanthamoeba griffini: a new species of marine amoeba. J Protozool 18(4):650–654. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1550-7408.1971.tb03391.x
Sawyer TK (1989) Free-living pathogenic and nonpathogenic amoebae in Maryland soils. Appl Environ Microbiol 55(5):1074–1077. https://doi.org/10.1128/aem.55.5.1074-1077.1989
Sawyer TK, Griffin JL (1971) Acanthamoeba comandoni and A. astronyxis: taxonomic characteristics of mitotic nuclei, “centrosomes” and cysts. J Protozool 18(3):382–388. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1550-7408.1971.tb03339.x
Sawyer TK, Visvesvara GS, Harke BA (1977) Pathogenic amoebas from brackish and ocean sediments, with a description of Acanthamoeba hatchetti, n. sp. Science 196(4296):1324–1325. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.867031
Sawyer TK, Nerad TA, Visvesvara GS (1992) Acanthamoeba jacobsi sp. n. (Protozoa: Acanthamoebidae) from sewage contaminated ocean sediments. J Helminthol Soc Wash 59(2):223–226
Sawyer TK, Nerad TA, Lewis EJ, McLaughlin AM (1993) Acanthamoeba stevensoni N. Sp. (Protozoa: Amoebida) from sewage-contaminated shellfish beds in Raritan Bay, New York. J Eukaryot Microbiol 40(6):742–746. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1550-7408.1993.tb04469.x
Schmöller H (1964) Description of some cultivated amoebae of marine origin. J Protozool 11(4):497–502. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1550-7408.1964.tb01787.x
Shadwick LL, Brown MW, Tice AK, Spiegel FW (2016) A new amoeba with protosteloid fruiting: Luapeleamoeba hula n. g. n. sp. (Acanthamoebidae, Centramoebida, Amoebozoa). Acta Protozool 55:123–134. https://doi.org/10.4467/16890027AP.16.012.5744
Singh BN (1952) Nuclear division in nine species of small free-living amoebae and its bearing on the classification of the order Amoebida. Phil Trans R Soc Lond B 236(636):405–461. https://doi.org/10.1098/rstb.1952.0007
Singh BN, Das SR (1970) Studies on pathogenic and non-pathogenic small free-living amoebae and the bearing of nuclear division on the classification of the order Amoebida. Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci 259(832):435–476. https://doi.org/10.1098/rstb.1970.0063
Stothard DR, Schroeder-Diedrich JM, Awwad MH, Gast RJ, Ledee DR, Rodriguez-Zaragoza S, Dean CL, Fuerst PA, Byers TJ (1998) The evolutionary history of the genus Acanthamoeba and the identification of eight new 18S rRNA gene sequence types. J Eukaryot Microbiol 45(1):45–54. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1550-7408.1998.tb05068.x
Stratford MP, Griffiths AJ (1978) Variations in the properties and morphology of cysts of Acanthamoeba castellanii. J Gen Microbiol 108(1):33–37. https://doi.org/10.1099/00221287-108-1-33
Tice AK, Shadwick LL, Fiore-Donno AM, Geisen S, Kang S, Schuler GA, Spiegel FW, Wilkinson KA, Bonkowski M, Dumack K, Lahr DJG, Voelcker E, Clauß S, Zhang J, Brown MW (2016) Expansion of the molecular and morphological diversity of Acanthamoebidae (Centramoebida, Amoebozoa) and identification of a novel life cycle type within the group. Biol Direct 11:69. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13062-016-0171-0
Uzuka A, Kobayashi Y, Onuma R, Hirooka S, Kanesaki Y, Yoshikawa H, Fujiwara T, Miyagishima SY (2019) Responses of unicellular predators to cope with the phototoxicity of photosynthetic prey. Nature Commun 10(1):5606. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-019-13568-6
Visvesvara GS, Schuster FL, Martinez AJ (1993) Balamuthia mandrillaris, N. G., N. Sp., agent of amebic meningoencephalitis in humans and other animals. J Eukaryot Microbiol 40(4):504–514. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1550-7408.1993.tb04943.x
Walker JJ, Spear JR, Pace NR (2005) Geobiology of a microbial endolithic community in the Yellowstone geothermal environment. Nature 434(7036):1011–1014. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature03447
Weekers PHH, Bodelier PLE, Wijen JPH, Vogels GD (1993) Effects of grazing by the free-living soil amoebae Acanthamoeba castellanii, Acanthamoeba polyphaga, and Hartmannella vermiformis on various bacteria. Appl Environ Microbiol 59(7):2317–2319. https://doi.org/10.1128/aem.59.7.2317-2319.1993
Willaert E, Stevens AR, Tyndall RL (1978) Acanthamoeba royreba sp. n. from a human tumor cell culture. J Protozool 25(1):1–14. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1550-7408.1978.tb03854.x
Wright SJL, Redhead K, Maudsley H (1981) Acanthamoeba castellanii, a predator of Cyanobacteria. J Gen Microbiol 125(2):293–300. https://doi.org/10.1099/00221287-125-2-293
Xuan YH, Chung BS, Hong YC, Kong HH, Hahn TW, Chung DI (2008) Keratitis by Acanthamoeba triangularis: report of cases and characterization of isolates. Korean J Parasitol 46(3):157–164. https://doi.org/10.3347/kjp.2008.46.3.157
Xuan Y, Shen Y, Ge Y, Yan G, Zheng S (2017) Isolation and identification of Acanthamoeba strains from soil and tap water in Yanji, China. Environ Health Prev Med 22(1):58. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12199-017-0655-2
Yang Q, Zwick MG, Paule MR (1994) Sequence organization of the Acanthamoeba rRNA intergenic spacer: identification of transcriptional enhancers. Nucleic Acids Res 22(22):4798–4805. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/22.22.4798
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The author declares that he has no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Handling Editor: Julia Walochnik
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Corsaro, D. Update on Acanthamoeba phylogeny. Parasitol Res 119, 3327–3338 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00436-020-06843-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00436-020-06843-9