Abstract
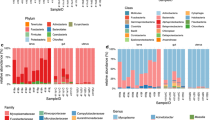
In the present work, we reported for the first time the microbiome from Phyllocaulis soleiformis and Biomphalaria glabrata assessed using high-throughput DNA sequencing pre- and post-infection with the helminth parasite Angiostrongylus cantonensis. B. glabrata and P. soleiformis were experimentally infected with A. cantonensis. Fecal DNAs from control and infected groups were extracted and subjected to 16S rRNA high-throughput sequencing survey. No significant differences were found in the alpha diversity indexes in Phyllocaulis and Biomphalaria experiments independently. PCoA analysis using the unweighted UniFrac measures showed that both microbiotas behaved differently depending on the host. In Biomphalaria microbiota, control and infected groups were significantly different (p = 0.0219), while Phyllocaulis samples were not (p = 0.5190). The microbiome of P. soleiformis infected with A. cantonensis showed a significant decrease of Sphingobacterium and a substantial increase of Cellvibrio when compared to a control group. The microbiome of B. glabrata infected with A. cantonensis showed a significant decline in the abundance of Flavobacterium, Fluviicola, Nitrospira, Vogesella and an OTU belonging to the family Comamonadaceae, and a significant increase of Uliginosibacterium and an OTU belonging to the family Weeksellaceae when compared to a control group. Overall, the microbiome data reported here provided valuable information with regard to the diversity of bacterial communities that comprise the gut microbiome of gastropods. Furthermore, we report here the effect of the infection of the helminth A. cantonensis in the ratio and distribution of the fecal microbiome of the snails. Further studies are highly valuable in order to better understand those interactions by comparing different microbiome profiles and mollusk models. By now, we anticipate that ecological studies will take significant advantage of these advances, particularly concerning improving our understanding of helminth-microbiome-host interactions.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Banevicius NM, Zanotti-Magalhães EM, Magalhães LA, Linhares AX (2006) Behavior of Angiostrongylus costaricensis in planorbids. Braz J Biol 66:199–204
Barçante TA, Barçante JMP, Fujiwara RT, Lima WS (2012) Analysis of circulant haemocytes from Biomphalaria glabrata following Angiostrongylus varosum infection using flow cytometry. J Parasitol Res 2012:314723
Bates ST, Berg-Lyons D, Caporaso JG, Walters WA, Knight R, Fierer N (2011) Examining the global distribution of dominant archaeal populations in soil. ISME Journal 5:908–917
Benson AK, Kelly SA, Legge R, Ma F, Low SJ, Kim J, Zhang M, Oh PL, Nehrenberg D, Hua K, Kachman SD, Moriyama EN, Walter J, Peterson DA, Pomp D (2010) Individuality in gut microbiota composition is a complex polygenic trait shaped by multiple environmental and host genetic factors. PNAS 107:18933–18938
Bowman JP (2014) The family Cryomorphaceae. In: Rosenberg E, DeLong EF, Lory S, Stackebrandt E, Thompson F (eds) The prokaryotes. Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg
Caporaso JG, Kuczynski J, Stombaugh J, Bittinger K, Bushman FD, Costelo EK, Fierer N et al (2010) QIIME allows analysis of high-throughput community sequencing data. Nat Methods 7:335–336
Cardoso AM, Cavalcante JJV, Cantão ME, Thompson CE, Flatschart RB, Glogauer A, Scapin SMN, Sade YB, Beltrão PJMSI, Gerber AL, Martins OB, Garcia ES, de Souza W, Vasconcelos ATR (2012) Metagenomic analysis of the microbiota from the crop of an invasive snail reveals a rich reservoir of novel genes. PLoS One 7:e48505
Charrier M, Combet-Blanc Y, Ollivier B (1998) Bacterial flora in the gut of Helix aspersa (Gastropoda Pulmonata): evidence for a permanent population with a dominant homolactic intestinal bacterium, Enterococcus casseliflavus. Can J Microbiol 44:20–27
Charrier M, Fonty G, Gaillard-Martinie B, Ainouche K, Andant G (2006) Isolation and characterization of cultivable fermentative bacteria from the intestine of two edible snails, Helix pomatia and Cornu aspersum (Gastropoda: Pulmonata). Biol Res 39:669–681
Clarke KR (1993) Non-parametric multivariate analyses of changes in community structure. Austral Ecology 18:117–143
Cole JR, Wang Q, Fish JA, Chai B, McGarrell DM, Sun Y, Brown CT et al (2014) Ribosomal Database Project: data and tools for high throughput rRNA analysis. Nucleic Acids Res 42:D633–D642
Cutler RG, Thompson KW, Camandola S, Mack KT, Mattson MP (2014) Sphingolipid metabolism regulates development and lifespan in Caenorhabditis elegans. Mech Ageing Dev 143-144:9–18
Dar MA, Pawar KD, Jadhav JP, Pandit RS (2015) Isolation of cellulolytic bacteria from the gastro-intestinal tract of Achatina fulica (Gastropoda: Pulmonata) and their evolution for cellulose biodegradation. Int Biodeterior Biodegradation 98:73–80
Dar MA, Pawar K, Pandit RS (2017) Gut microbiome analysis of snails: a biotechnological approach. In: Ray S (ed) Organismal and molecular malacology. European Union, IntechOpen
Davis J, Fricke WF, Hamann MT, Esquenazi E, Dorrestein PC, Hill RT (2013) Characterization of the bacterial community of the chemically defended Hawaiian sacoglossan Elysia rufescens. Appl Environ Microbiol 79:7073–7081
DeSantis TZ, Hugenholtz P, Larsen N, Rojas M, Brodie EL, Keller K, Huber T et al (2006) Greengenes, a chimera-checked 16S rRNA gene database and workbench compatible with ARB. Appl Environ Microbiol 72:5069–5072
Ducklow HW, Boyle PJ, Maugel PW, Strong C, Mitchell R (1979) Bacterial flora of the schistosome vector snail Biomphalaria glabrata. Appl Environ Microbiol 38:667–672
Edgar RC (2010) Search and clustering orders of magnitude faster than BLAST. Bioinformatics 26:2460–2461
Edgar RC (2013) UPARSE: highly accurate OTU sequences from microbial. Nat Methods 10:996–998
Engelbrektson A, Kunin V, Wrighton KC, Zvenigorodsky N, Chen F, Ochman H, Hugenholtz P (2010) Experimental factors affecting PCR-based estimates of microbial species richness and evenness. The ISME Journal 4:642–647
Giongo A, Gano KA, Crabb DB, Mukherjee N, Novelo LL, Casella G, Drew JC et al (2010) Toward defining the autoimmune microbiome for type 1 diabetes. The ISME Journal 5:82–91
Gkarmini K, Mahmood S, Ekblad A, Alström HN, Finlay R (2017) Identifying the active microbiome associated with roots and rhizosphere soil of oilseed rape. Appl Environ Microbiol 83:e01938–e01917
Guo Y, Xun Z, Coffman SR, Chen F (2017) The shift of the intestinal microbiome in the innate immunity-deficient mutant rde-1 strain of C. elegans upon Orsay virus infection. Front Microbiol 8:933
Hu Z, Chen X, Chang J, Yu J, Tong Q, Li S, Niu H (2018) Compositional and predicted functional analysis of the gut microbiota of Radix auricularia (Linnaeus) via high-throughput Illumina sequencing. PeerJ 6:e5537
Ilseung C, Blaser MJ (2012) The human microbiome: at the interface of health and disease. Nature 13:260–270
Johnson WR, Torralba M, Fair PA, Bossart GD, Nelson KE, Morris PJ (2009) Novel diversity of bacterial communities associated with bottlenose dolphin upper respiratory tracts. Environ Microbiol Rep 1:555–562
Kay GL, Millard A, Sergeaunt MJ, Midzi N, Gwisai R, Mduluza T, Ivens A et al (2015) Differences in the faecal microbiome in Schistosoma haematobium infected children vs. uninfected children. PLoS Neglected Tropical Diseases 9:e0003861
Leung JM, Graham AL, Knowles SCL (2018) Parasite-microbiota interactions with the vertebrate gut: synthesis through an ecological lens. Front Microbiol 9:843
Llewellyn MS, Leadbeater S, Garcia C, Sylvain F-E, Custodio M, Ang KP, Powell F, Carvalho GR, Creer S, Elliot J, Derome N (2017) Parasitism perturbs the mucosal microbiome of Atlantic Salmon. Sci Rep 7:43465
Lozupone CA, Knight R (2008) Species divergence and the measurement of microbial diversity. Federation of European Microbiological Societies of Microbiology Reviews 32:557–578
Lozupone C, Lladser ME, Knights D, Stombaugh J, Knight R (2011) UniFrac: an effective distance metric for microbial community comparison. The ISME Journal 5:169–172
McMurdy PJ, Holmes S (2013) Phyloseq: an R package for reproducible interactive analysis and graphics of microbiome census data. PLoS ONE 8:e61217
Mergaert J, Lednická D, Goris J, Cnockaert MC, De Vos P, Swings J (2003) Taxonomic study of Cellvibrio strains and description of Cellvibrio ostraviensis sp. nov., Cellvibrio fibrivorans sp. nov. and Cellvibrio gandavensis sp. nov. Int J Evol Microbiol 53:465–471
Morera P (1973) Life history and redescription of Angiostrongylus costaricensis Morera and Céspedes, 1971. The American Society of Tropical Medicine and Hygiene 22:613–621
Mouchka ME, Hewson I, Harvell CD (2010) Coral-associated bacterial assemblages: current knowledge and the potential for climate-driven impacts. Integr Comp Biol 50:662–674
Nakagawa Y, Sakane T, Yokota A (1996) Transfer of “Pseudomonas riboflavina” (Foster 1944), a gram-negative, motile rod with long-chain 3-hydroxy fatty acids, to Devosia riboflavina gen. nov., sp. nov., nom. rev. Int J Syst Bacteriol 46:16–22
Neupane S, Modry D, Pafčo B, Zurek L (2019) Bacterial community of the digestive tract of the European medicinal leech (Hirudo verbana) from the Danube River. Microb Ecol 77:1082–1090
Newton RJ, McLellan SL (2015) A unique assemblage of cosmopolitan freshwater bacteria and higher community diversity differentiate an urbanized estuary from oligotrophic Lake Michigan. Front Microbiol 6:1028
Nobre V, Serufo JC, Carvalho OS, Mendonça CLGF, Santos G, Mota EM, Gomes D et al (2004) Alteration in the endogenous intestinal flora of Swiss Webster mice by experimental Angiostrongylus costaricensis infection. Mem Inst Oswaldo Cruz 99:717–720
O'Sullivan LA, Rinna J, Humphreys G, Weightman AJ, Fry JC (2005) Fluviicola taffensis gen. nov., sp. nov., a novel freshwater bacterium of the family Cryomorphaceae in the phylum ‘Bacteroidetes’. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 55:2189–2194
Pantos O, Bythell JC (2006) Bacterial community structure associated with white band disease in the elkhorn coral Acroporapalmata determined using culture-independent 16S rRNA technique. Dis Aquat Org 69:79–88
Pantos O, Cooney RP, Le Tissier MD, Barer MR, O’Donnell AG, Bythell JC (2003) The bacterial ecology of a plague-like disease affecting the Caribbean coral Montastrea annularis. Environ Microbiol 5:370–382
Paraense WL (2001) The schistosome vectors in the Americas. Mem Inst Oswaldo Cruz 96:7–16
Parks DH, Tyson GW, Hugenholtz P, Beiko RG (2014) STAMP: statistical analysis of taxonomic and functional profiles. Bioinformatics 30:3123–3124
Pindling S, Azulai D, Zheng B, Dahan D, Perron GG (2018) Dysbiosis and early mortality of zebrafish larvae exposed to subclinical concentrations of streptomycin. FEMS Microbiol Lett 365:fny188
Pinheiro GL, Correa RF, Cunha RS, Cardoso AM, Chaia C, Clementino MM, Garcia ES et al (2015) Isolation of aerobic cultivable cellulolytic bacteria from different regions of the gastrointestinal tract of giant land snail Achatina fulica. Front Microbiol 6:860
Portet A, Toulza E, Lokmer A, Huot C, Duval D, Galinier R, Gourbal B (2018) Dysbiosis of the Biomphalaria glabrata vector snail microbiota following infection by Schistosoma parasites. bioRxiv. https://doi.org/10.1101/386623
R Core Team (2013) R: A language and environment for statistical computing. R Foundation for Statistical Computing, Vienna, Austria. URL http://www.R-project.org/
Romalde JL, Barja JL (2010) Bacteria in molluscs: good and bad guys. In: Méndez-Vilas A (ed) Current research, technology and education topics in applied microbiology and microbial biotechnology: microbiology series, vol 1, pp 136–147
Scheiermann J, Klinman DM (2017) Three distinct pneumotypes characterize the microbiome of the lung in BALB/cJ mice. PLoS One 12:e0180561
Schmieder R, Edwards R (2011) Quality control and preprocessing of metagenomic datasets. Bioinformatics 27:863–864
Silva TM, Melo ES, Lopes ACS, Veras DL, Duarte CR, Alves LC, Brayner FA (2013) Characterization of the bacterial microbiota of Biomphalaria glabrata (Say, 1818) (Mollusca: Gastropoda) from Brazil. Lett Appl Microbiol 57:19–25
Steenhard NR, Jungersen G, Kokotovic B, Beshah E, Dawson HD, Urban JF Jr, Roepstorff A, Sm T (2009) Ascaris suum infection negatively affects the response to a Mycoplasma hyopneumoniae vaccination and subsequent challenge infection in pigs. Vaccine 27:5161–5169
Teixeira CG, Thiengo SC, Thome JW, Medeiros AB, Camillo-Coura L, Agostini AA (1993) On the diversity of mollusk intermediate hosts of Angiostrongylus costaricensis Morera & Cespedes, 1971 in southern Brazil. Mem Inst Oswaldo Cruz 88:487–489
Van Horn DJ, Garcia JR, Loker ES, Mitchell KR, Garcia JR, Loker ES, Mitchell KR et al (2012) Complex intestinal bacterial communities in three species of planorbid snails. J Molluscan Stud 78:74–80
Vázquez-Baeza Y, Pirrung M, Gonzalez A, Knight R (2013) EMPeror: a tool for visualizing high-throughput microbial community data. Gigascience 2:16
Wallace GD, Rosen L (1969) Techniques for recovering and identifying larvae of Angiostrongylus cantonensis. Malacologia 7:427–438
Wang Q, Garrity GM, Tiedje JM, Cole JR (2007) Naive Bayesian classifier for rapid assignment of rRNA sequences into the new bacterial taxonomy. Appl Environ Microbiol 73:5261–5267
Wang Q-P, Lai D-H, Zhu X-Q, Chen X-G, Lun Z-R (2008) Human angiostrongyliasis. Lancet Infect Dis 8:621–630
Willcox HP, Coura JR (1989) A new design of the Baermann, Moraes, Coutinho’s technique for the isolation of nematode larva. Memorias do Instituto Oswaldo Cruz 84(4):563–565
Yong HS, Song SL, Chua KO, Lim PE (2017) High diversity of bacterial communities in developmental stages of Bactrocera carambolae (Insecta: Tephritidae) revealed by Illumina MiSeq sequencing of 16S rRNA gene. Curr Microbiol 74:1076–1082
Zaneveld JR, McMinds R, Thurber RV (2017) Stress and stability: applying the Anna Karenina principle to animal microbiomes. Nat Microbiol 2:17121
Zhang M, Sun Y, Liu Y, Qiao F, Chen L, Liu W-T, Du Z, Li E (2015) Response of gut microbiota to salinity change in two euryhaline aquatic animals with reverse salinity preference. Aquaculture 454:72–80
Zhang F, Berg M, Dierking K, Félix MA, Shapira M, Samuel BS, Schulenburg H (2017) Caenorhabditis elegans as a model for microbiome research. Front Microbiol 8:485
Acknowledgments
We thank the High-Performance Computing Lab - LAD/PUCRS for allowing us access to run high-throughput sequence analyses for this study.
Funding
This work was supported by the Conselho Nacional de Pesquisa e Desenvolvimento Tecnológico do Brasil (CNPq)—grant nos. CNPq PQ1D 307005/2014-3 (2014) and 406149/2016-0 (2016).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Section Editor: Charlotte Oskam
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Osório, J.B., de Mattos Pereira, L., Giongo, A. et al. Mollusk microbiota shift during Angiostrongylus cantonensis infection in the freshwater snail Biomphalaria glabrata and the terrestrial slug Phillocaulis soleiformis. Parasitol Res 119, 2495–2503 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00436-020-06743-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00436-020-06743-y