Abstract
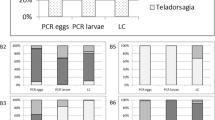
Standard diagnostic methods currently in use for the identification of helminth infections in ruminants are based on the morphological analysis of immature and adult stages of parasites. This paper describes a method for the semiquantitative identification of nematodes, mainly Trichostrongyloidea, at species-level resolution. The method is based on amplification and fragment analysis followed by minisequencing of the ITS-2 region (internal transcribed spacer 2) of the ribosomal DNA of parasite eggs or larvae. This method allows for the identification of seven genera (Chabertia, Cooperia, Haemonchus, Oesophagostomum, Ostertagia, Teladorsagia, and Trichostrongylus) and 12 species (Chabertia ovina, Cooperia curticei, Cooperia punctata, Cooperia oncophora/Cooperia surnabada, Haemonchus contortus, Haemonchus placei, Haemonchus longistipes, Oesophagostomum asperum, Oesophagostomum radiatum, Ostertagia ostertagi, Trichostrongylus axei, and Trichostrongylus colubriformis) of infectious nematodes of domestic ruminants. The concordance between the morphological and molecular analyses in the detection of genera ranged from 0.84 to 0.99, suggesting the proposed detection method is specific, semiquantitative, less laborious, and highly cost-efficient.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ahid SMM, Suassuna ACD, Maia MB, De Mendonça Costa VM, Soares HS (2008) Parasitos gastrintestinais em caprinos e ovinos da região oeste do Rio Grande do Norte, Brasil. Ciênc Anim Bras 9:212–218
Amarante MRV, Santos MC, Bassetto CC, Amarante AFT (2017) PCR primers for straightforward differentiation of Haemonchus contortus, Haemonchus placei and their hybrids. J Helminthol 91:757–761
Araújo RN, Lima WS (2005) Infecções helmínticas em um rebanho leiteiro na região Campo das Vertentes de Minas Gerais. Arq Bras Med Vet Zootec 57:186–193
Avramenko RW, Redman EM, Lewis R, Yazwinski TA, Wasmuth JD, Gilleard JS (2015) Exploring the gastrointestinal “nemabiome”: deep amplicon sequencing to quantify the species composition of parasitic nematode communities. PLoS One 10:1–18
Avramenko RW, Redman EM, Lewis R, Bichuette MA, Palmeira BM, Yazwinski TA, Gilleard JS (2017) The use of nemabiome metabarcoding to explore gastro-intestinal nematode species diversity and anthelmintic treatment effectiveness in beef calves. Int J Parasitol 47:893–902
Avramenko RW, Bras A, Redman EM, Woodbury MR, Wagner B, Shury T, Liccioli S, Windeyer MC, Gilleard JS (2018) Exploring the Gastrointestinal “Nemabiome”: Deep Amplicon Sequencing to Quantify the Species Composition of Parasitic Nematode Communities. Parasit Vectors 11:299 – 311
Benson DA, Clark K, Karsch-Mizrachi I, Lipman DJ, Ostell J, Sayers EW (2014) GenBank. Nucleic Acids Res 42:D32–D37
Blouin MS (2002) Molecular prospecting for cryptic species of nematodes: mitochondrial DNA versus internal transcribed spacer. Int J Parasitol 32:527–531
Bott NJ, Campbell BE, Beveridge I, Chilton NB, Rees D, Hunt PW, Gasser RB (2009) A combined microscopic-molecular method for the diagnosis of strongylid infections in sheep. Int J Parasitol 39:1277–1287
Bouakaze C, Keyser C, De Martino SJ, Sougakoff W, Veziris N, Dabernat H, Ludes B (2010) Identification and genotyping of Mycobacterium tuberculosis complex species by use of a SNaPshot minisequencing-based assay. J Clin Microbiol 48:1758–1766
Brasil BS, Nunes RL, Bastianetto E, Drummond MG, Carvalho DC, Leite RC, Molento MB, Oliveira DA (2012) Genetic diversity patterns of Haemonchus placei and Haemonchus contortus populations isolated from domestic ruminants in Brazil. Int J Parasitol 425:469–479
Carrasco JL, Puig Martinez J (2015) cccrm: concordance correlation coefficient for repeated (and non-repeated) measures. R package version 1.2.1. https://cran.r-project.org/web/packages/cccrm/index.html
Carrasco JL, Phillips BR, Puig-Martinez J, King TS, Chinchilli VM (2013) Estimation of the concordance correlation coefficient for repeated measures using SAS and R. Comput Methods Prog Biomed 109:293–304
Charlier J, Thamsborg SM, Bartley DJ, Skuce PJ, Kenyon F, Geurden T, Hoste H, Williams AR, Sotiraki S, Höglund J, Chartier C, Geldhof P, Van Dijk J, Rinaldi L, Morgan ER, Von Samson-Himmelstjerna G, Vercruysse J, Claerebout E (2018) Mind the gaps in research on the control of gastrointestinal nematodes of farmed ruminants and pigs. Transbound Emerg Dis 65:217–234
Coelho WAC, Ahid SMM, Vieira LS, Fonseca ZAAS, Silva IP (2010) Resistência anti-helmíntica em caprinos no município de Mossoró, RN. Ciênc Anim Bras 11:589–599
Cort WW, Ackert JE, Augustine DL, Payne FK (1922) Investigations on the control of hooworm disease. II. The description of an apparatus for isolating infective hookworm larvae from soil. Am J Hyg 2:1–16
Dalmasso A, Rantsiou K, Cocolin L, Bottero MT (2010) Development of a biomolecular assay for the identification of Listeria at species level. Foodborne Pathog Dis 7:565–571
Dobson RJ, Le Jambre L, Gill JH (1996) Management of anthelmintic resistance: inheritance of resistance and selection with persistent drugs. Int J Parasitol 26:993–1000
Domingues LF, Giglioti R, Feitosa KA, Fantatto RR, Rabelo MD, De Sena Oliveira MC, Bechara GH, Oliveira GP, Braioni Junior W, Souza Chagas AC (2013) In vitro and in vivo evaluation of the activity of pineapple (Ananas comosus) on Haemonchus contortus in Santa Inês sheep. Vet Parasitol 197:263–270
Elmahalawy ST, Halvarsson P, Skarin M, Höglund J (2018) Droplet digital polymerase chain reaction (ddPCR) as a novel method for absolute quantifica of major gastrointestinal nematodes in sheep. Vet Parasitol 261:1–8.
Gasser RB (2006) Molecular tools—advances, opportunities and prospects. Vet Parasitol 136(2):69–89
Gasser RB, Monti JR, Zhu X, Chilton NB, Hung GC, Guldberg P (1997) Polymerase chain reaction-linked single-strand conformation polymorphism of ribosomal DNA to fingerprint parasites. Electrophoresis 18:1564–1566
Gilleard JS (2006) Understanding anthelmintic resistance: the need for genomics and genetics. Int J Parasitol 36:1227–1239
Gordon NM, Withlock HV (1939) A new technique for counting nematode eggs in sheep faeces. J Counc Sci Ind Res 12:50–52
Hansen J, Perry B (1994) The epidemiology, diagnosis and control of helminth parasites of ruminants. International Laboratory on Animal Diseases, Nairobi, pp 83–90
Höglund J, Engström A, Von Samson-Himmelstjerna G, Demeler J, Tydén E (2013) Real-time PCR detection for quantification of infection levels with Ostertagia ostertagi and Cooperia oncophora in cattle faeces. Vet Parasitol 197:251–257
Huang CH, Chang MT, Huang MC, Lee FL (2011) Application of the SNaPshot minisequencing assay to species identification in the Lactobacillus casei group. Mol Cell Probes 25:153–157
Huang CH, Chang MT, Huang MC, Wang LT, Huang L, Lee FL (2012) Discrimination of the Lactobacillus acidophilus group using sequencing, species-specific PCR and SNaPshot mini-sequencing technology based on the recA gene. J Sci Food Agric 92:2703–2708
Kaplan RM (2004) Drug resistance in nematodes of veterinary importance: a status report. Trends Parasitol 20:477–481
Landis JR, Koch GG (1977) The measurement of observer agreement for categorical data. Biometrics 33:159–174
Learmount J, Conyers C, Hird H, Morgan C, Craig BH, Von Samson-Himmelsterna G, Taylor M (2009) Development and validation of real-time PCR methods for diagnosis of Teladorsagia circumcincta and Haemonchus contortus in sheep. Vet Parasitol 166:268–274
Ljungström S, Melville L, Skuce PJ, Höglund J (2018) Comparison of four diagnostic methods for detection and relative quantification of Haemonchus contortus eggs in feces samples. Front Vet Sci 4:1–7
Mukaka MM (2012) A guide to appropriate use of correlation coefficient in medical research. Malawi Med J 24:69–71
Nielsen MK, Peterson DS, Monrad J, Thamsborg SM, Olsen SN, Kaplan RM (2008) Detection and semi-quantification of Strongylus vulgaris DNA in equine faeces by real-time quantitative PCR. Int J Parasitol 38:443–453
Rashid MH, Gebrekidan H, Jabbar A (2018) Multiplexed-tandem PCR (MT-PCR) assay to detect and differentiate gastrointestinal nematodes of alpacas. Parasit Vectors 11:370
RAUE K, Heuer L, BÖHM C, WOLKEN S, EPE C, STRUBE C (2017) 10-year parasitological examination results (2003 to 2012) of faecal samples from horses, ruminants, pigs, dogs, cats, rabbits and hedgehogs. Parasitol Res 116:3315–3330
Reale S, Campanella A, Merigioli A, Pilla F (2008) A novel method for species identification in milk and milk-based products. J Dairy Res 75:107–112
Redman EM, Queiroz C, Bartley DJ, Levy M, Avramenko RW, Gilleard JS (2019) Validation of ITS-2 rDNA nemabiome sequencing for ovine gastrointestinal nematodes and its application to a large scale survey of UK sheep farms. Vet Parasitol 275
Revelle W (2015) Psych: procedures for personality and psychological research. Northwestern University, Evanston http://CRAN.R-project.org/package=psychVersion=1.5.8
Roberts FHS, O'Sullivan PJ (1950) Methods for egg counts and larval cultures for strongyles infesting the gastro-intestinal tract of cattle. Crop Pasture Sci 1:99–102
Roeber F, Jex AR, Campbell AJ, Campbell BE, Anderson GA, Gasser RB (2011) Evaluation and application of a molecular method to assess the composition of strongylid nematode populations in sheep with naturally acquired infections. Infect Genet Evol 11:849–854
Roeber F, Jex AR, Campbell AJ, Nielsen R, Anderson GA, Stanley KK, Gasser RB (2012) Establishment of a robotic, high-throughput platform for the specific diagnosis of gastrointestinal nematode infections in sheep. Int J Parasitol 42:1151–1158
Roeber F, Hassan EB, Skuce P, Morrison A, Claerebout E, Casaert S, Homer DR, Firestone S, Stevenson M, Smith L, Larsen J (2017a) An automated, multiplex-tandem PCR platform for the diagnosis of gastrointestinal nematode infections in cattle: an Australian-European validation study. Vet Parasitol 30:62–75
Roeber F, Morrison A, Casaert S, Smith L, Claerebout E, Skuce P (2017b) Multiplexed-tandem PCR for the specific diagnosis of gastrointestinal nematode infections in sheep: an European validation study. Parasit Vectors 10:226–237
Salgado JA, Santos CP (2016) Overview of anthelmintic resistance of gastrointestinal nematodes of small ruminants in Brazil. Rev Bras Parasitol Vet 25:3–17
Silvestre A, Humbert JF (2000) A molecular tool for species identification and benzimidazole resistance diagnosis in larval communities of small ruminant parasites. Exp Parasitol 95:271–276
Sim J, Wright CC (2005) The kappa statistic in reliability studies: use, interpretation, and sample size requirements. Phys Ther 85:257–268
Stevenson LA, Chilton NB, Gasser RB (1995) Differentiation of Haemonchus placei from H.contortus (Nematoda: Trichostrongylidae) by the ribosomal DNA second internaltranscribed spacer. Int J Parasitol 25:483–488
Sutherland IA, Leathwick DM (2011) Anthelmintic resistance in nematode parasites of cattle: a global issue? Trends Parasitol 27:176–181
Tamura K, Stecher G, Peterson D, Filipski IA, Kumar S (2013) MEGA6: molecular evolutionary genetics analysis version 6.0. Mol Biol Evol 30:2725–2729
Torres-Acosta JFJ, Mendoza-de-Gives P, Aguilar-Caballero AJ, Cuéllar-Ordaz JA (2012) Anthelmintic resistance in sheep farms: update of the situation in the American continent. Vet Parasitol 189:89–96
Ueno H, Gonçalves PC (1998) Manual para diagnóstico da helmintoses de ruminantes, 4th edn. Japan International Cooperation Agency, p 72
Van Wyk JA, Mayhew E (2013) Morphological identification of parasitic nematode infective larvae of small ruminants and cattle: a practical lab guide. Onderstepoort J Vet Res 80:539–553
Van Wyk JA, Cabaret J, Michael L (2004) Morphological identification of nematode larvae of small ruminants and cattle simplified. Vet Parasitol 119:277–306
Várady JA, Cudekova P, Corba J (2007) In vitro detection of benzimidazole resistance in Haemonchus contortus: egg hatch test versus larval development test. Vet Parasitol 149:104–110
Von Samson-Himmelstjerna G (2006) Molecular diagnosis of anthelmintic resistance. Vet Parasitol 136:99–107
Zarlenga DS, Barry Chute M, Gasbarre LC, Boyd PC (2001) A multiplex PCR assay for differentiating economically important gastrointestinal nematodes of cattle. Vet Parasitol 97:201–211
Zhang Z, Schwartz S, Wagner L, Miller W (2000) A greedy algorithm for aligning DNA sequences. J Comput Biol 7:203–214
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to thank Ricardo Land Lomardo, the other farm owners, and Letícia Vidal Cruz for their technical support.
Funding
Financial support for this study was provided by the Brazilian research funding agencies CNPq (National Council for Scientific and Technological Development) (INCT 573899/2008-8), FAPEMIG (Minas Gerais State Research Foundation) (INCT APQ-0084/08), FAPERJ (Rio de Janeiro Research Foundation), and CAPES (Coordination for the Improvement of Higher Education Personnel) (Finance Code 001).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Additional information
Section Editor: Georg von Samson-Himmelstjerna
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Santos, L.L., Salgado, J.A., Drummond, M.G. et al. Molecular method for the semiquantitative identification of gastrointestinal nematodes in domestic ruminants. Parasitol Res 119, 529–543 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00436-019-06569-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00436-019-06569-3