Abstract
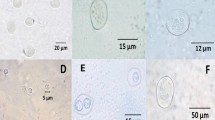
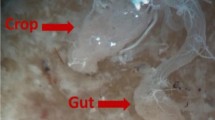
The German cockroach (Blattella germanica) is a common domestic pest, which produces allergens that have been associated with broncho-pulmonary disease. Various protozoan species have been identified in the intestine of this cockroach and it has been hypothesised that these protozoa, or their proteases, may contribute to the burden of cockroach-associated allergens and adjuvants present in domestic dust. The aim of this study was therefore to determine the prevalence of protozoan species in the intestine of Blattella germanica. German cockroaches were anesthetised and dissected and gut contents are used to produce wet slides for microscopy. Both, Giemsa and Papanicolaou stains were used to confirm correct identification of Lophomonas blattarum. Representatives of four genera of protozoa were identified in 110 cockroaches: Nyctoterus sp. was observed in 91.8% of cases, Gregarina sp. in 64.5%, Amoeba sp. in 25.4% and Lophomonas blattarum in 13.6%. Nyctoterus and Gregarina were statistically significantly more likely to be found in diseased cockroaches compared to Amoeba or Lophomonas. The prevalence of Lophomonas blattarum was similar to that in published studies of a different species of cockroach, Periplaneta americana. Further work is needed to assess the interplay between protozoa, cockroaches and broncho-pulmonary diseases.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alam-Eldin YH, Abdulaziz AM (2015) Identification criteria of the rare multi-flagellate Lophomonas blattarum: comparison of different staining techniques. Parasitol Res 114:3309–3314
Armer JM (1944) Influence of the diet of blattidae on some of their intestinal protozoa. J Parasitol 30:131–142
Beams HW, Sekhon SS (1969) Further studies on the fine structure of Lophomonas blattarum with special reference to the so-called calyx, axial filament, and parabasal body. J Ultrastruct Res 26:296–315
Cazorla Perfetti D, Morales P, Navas P (2015) Isolation of intestinal parasites from American cockroach (Periplaneta americana) in Coro, Falcon state, Venezuela. Bol Mal Salud Amb 55:184–193 [Article in Spanish]
Chamavit P, Sahaisook P, Niamnuy N (2011) The majority of cockroaches from the Samutprakarn province of Thailand are carriers of parasitic organisms. EXCLI J 10:218–222
Chinchilla M, Guerrero OM, Castro A, Sabah J (1994) Cockroaches as transport hosts of the protozoan Toxoplasma gondii. Rev Biol Trop 42:329–331
Clopton RE, Gold RE (1996) Host specificity of Gregarina blattarum von Siebold, 1938 (Apicomplexa: Eugregarinida) among five species of domiciliary cockroaches. J Invertebr Pathol 67:219–223
Day SB, Ledford JR, Zhou P, Lewkowich IP, Page K (2012) German cockroach proteases and protease-activated receptor-2 regulate chemokine production and dendritic cell recruitment. J Innate Immun 4:100–110
De Coursey JD, Otto JS (1956) Endamoeba histolytica and certain other protozoan organisms found in cockroaches in Cairo, Egypt. J NY Entomol Soc 64:157–163
Do DC, Zhao Y, Gao P (2016) Cockroach allergen exposure and risk of asthma. Allergy 71:463–474
Elgderi RM, Ghenghesh KS, Berbash N (2006) Carriage by the German cockroach (Blattella germanica) of multiple-antibiotic-resistant bacteria that are potentially pathogenic to humans, in hospitals and households in Tripoli, Libya. Ann Trop Med Parasitol 100:55–62
El-Sherbini GT, Gneidy MR (2012) Cockroaches and flies in mechanical transmission of medical important parasites in Khaldyia Village, El-Fayoum, Governorate, Egypt. J Egypt Soc Parasitol 42:165–174
Fakoorziba MR, Eghbal F, Hassanzadeh J, Moemenbellah-Fard MD (2010) Cockroaches (Periplaneta americana and Blattella germanica) as potential vectors of the pathogenic bacteria found in nosocomial infections. Ann Trop Med Parasitol 104:521–528
Fotedar R, Shriniwas UB, Verma A (1991) Cockroaches (Blattella germanica) as carriers of microorganisms of medical importance in hospitals. Epidemiol Infect 107:181–187
Gijzen HJ, Barugahare M (1992) Contribution of anaerobic protozoa and methanogens to hindgut metabolic activities of the American cockroach, Periplaneta americana. Appl Environ Microbiol 58:2565–2570
Graczyk TK, Knight R, Tamang L (2005) Mechanical transmission of human protozoan parasites by insects. Clin Microbiol Rev 18:128–132
Hamu H, Debalke S, Zemene E, Birlie B, Mekonnen Z, Yewhalaw D (2014) Isolation of intestinal parasites of public health importance from cockroaches (Blattella germanica) in Jimma Town, Southwestern Ethiopia. J Parasitol Res 2014:186240. https://doi.org/10.1155/2014/186240
Hoyte HMD (1961) The protozoa occurring in the hind-gut of cockroaches (I). Response to changes in environment. Parasitology 51:415–436
Isaac C, Orue PO, Iyamu MI, Ehiaghe JI, Isaac O (2014) Comparative analysis of pathogenic organisms in cockroaches from different community settings in Edo State, Nigeria. Korean J Parasitol 52:177–1781
Kessel RG, Beams HW (1990) Freeze fracture and scanning electron microscope studies on the nuclear envelope and perinuclear cytomembranes (parabasal apparatus) in the protozoan, Lophomonas blattarum. J Submicrosc Cytol Pathol 22:367–378
Kudo R (1926) Observations on Lophomonas blattarum, a flagellate inhabiting the colon of the cockroach Blatta orientalis. Arch Protistenkd 53:191–214
Li R, Gao ZC (2016) Lophomonas blattarum infection or just the movement of ciliated epithelial cells? Chin Med J 129:739–742
Lopes RB, Alves SB (2005) Effect of Gregarina sp. parasitism on the susceptibility of Blattella germanica to some control agents. J Invertebr Pathol 88:261–264
Martínez-Girón R, Doganci L (2010) Lophomonas blattarum: a bronchopulmonary pathogen. Acta Cytol 54:1050–1051
Martínez-Girón R, Ribas A (2006) Asthma, cockroaches, and protozoal forms: chance or not chance? Ann Allergy Asthma Immunol 97:818–819
Martinez-Girón R, van Woerden HC (2013) Lophomonas blattarum and bronchopulmonary disease. J Med Microbiol 62:1641–1648
Martínez-Girón R, van Woerden HC (2014a) Bronchopulmonary lophomoniasis: emerging disease or unsubstantiated legend? Parasit Vectors 7:284
Martínez-Girón R, van Woerden HC (2014b) The burden of Lophomonas blattarum under the light microscope. J Thorac Dis 6:E191–E192
Martínez-Girón R, van Woerden HC (2015) On cilia, flagella, and pulmonary pseudoprotozoa. Korean J Parasitol 53:247
Martínez-Girón R, Van Woerden HC (2017) Challenges in differentiating cilia and protozoal flagella. Lung India 34:306
Martínez-Girón R, Ribas A, Astudillo-González A (2007) Flagellated protozoa in cockroaches and sputum: the unhygienic connection? Allergy Asthma Proc 28:608–609
McKerrow JH, Sun E, Rosenthal PJ, Bouvier J (1993) The proteases and pathogenicity of parasitic protozoa. Annu Rev Microbiol 47:821–853
Menasria T, Moussa F, El-Hamza S, Tine S, Megri R, Chenchouni H (2014) Bacterial load of German cockroach (Blattella germanica) found in hospital environment. Pathog Glob Health 108:141–147
Nasirian H (2017) Infestation of cockroaches (Insecta: Blattaria) in the human dwelling environments: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Acta Trop 167:86–98
Oliva GR, Díaz C, Fuentes González O, Martínez MD, Fernández C, Cordoví R, Lago PM, Herrera N (2010) Blattella germanica as a possible cockroach vector of micro-organisms in a hospital. J Hosp Infect 74:93–95
Page K, Ledford JR, Zhou P, Dienger K, Wills-Karp M (2010) Mucosal sensitization to German cockroach involves protease-activated receptor-2. Respir Res 11:62. https://doi.org/10.1186/1465-9921-11-62
Pai HH, Ko YC, Chen ER (2003) Cockroaches (Periplaneta americana and Blattella germánica) as potential mechanical disseminators of Entamoeba histolytica. Acta Trop 87:355–359
Pai HH, Chen WC, Peng CF (2005) Isolation of bacteria with antibiotic resistance from household cockroaches (Periplaneta americana and Blattella germanica). Acta Trop 93:259–265
Poinar GO Jr (2009) Early Cretaceous protist flagellates (Parabasalia: Hypermastigia: Oxymonada) of cockroaches (Insecta: Blattaria) in Burmese amber. Cretac Res 30:1066–1072
Rabito FA, Carlson J, Holt EW, Iqbal S, James MA (2011) Cockroach exposure independent of sensitization status and association with hospitalizations for asthma in inner-city children. Ann Allergy Asthma Immunol 106:103–109
Rina S, Melva P, Geminis V (2015) Primer hallazgo de Lophomonas spp. (Metamonada, Lophomonadida) en la cucaracha doméstica (Periplaneta americana Linnaeus) en Panamá. Rev Arg Parasitol 3:16–21 [Article in Spanish]
Salehzadeh A, Tavacol P, Mahjub H (2007) Bacterial, fungal and parasitic contamination of cockroaches in public hospitals of Hamadan, Iran. J Vector Borne Dis 44:105–110
Schuster EHJ (1898) On a new flagellate protozoon of the genus Lophomonas. Proc Zool Soc London 1898:242–246
Smith DD, Frenkel JK (1978) Cockroaches as vectors of Sarcocystis muris and of other coccidia in the laboratory. J Parasitol 64:315–319
Sohn MH, Kim KE (2012) The cockroach and allergic diseases. Allergy Asthma Immunol Res 4:264–269
Strand MA, Brooks MA (1977) Pathogens of Blattidae (cockroaches). Bull World Health Organ 55:289–286
Tatfeng YM, Usuanlele MU, Orukpe A, Digban AK, Okodua M, Oviasogie F, Turay AA (2005) Mechanical transmission of pathogenic organisms: the role of cockroaches. J Vector Borne Dis 42:129–134
Tsai YH, Cahill KM (1970) Parasites of the German cockroach (Blattella germánica L.) in New York City. J Parasitol 56:375–377
van Woerden HC, Martinez-Giron R (2017) Lophomonas blattarum: is it only its morphology that prevents its recognition? Chin Med J 130:117
Yahaya ZS, Izzaudin NAI, Razak AFA (2017) Parasitic Gregarine blattarum found infecting American cockroaches, Periplaneta Americana, in a population in Pulau Pinang, Malaysia. Trop Life Sci Res 28:145–149
Yang JX, Tang YY, Fang ZM, Tong ZZ, Li YL, Wang T (2014) Investigation on Lophomonas blattarum infection in Periplaneta americana in Wuhan City. Zhongguo Ji Sheng Chong Xue Yu Ji Sheng Chong Bing Za Zhi 32:161–162 [Article in Chinese]
Zerpa R, Ore E, Patiño L, Espinoza YA (2010) Lophomonas sp. in respiratory tract secretions in hospitalized children with severe lung disease. Rev Peru Med Exp Salud Pública 27:575–577 [Article in Spanish]
Acknowledgments
The authors wish to thank Prof. José Rafael González for his technical assistance in the recognition and dissection of specimens.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Martínez-Girón, R., Martínez-Torre, C. & van Woerden, H.C. The prevalence of protozoa in the gut of German cockroaches (Blattella germanica) with special reference to Lophomonas blattarum . Parasitol Res 116, 3205–3210 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00436-017-5640-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00436-017-5640-6