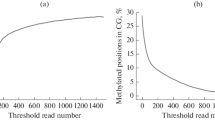
Abstract
To date, little is known about cytosine methylation in the genomic DNA of apicomplexan parasites, although it has been confirmed that this important epigenetic modification exists in many lower eukaryotes, plants, and animals. In the present study, ELISA-based detection demonstrated that low levels of 5-methylcytosine (5-mC) are present in Eimeria spp., Toxoplasma gondii, Cryptosporidium spp., and Neospora caninum. The proportions of 5-mC in genomic DNA were 0.18 ± 0.02% in E tenella sporulated oocysts, 0.19 ± 0.01% in E. tenella second-generation merozoites, 0.22 ± 0.04% in T. gondii tachyzoites, 0.28 ± 0.03% in N. caninum tachyzoites, and 0.06 ± 0.01, 0.11 ± 0.01, and 0.09 ± 0.01% in C. andersoni, C. baileyi, and C. parvum sporulated oocysts, respectively. In addition, we found that the percentages of 5-mC in E. tenella varied considerably at different life stages, with sporozoites having the highest percentage of 5-mC (0.78 ± 0.10%). Similar stage differences in 5-mC were also found in E. maxima, E. necatrix, and E. acervulina, the levels of 5-mC in their sporozoites being 4.3-, 1.8-, 2.5-, and 2.0-fold higher than that of sporulated oocysts, respectively (p < 0.01). Furthermore, a total DNA methyltransferase-like activity was detected in whole cell extracts prepared from E. tenella sporozoites. In conclusion, genomic DNA methylation is present in these apicomplexan parasites and may play a role in the stage conversion of Eimeria.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Blake DP, Smith AL, Shirley MW (2003) Amplified fragment length polymorphism analyses of Eimeria spp.: an improved process for genetic studies of recombinant parasites. Parasitol Res 90:473–475
Bollati V, Schwartz J, Wright R, Litonjua A, Tarantini L, Suh H, Sparrow D, Vokonas P, Baccarelli A (2009) Decline in genomic DNA methylation through aging in a cohort of elderly subjects. Mech Ageing Dev 130:234–239
Braun R, Shirley MW (1995) Eimeria species and strains of chicken. In: Eckert J, Braun R, Shirley MW, Coudert P (eds) Guidelines on techniques in coccidiosis research. European Commission, Luxemburg, pp 146–147
Capuano F, Mulleder M, Kok R, Blom HJ, Ralser M (2014) Cytosine DNA methylation is found in Drosophila melanogaster but absent in Saccharomyces cerevisiae, Schizosaccharomyces pombe, and other yeast species. Anal Chem 86:3697–3702
Choi SW, Keyes MK, Horrocks P (2006) LC/ESI-MS demonstrates the absence of 5-methyl-2′-deoxycytosine in Plasmodium falciparum genomic DNA. Mol Biochem Parasitol 150:350–352
Feng S, Cokus SJ, Zhang X, Chen PY, Bostick M, Goll MG, Hetzel J, Jain J, Strauss SH, Halpern ME, Ukomadu C, Sadler KC, Pradhan S, Pellegrini M, Jacobsen SE (2010) Conservation and divergence of methylation patterning in plants and animals. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 107:8689–8694
Field LM, Lyko F, Mandrioli M, Prantera G (2004) DNA methylation in insects. Insect Mol Biol 13:109–115
Fisher O, Siman-Tov R, Ankri S (2004) Characterization of cytosine methylated regions and 5-cytosine DNA methyltransferase (Ehmeth) in the protozoan parasite Entamoeba histolytica. Nucleic Acids Res 32:287–297
Fisher O, Siman-Tov R, Ankri S (2006) Pleiotropic phenotype in Entamoeba histolytica overexpressing DNA methyltransferase (Ehmeth). Mol Biochem Parasitol 147:48–54
Gao F, Liu X, Wu XP, Wang XL, Gong D, Lu H, Xia Y, Song Y, Wang J, Du J, Liu S, Han X, Tang Y, Yang H, Jin Q, Zhang X, Liu M (2012) Differential DNA methylation in discrete developmental stages of the parasitic nematode Trichinella spiralis. Genome Biol 13:R100–R113
Geyer KK, Chalmers IW, Mackintosh N, Hirst JE, Geoghegan R, Badets M, Brophy PM, Brehm K, Hoffmann KF (2013) Cytosine methylation is a conserved epigenetic feature found throughout the phylum Platyhelminthes. BMC Genomics 14:462–475
Geyer KK, Rodriguez Lopez CM, Chalmers IW, Munshi SE, Truscott M, Heald J, Wilkinson MJ, Hoffmann KF (2011) Cytosine methylation regulates oviposition in the pathogenic blood fluke Schistosoma mansoni. Nat Commun 2:424–434
Gissot M, Choi SW, Thompson RF, Greally JM, Kim K (2008) Toxoplasma gondii and Cryptosporidium parvum lack detectable DNA cytosine methylation. Eukaryot Cell 7:537–540
Gissot M, Kelly KA, Ajioka JW, Greally JM, Kim K (2007) Epigenomic modifications predict active promoters and gene structure in Toxoplasma gondii. PLoS Pathog 3:e77. doi:10.1371/journal.ppat.0030077
Glastad KM, Hunt BG, Yi SV, Goodisman MA (2011) DNA methylation in insects: on the brink of the epigenomic era. Insect Mol Biol 20:553–565
Goll MG, Bestor TH (2005) Eukaryotic cytosine methyltransferases. Annu Rev Biochem 74:481–514
Gowher H, Ehrlich KC, Jeltsch A (2001) DNA from Aspergillus flavus contains 5-methylcytosine. FEMS Microbiol Lett 205:151–155
Hahn MA, Pfeifer GP (2010) Methods for genome-wide analysis of DNA methylation in intestinal tumors. Mutat Res 693:77–83
Hakimi MA, Deitsch KW (2007) Epigenetics in Apicomplexa: control of gene expression during cell cycle progression, differentiation and antigenic variation. Curr Opin Microbiol 10:357–362
Hu CW, Chen JL, Hsu YW, Yen CC, Chao MR (2015) Trace analysis of methylated and hydroxymethylated cytosines in DNA by isotope-dilution LC-MS/MS: first evidence of DNA methylation in Caenorhabditis elegans. Biochem J 465:39–47
Jaenisch R, Bird A (2003) Epigenetic regulation of gene expression: how the genome integrates intrinsic and environmental signals. Nat Genet 33(Suppl):245–254
Katrib M, Ikin RJ, Brossier F, Robinson M, Slapetova I, Sharman PA, Walker RA, Belli SI, Tomley FM, Smith NC (2012) Stage-specific expression of protease genes in the apicomplexan parasite, Eimeria tenella. BMC Genomics 13:685–703
Lee TF, Zhai J, Meyers BC (2010) Conservation and divergence in eukaryotic DNA methylation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 107:9027–9028
Liu SY, Lin JQ, Wu HL, Wang CC, Huang SJ, Luo YF, Sun JH, Zhou JX, Yan SJ, He JG, Wang J, He ZM (2012) Bisulfite sequencing reveals that Aspergillus flavus holds a hollow in DNA methylation. PLoS One 7:e30349. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0030349
Lou J, Wang Y, Yao C, Jin L, Wang X, Xiao Y, Wu N, Song P, Song Y, Tan Y, Gao M, Liu K, Zhang X (2013) Role of DNA methylation in cell cycle arrest induced by Cr (VI) in two cell lines. PLoS One 8:e71031. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0071031
Militello KT, Wang P, Jayakar SK, Pietrasik RL, Dupont CD, Dodd K, King AM, Valenti PR (2008) African trypanosomes contain 5-methylcytosine in nuclear DNA. Eukaryot Cell 7(11):2012–2016
Motohashi K (2015) A simple and efficient seamless DNA cloning method using SLiCE from Escherichia coli laboratory strains and its application to SLiP site-directed mutagenesis. BMC Biotechnol 15:47–56
Osabe K, Clement JD, Bedon F, Pettolino FA, Ziolkowski L, Llewellyn DJ, Finnegan EJ, Wilson IW (2014) Genetic and DNA methylation changes in cotton (Gossypium) genotypes and tissues. PLoS One 9:e86049. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0086049
Padmanabhan N, Jia D, Geary-Joo C, Wu X, Ferguson-Smith AC, Fung E, Bieda MC, Snyder FF, Gravel RA, Cross JC, Watson ED (2013) Mutation in folate metabolism causes epigenetic instability and transgenerational effects on development. Cell 155:81–93
Pegoraro M, Bafna A, Davies NJ, Shuker DM, Tauber E (2016) DNA methylation changes induced by long and short photoperiods in Nasonia. Genome Res 26:203–210
Ponts N, Fu L, Harris EY, Zhang J, Chung DW, Cervantes MC, Prudhomme J, Atanasova-Penichon V, Zehraoui E, Bunnik EM, Rodrigues EM, Lonardi S, Hicks GR, Wang Y, Le Roch KG (2013) Genome-wide mapping of DNA methylation in the human malaria parasite Plasmodium falciparum. Cell Host Microbe 14:696–706
Raddatz G, Guzzardo PM, Olova N, Fantappie MR, Rampp M, Schaefer M, Reik W, Hannon GJ, Lyko F (2013) Dnmt2-dependent methylomes lack defined DNA methylation patterns. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 110:8627–8631
Schulz EC, Roth HM, Ankri S, Ficner R (2012) Structure analysis of Entamoeba histolytica DNMT2 (EhMeth). PLoS One 7:e38728. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0038728
Shirley MW (1995) Eimeria species and strains of chicken. In: Eckert J, Braun R, Shirley MW, Coudert P (eds) Guidelines on techniques in coccidiosis research. European Commission, Luxemburg, pp 1–24
Simpson VJ, Johnson TE, Hammen RF (1986) Caenorhabditis elegans DNA does not contain 5-methylcytosine at any time during development or aging. Nucleic Acids Res 14:6711–6719
Suzuki MM, Bird A (2008) DNA methylation landscapes: provocative insights from epigenomics. Nat Rev Genet 9:465–476
Takayama S, Dhahbi J, Roberts A, Mao G, Heo SJ, Pachter L, Martin DI, Boffelli D (2014) Genome methylation in D. melanogaster is found at specific short motifs and is independent of DNMT2 activity. Genome Res 24:821–830
Tang Y, Gao XD, Wang Y, Yuan BF, Feng YQ (2012) Widespread existence of cytosine methylation in yeast DNA measured by gas chromatography/mass spectrometry. Anal Chem 84:7249–7255
Tomley F (1997) Techniques for isolation and characterization of apical organelles from Eimeria tenella sporozoites. Methods 13:171–176
Xie M, Gilbert JM, McDougald LR (1992) Electrophoretic and immunologic characterization of proteins of merozoites of Eimeria acervulina, E. maxima, E. necatrix, and E. tenella. J Parasitol 78:82–86
Yi S (2012) Birds do it, bees do it, worms and ciliates do it too: DNA methylation from unexpected corners of the tree of life. Genome Biol 13:174–176
Zhao X, Duszynski DW, Loker ES (2001) A simple method of DNA extraction for Eimeria species. J Microbiol Methods 44:131–137
Acknowledgements
This research was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (NSFC Grant No. 31272554) and the Agricultural Science and Technology Innovation Program (CAAS-ASTIP-2014-LVRI-09) to JPC. Authors are also indebted to Prof. Xingquan Zhu, Longxian Zhang, and Qun Liu for kindly providing the T. gondii, Cryptosporidium spp., and N. caninum genomic DNA.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
ZXG, HY, and XTM performed the experiments. BHL and ZLH analyzed the data. LQG contributed the reagents/materials. ZXG and HY wrote the paper. JPC designed the experiments and revised the manuscript. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Availability of data and materials
The dataset supporting the conclusions of this article is included within the article.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gong, Z., Yin, H., Ma, X. et al. Widespread 5-methylcytosine in the genomes of avian Coccidia and other apicomplexan parasites detected by an ELISA-based method. Parasitol Res 116, 1573–1579 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00436-017-5434-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00436-017-5434-x