Abstract
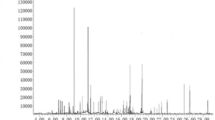
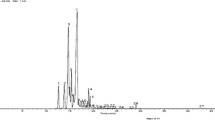
For control of Aedes aegypti, the main vector of dengue, botanical insecticides can be a viable alternative. Herein, we evaluated the chemical composition and insecticidal activity of the essential oils of the leaves of Croton tetradenius on Ae. aegypti larvae and adults. We also evaluated the acute toxicity in Mus musculus. The essential oil chemical analysis was performed using chromatography coupled with mass spectrometry and flame ionization detection. Female mice were used for assessing toxicity according to the Organization for Economic Cooperation and Development’s Test Guideline 423/2001. Doses administered to mice orally and intraperitoneally were 5, 50, 300, and 2000 mg kg−1. There was a greater toxic effect on larvae (LC50 = 0.152 mg mL−1 and LC90 = 0.297 mg mL−1) and on adults (LC50 = 1.842 mg mL−1 and LC90 = 3.156 mg mL−1) of Ae. aegypti after 24 h of exposure, when compared to other periods of exposure. Chemical analysis revealed 26 components, with camphor (25.49 %) as the major component. The acute toxicity via the intraperitoneal route identified an LD50 = 200 mg kg−1 and by the oral route an LD50 = 500 mg kg−1. Thus, the essential oil of C. tetradenius presents insecticidal potential for Ae. aegypti and has high safety threshold at the concentrations evaluated in this study.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adams RP (2007) Identification of essential oil components by gas chromatography/quadrupole mass spectrometry. Allured Publishing, United States of America, Illions
Braga IA, Valle D (2007) Aedes aegypti: inseticidas, mecanismos de ação e resistência. Epidemiol Serv Saúde 16:279–293. doi:10.5123/S1679-49742007000400006
Brunton LL, Chabner BA, Knollmann BC (2012) As Bases Farmacológicas da Terapêutica de Goodman & Gilman-12. McGraw Hill, Brasil
Burkhard PR, Burkhardt K, Haenggeli CA, Landis T (1999) Plant-induced seizures: reappearance of an old problem. J Neurol 246:667–670. doi:10.1007/s004150050429
Ceccarelli I, Lariviere WR, Fiorenzani P, Sacerdote P, Aloisi AM (2004) Effects of long-term exposure of lemon essential oil odor on behavioral, hormonal and neuronal parameters in male and female rats. Brain Res 1001:78–86. doi:10.1016/j.brainres.2003.10.063
De Lima GPG, De Souza TM, Freire GP, Farias DF, Cunha AP, Ricardo NMPS, De Morais SM, Carvalho AFU (2013) Further insecticidal activities of essential oils from Lippia sidoides and Croton species against Aedes aegypti L. Parasitol Res 112:1953–1958. doi:10.1007/s00436-013-3351-1
Dias CN, Moraes DFC (2014) Essential oils and their compounds as Aedes aegypti L. (Diptera: Culicidae) larvicides: review. Parasitol Res 113:565–592. doi:10.1007/s00436-013-3687-6
Globally Harmonized System of Classification and Labelling of Chemicals (GHS), (2011). Fourth edition revised, United Nations: New York and Geneva. http://www.unece.org/fileadmin/DAM/trans/danger/publi/ghs/ghs_rev04/English/ST-SG-AC10-30-Rev4e.pdf. Acessado 10 julho 2015.
Hold KM, Sirisoma NS, Ikeda T, Narahashi T, Casida JE (2000) Thujone (the active component of absinthe): γ-aminobutyric acid type A receptor modulation and metabolic detoxification. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 97:3826–3831. doi:10.1073/pnas.070042397
Horta MAP, Castro FI, Rosa CS, Daniel MC, Melo AL (2011) Resistance of Aedes aegypti (L.) (Diptera: Culicidae) to Temephos in Brazil: a revision and new data for Minas Gerais state. Bio Assay 6:1–6. doi:10.14295/BA.v6.0.103
López MD, Pascual-Villalobos MJ (2008) Mode of inhibition of acetylcholinesterase by monoterpenoids and implications for pest control. Ind Crop Prod 31:284–288. doi:10.1016/j.indcrop.2009.11.005
Macedo ITF, Bevilaqua CML, Oliveira LMB, Camurça-Vasconcelos VLS (2010) Anthelmintic effect of Eucalyptus staigeriana oil against goat gastrointestinal nematodes. Vet Parasitol 173:93–98. doi:10.1016/j.vetpar.2010.06.004
Machado WJ, Prata APN, Mello AA (2012) Floristic composition in areas of Caatinga and Brejo de Altitude in Sergipe state, Brazil. J species lists and distribution 8:1089–1101
Mariz SR, Borges ACR, Melo-Diniz MFF, Medeiros IA (2010) Possibilidades terapêuticas e risco toxicológico de Jatropha gossypiifolia L.: uma revisão narrativa. Rev Bras Plantas Med 12(3):346–357. doi:10.1590/S1516-05722010000300013
Morais SM, Cavalcanti ESB, Bertini LM, Oliveira CLL, Rodrigues JR, Cardoso JH (2006) Larvicidal activity of essential oils from Brazilian Croton species against Aedes aegypti L. J Am Mosq Control Assoc 22:161–164. doi:10.2987/8756-971X(2006)22[161:LAOEOF]2.0.CO;2
Niculau ES, Alves PB, Nogeira PC, Moraes VRS, Matos AP, Bernardo AR, Volante AC, Fernandes JB, Silva MFGF, Correa AG (2013) Insecticidal activity of essential oils of Pelargonium graveolens l’Herit and Lippia alba (Mill) NE Brown against Spodoptera frugiperda (JE Smith). Quim Nov. 36:1391–1394. doi:10.1590/S0100-40422013000900020
NIST08/EPA/NIH (2008) Mass Spectral Library with Search Program
Oliveira ACB, Oliveira AP, Guimarães AL, Oliveira RA, Silva FS, Reis SAGB, Ribeiro LAA, Almeida JRGS (2013) Avaliação toxicológica pré-clínica do chá das folhas de Morus nigra L. (Moraceae). Rev Bras Plantas Med 15:244–249. doi:10.1590/S1516-05722013000200012
Oliveira GP, Silva SLCE, Gualberto SA, Cruz RCD, Carvalho KS (2014) Atividade larvicida do extrato etanólico da raiz de Croton linearifolius sobre Aedes aegypti. Enciclop Biosfera 10:442–448
Organisation for Economic Cooperation and Development (OECD) (2001) Guidelines for the testing of chemicals, OECD 423, Acute oral toxicity-acute toxic class method. Organisation for Economic Cooperation and Development, Paris
Ramos CAF, Sá RCS, Alves MF, Benedito RB, Sousa DP, Diniz MF, Araújo MS, Almeida R (2015) Histopathological and biochemical assessment of d-limonene-induced liver injury in rats. Toxicol Rep 2:482–488. doi:10.1016/j.toxrep.2015.01.001
Salatino A, Salatino MLF, Negri G (2007) Traditional uses, chemistry and pharmacology of Croton species (Euphorbiaceae). J Brazil Chem Soc 18:11–33. doi:10.1590/S0103-50532007000100002
Santos AS, Alves SDM, Figueiredo FJC, Da Rocha Neto OG (2004) Descrição de sistema e de métodos de extração de óleos essenciais e determinação de umidade de biomassa em laboratório. Embrapa Amazônia Oriental. Comunicado técnico 1-6.
Santos GKN, Dutra KA, Lira CS, Lima BN, Napoleão TH, Paiva PMG, Maranhão CA, Brandão SF, Navarro DMAF (2014) Effects of Croton rhamnifolioides essential oil on Aedes aegypti oviposition, larval toxicity and trypsin activity. Molecules 19:16573–16587. doi:10.3390/molecules191016573
Shah W, Jadhav NR, Pimpliskar M, Vaidya V (2015) Evaluation of acute toxicity effect of Smilax glabra extract on white albino rats. J Advanc Sci Res 6:45–47
Silva JS, Sales MF, Gomes AP, Carneiro-Torres DS (2010) Sinopse das espécies de Croton L. (Euphorbiaceae) no estado de Pernambuco, Brasil. Acta Bot Bras 24:441–453. doi:10.1590/S0102-33062010000200015
Silva SLCE, Gualberto AS, Carvalho KS, Fries DD (2014) Avaliação da atividade larvicida de extratos obtidos do caule de Croton linearifolius Mull. Arg. (Euphorbiaceae) sobre larvas de Aedes aegypti (Linnaeus, 1762) (Diptera: Culicidae). Rev Biotemas 27:79–85. doi:10.5007/2175-7925.2014v27n2p79
Silva SLCE, Gualberto SA, Macedo GEL, Silveira CT, Silva DC (2012) Plantas medicinais usadas pela comunidade do povoado de laços (Tanhaçú/Bahia) e encontradas na Floresta Nacional Contendas do Sincorá. Rev Caatinga 5:130–136
Tariku Y, Hymete A, Hailu A, Rohloff J (2010) Constituents, antileishmanial activity and toxicity profile of volatile oil from berries of Croton macrostachyus. Nat Prod Commun 5:975–980
Tisserand R, Young R (2013) Essential oil safety: a guide for health care professionals. Elsevier Health Sciences, China
Torres MC, Assunção JC, Santiago GMP, Andrade-Neto M, Silveira ER, Costa-Lotufo LV (2008) Larvicidal and nematicidal activities of the leaf essential oil of Croton regelianus. Chem Biodivers 8:2724–2728. doi:10.1002/cbdv.200890227
Veiga MM, Silva DM, Veiga LBE, Faria MVC (2006) Análise da contaminação dos sistemas hídricos por agrotóxicos numa pequena comunidade rural do Sudeste do Brasil. Cad Saude Publica 22:2391–2399. doi:10.1590/S0102-311X2006001100013
Wang K, Li Z, Chen Y, Su C (2005) The pharmacokinetics of a novel anti-tumor agent, β-elemene, in Sprague-Dawley rats. Biopharm Drug Dispos 26:301–307. doi:10.1002/bdd.463
World Health Organization (WHO) (2012). Global strategy for dengue prevention and control. http://www.who.int/denguecontrol/9789241504034/en/>. Accessed 2014 jun. 13.
Zhu L, Tian Y (2012) Chemical composition and larvicidal activity of essential oil of Artemisia gilvescens against Anopheles anthropophagus. Parasitol Res 112:1137–1142. doi:10.1007/s00436-012-3243-9
Zuccarini P (2009) Camphor: risks and benefits of a widely used natural product. J Appl Sci Environ Manag 13:69–74. doi:10.4314/jasem.v13i2.55317
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to appreciate Fundação de Amparo à Pesquisa do Estado da Bahia for funding (Grant n° PET 0003/2013) and Mr. Antonio Correia Freire, who helped in the field activities. In addition, we thank the Fundação Carlos Chagas Filho de Amparo a Pesquisa do State Rio de Janeiro for providing financing.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Carvalho, K.d.S., e Silva, S.L.d.C., de Souza, I.A. et al. Toxicological evaluation of essential oil from the leaves of Croton tetradenius (Euphorbiaceae) on Aedes aegypti and Mus musculus . Parasitol Res 115, 3441–3448 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00436-016-5106-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00436-016-5106-2