Abstract
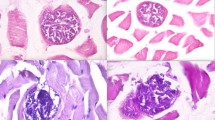
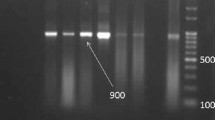
Cattle are common intermediate hosts of Sarcocystis, and the prevalence in adult bovine muscle is close to 100 % in most regions of the world. Three Sarcocystis spp. are known to infect cattle as intermediate hosts, namely, S. cruzi, S. hirsuta, and S. hominis. The aim of the present study was the molecular identification and differentiation of these three species, Neospora caninum and Besnoitia by PCR and RFLP methods. Tissue samples were obtained from diaphragmatic muscle of 101 cattle slaughtered in Shiraz, Fars Province, Iran, for both smear preparation and DNA extraction. The samples were digested by Pepsin, washed three times with PBS solution before taking smears, fixed in absolute methanol and stained with 10 % Giemsa. The slides were examined microscopically for Sarcocystis bradyzoites and DNA was extracted from 100 mg of Sarcocystis-infected meat samples. Since the primers also bind to 18S rRNA gene of some tissue cyst-forming coccidian protozoa, DNA was also extracted from 100 μl of tachyzoite-containing suspension of N. caninum and Besnoitia isolated from goat to compare RFLP pattern. Polymerase chain reaction (PCR) was performed on DNA of samples which were microscopically positive for Sarcocystis. Five restriction enzymes Dra1, EcoRV, RsaI, AvaI, and SspI were used for RFLP and DNA of one sample from protozoa was sequenced. Based on the RFLP results, 87 (98.9 %) DNA samples were cut with DraI, indicating infection by S. cruzi. One sample (1.1 %) of PCR products of infected samples was cut only with EcoRV which showed S. hominis infection. Forty-eight samples (53.3 %) of PCR products were cut with both DraI, EcoRV, or with DraI, EcoRV, and RsaI while none of them was cut with SspI, which shows the mixed infection of both S. cruzi and S. hominis and no infection with S. hirsuta. It seems by utilizing these restriction enzymes, RLFP could be a suitable method not only for identification of Sarcocystis species but also for differentiating them from N. caninum and Besnoitia.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abdel-Ghaffar F, Al-Johany AM (2002) A light and electron microscope study of Sarcocystis mitrani (sp. Nov.) infecting the skink Scincus mitranus in the central region of Saudi Arabia. Parasitol Res 88:102–106
Abdel-Ghaffar F, Mehlhorn H, Bashtar AR, Al-Rasheid K, Sakran T, El-Fayoumi H (2009) Life cycle of Sarcocystis camelicanis infecting the camel (Camelus dromedarius) and the dog (Canis familiaris), light and electron microscopic study. Parasitol Res 106:189–195
Bunyaratvej S, Unpunyo P (1992) Combined Sarcocystis and gram-positive bacterial infections: a possible cause of segmental enterocolitis in Thailand. J Med Assoc Thai 75:38–44
Bunyaratvej S, Bunyawongwiroj P, Nitiyanant P (1982) Human intestinal sarcosporidiosis: report of six cases. Am J Trop Med Hyg 31:36–41
Bunyaratvej S, Unpunyo P, Pongtippan A (2007) The Sarcocystis-cyst containing beef and pork as the sources of natural intestinal sarcocystosis in Thai people. J Med Assoc Thai 90:2128–2135
Dahlgren S, Gjerde B (2007) Genetic characterization of six Sarcocystis species from reindeer (Rangifer tarandus tarandus) in Norway based on the small subunit rRNA gene. Vet Parasitol 146:204–213
Dalimi A, Paykari A, Esmaeilzadeh M, Valizadeh M, Karimi G, Motamedi G, Abdi Goodarzi M (2008) Identification of Sarcocystis species of infected sheep in Ziaran abattoir, Qazvin using PCR-RFLP (In Persian). Modares Med Sci 11:65–72
Dissanaike AS, Kan SP (1978) Studies in Sarcocystis in Malaysia. I. Sarcocystis levinei n. sp. from the water buffalo Bubalus bubalus. Zeitschrift für Parasitenkunde 55:127–138
Dubey JP (1976) A review of Sarcocystis of domestic animals and of other coccidia of cats and dogs. J Am Vet Med Assoc 169:1061–1078
Dubey JP, Lindsay DS (2006) Neosporosis, toxoplasmosis, and sarcocystosis in ruminants. Vet Clin North Am Food Anim Pract 22:645–671
Dubey JP, Speer CA, Fayer R (1989) Sarcocystosis of animals and man, vol 1. CRC, Boca Raton
Entzeroth R, Chobotar B, Scholtyseck E, Nemeseri L (1985) Light and electron microscope study of Sarcocystis sp. from the fallow deer (Cervius lama). Parasitol Res 71:33–39
Fatina A, Hilali M, Al-Atiya S, Al-Shami S (1996) Prevalence of Sarcocystis in camels (Camelus dromedarius) from Al-Asha, Saudi Arabia. Vet Parasitol 62:241–245
Fayer R (2004) Sarcocystis spp. in human infections. Clin Microbiol Rev 17:894–902
Fischer S, Odening K (1998) Characterization of bovine Sarcocystis species by analysis of their 18S ribosomal DNA sequences. J Parasitol 84:50–54
Frenkel JK, Smith DD (2003) Determination of the genera of cyst-forming coccidian. Parasitol Res 91:384–389
Giboda M, Ditrich O, Scholz T, Viengsay T, Bouaphanh S (1991) Current status of food-borne parasitic zoonoses in Laos. Southeast Asian J Trop Med Public Health 22:56–61
Gracy J F, Collins DS, Huey RJ (1999) Meat Hygiene.10th ed WB Saunders
Guo ZG, Johnson AM (1995) Genetic comparison of Neospora caninum with Toxoplasma and Sarcocystis by random amplified polymorphic DNA-polmerase chain reaction. Parasitol Res 81:365–370
Hajimohammadi B, Dehghani A, Moghadam Ahmadi M, Eslami G, Oryan A, Khamesipour A (2014) Prevalence and species identification of Sarcocystis in raw hamburgers distributed in Yazd, Iran using PCR-RFLP. J Food Qual and Hazards Control 1:15–20
Hilda F, de Pena J, Ogassawara S, Sinhorini IL (2001) Occurrence of cattle Sarcocystis species in raw kibbe from Arabian food establishments in the city of São Paulo, Brazil, and experimental transmission to humans. J Parasitol 87:1459–1465
Hinz E (1991) Current status of food-borne parasitic zoonoses in West Germany. Southeast Asian J Trop Med Public Health 22:78–84
Jeffries AC, Schnitzler B, Heydorn AO, Johnson AM, Tenter AM (1997) Identification of synapomorphic characters in the genus Sarcocystis based on 18S rDNA sequence comparison. J Eukaryot Microbiol 44:388–392
Kalubowila DG, Udagama-Randeniya PV, Perera NA, Rajapakse RP (2004) Seroprevalence of Sarcocystis spp. in cattle and buffaloes from the wet and dry zones of Sri Lanka. J Vet Med B Infect Dis Vet Public Health 51:89–93
Kia EB, Mirhendi H, Rezaeian M, Zahabiun F, Sharbatkhori M (2011) First molecular identification of Sarcocystis meischeriana (Protozoa, Apicomplexa) from wild boar (Sus scrofa) in Iran. Exp Parasitol 127:724–726
Latif B, Vellayan S, Heo CC, Kannan Kutty M, Omar E, Abdullah S, Tappe D (2013) High prevalence of muscular sarcocystosis in cattle and water buffaloes from Selangor. Malaysia Trop Biomed 30:699–705
Levine ND (1986) The taxonomy of Sarcocystis (Protozoa, Apicomplexa) species. J Parasitol 72:372–382
Li QQ, Yang ZQ, Zuo YX, Attwood SW, Chen XW, Zhang YP (2002) A PCR-based RFLP analysis of Sarcocystis cruzi (Protozoa: Sarcocystiidae) in Yunnan province, PR China, reveals the water buffalo (Bubalus bubalis) as a natural intermediate host. J Parasito 88:1259–1261
Lian Z, Ma J, Wang Z, Fu L, Zhou Z, Li W, Wang X (1990) Studies on man-cattle-man infection cycle of Sarcocystis hominis in Yunnan. Zhongguo Ji Sheng Chong Xue Yu Ji Sheng Chong Bing Za Zhi 8:50–53
Mehlhorn H, Heydorn AO (1979) Electron microscopical study on gamogony of Sarcocystis suihominis in human tissue cultures. Parasitol Res 58:97–113
Moré G, Basso W, Bacigalupe D, Venturini MC, Venturini L (2008) Diagnosis of Sarcocystis cruzi, Neospora caninum, and Toxoplasma gondii infections in cattle. Parasitol Res 102:671–675
Motamedi GR, Dalimi A, Nouri A, Aghaeipour K (2011) Ultrastructural and molecular characterization of Sarcocystis isolated from camel (Camelus dromedarius) in Iran. Parasitol Res 108:949–954
Naghibi A, Razmi G, Ghasemifard M (2002) Identification of Sarcocystis cruzi in cattle by using of experimentally infection in final and intermediate hosts (In Persian). J Fac Vet Med Univ Tehran 57:67–69
Nourani H, Matin S, Nouri A, Azizi H (2010) Prevalence of thin-walled Sarcocystis cruzi and thick-walled Sarcocystis hirsuta or Sarcocystis hominis from cattle in Iran. Trop Anim Health Prod 42:1225–1227
Nourollahi Fard SR, Asghari M, Nouri F (2009) Survey of Sarcocystis infection in slaughtered cattle in Kerman, Iran. Trop Anim Health Prod 41:1633–1636
Odening K, Wesemeier HH, Walter G, Bockhardt I (1994) The wisent (Bison bonasus, Bovidae) as an intermediate host of three Sarcocystis species (Apicomplexa: Sarcocystidae) of cattle. Folia Parasitologica 41:115–121
Odening K, Wesemeier HH, Walter G, Bockhardt I (1995) On the morphological diagnostics and host specificity of the Sarcocystis species of some domesticated and wild bovini (cattle, banteng and bison). App Parasitol 36:161–178
Oryan A, Moghaddar N, Gaur SNS (1996) The distribution pattern of Sarcocystis species, their transmission and pathogenesis in sheep in Fars Province of Iran. Vet Res Commun 20:243–253
Oryan A, Ahmadi N, ModarresMousavi SM (2010) Prevalence, biology and distribution pattern of Sarcocystis infection in water buffalo (Bubalus bubalis) in Iran. Trop Anim Health Prod 42:1513–1518
Oryan A, Sharifiyazdi H, Khordadmehr M, Larki S (2011) Characterization of Sarcocystis fusiformis based on sequencing and PCR-RFLP in water buffalo (Bubalus bubalis) in Iran. Parasitol Res 109:1563–1570
Pamphlett R, O’Donoghue P (1990) Sarcocystis infection of human muscle. Aust N Z J Med 20:705–707
Pena HF, Ogassawara S, Sinhorini IL (2001) Occurrence of cattle Sarcocystis sp. in raw kibbe from Arabian food establishments in the city of Sao Paolo, Brazil, and experimental transmission to humans. J Parasitol 87:1459–1465
Pritt B, Trainer T, Simmons-Arnold L, Evans M, Dunams D, Rosenthal BM (2008) Detection of Sarcocystis parasites in retail beef: a regional survey combining histological and genetic detection methods. J Food Prot 71:2144–2147
Saito M, Shibata Y, Kubo M, Sakakibara I, Yamada A, Itagaki H (1999) First isolation of Sarcocystis hominis from cattle in Japan. J Vet Med Sci 61:307–309
Savini G, Dunsmore JD, Robertson ID, Seneviratna P (1992) The epidemiology of Sarcocystis spp. In cattle of Western Australia. Epidemiol Infect 108:107–113
Shekarforoush SS, Razavi SM, Dehghan SA, Sarihi K (2005) Prevalence of Sarcocystis species in slaughtered goats in Shiraz, Iran. Vet Rec 156:418–420
Valinezhad A, Oryan A, Ahmadi N (2008) Sarcocystis and its complications in camels (Camelus dromedarius) of eastern provinces of Iran. Korean J Parasitol 46:229–234
Vangeel L, Houf K, Chier K, Vercruysse J, D’Herde K, Ducatelle R (2007) Molecular-based identification of Sarcocystis hominis in Belgian minced beef. J Food Prot 70:1523–1526
Wee SH, Shin SS (2001) Experimental induction of the two host life cycle of Sarcocystis cruzi between dogs and Korean native calves. Korean J Parasitol 39:227–232
Xiang Z, Chen X, Yang L, He Y, Jiang R, Rosenthal BM, Luan P, Attwood SW, Zuo Y, Zhang YP, Yang Z (2009) Non-invasive methods for identifying oocysts of Sarcocystis spp. from definitive hosts. Parasitol International 58:293–296
Yang ZQ, Zuo YX (2000) The new views of the researchers on cyst forming coccidia species including Sarcocystis by using the molecular biological techniques. Chin J Parasitol Parasit Dis 18:120–126
Yang ZQ, Zuo YX, Yao YG, Cheng XW, Yang GC, Zhang YP (2001) Analysis of the 18S rRNA genes of Sarcocystis species suggests that the morphologically similar organisms from cattle and water buffalo should be considered the same species. Mol Biochem Parasitol 115:283–288
Yang ZQ, Li QQ, Zuo YX, Chen XW, Chen YJ, Nie L, Wei CG, Zen JS, Attwood SW, Zhang XZ, Zhang YP (2002) Characterization of Sarcocystis species in domestic animals using a PCR-RFLP analysis of variation in the 18S rRNA gene: A cost-effective and simple technique for routine species identification. Exp Parasitol 102:212–217
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to thank the Research Council of Shiraz University and School of Veterinary Medicine, Shiraz University for financial support. We also thank Mr. M. Sorbi and Mrs. F. Nejati for their technical assistance.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Akhlaghi, M., Razavi, M. & Hosseini, A. Molecular differentiation of bovine sarcocysts. Parasitol Res 115, 2721–2728 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00436-016-5020-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00436-016-5020-7