Abstract
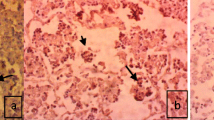
Bronchopulmonary lophomoniasis (BPL) is an emerging disease of potential importance. BPL is presented by non-specific clinical picture and is usually accompanied by immunosuppression. Culture of Lophomonas blattarum is difficult and its molecular diagnosis has not yet been developed. Therefore, microscopic examination of respiratory samples, e.g., bronchoalveolar lavage (BAL) or sputum, is the mainstay of BPL diagnosis. Creola bodies and ciliocytophthoria are two forms of bronchial cells which occur in chest diseases with non-specific clinical picture like that of BPL. Both forms could be misrecognized as multi-flagellates because of their motile cilia in the wet mounts and due to shape variability of L. blattarum in stained smears. The aim of the study is to compare different staining techniques for visualizing L. blattarum to improve the recognition and diagnosis of BPL, to distinguish respiratory epithelial cells from L. blattarum and to decide which stain is recommended in suspected cases of BPL. BAL samples from patients which contain L. blattarum, creola bodies, and ciliocytophthoria were collected then wet mounts were examined. The BAL samples were also stained by Papanicolaou (PAP), Giemsa, hematoxylin and eosin (H & E), trichrome, Gram, and Diff-Quik (DQ) stains. The different staining techniques were compared regarding the stain quality. In wet mounts, the ciliary movement was coordinate and synchronous while the flagellar movement was wavy and leaded to active swimming of L. blattarum. In stained slides, bronchial cells were characterized by the presence of basal nucleus and the terminal bar from which the cilia arise. Trichrome was the best stain in demonstration of cellular details of L. blattarum. H & E, PAP, and Giemsa stains showed good quality of stains. Gram and DQ stains showed only pale hues of L. blattarum. We recommended adding Wheatley’s trichrome staining to the differential diagnosis workup of cases of non-specific chest infections, especially when BPL is suspected, to avoid overdiagnosis or underdiagnosis of it.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aykan B, Caglar K, Kustımur S (2005) Evaluation of the protozoa found in fecal samples using the trichrome staining method. Turkiye Parazitol Derg 29(1):34–38
Bittencourt-Silvestre J, Lemgruber L, de Souza W (2010) Encystation process of Giardia lamblia: morphological and regulatory aspects. Arch Microbiol 192:259–265
Brugerolle G, Lee JJ (2000) Phylum parabasalia. In: Lee JJ, Leedale GF, Bradbury P (eds) An illustrated guide to the protozoa (vol. 2), 2nd edn. Society of Protozoologists, Lawrence
Brugerolle G, Silva-Neto ID, Pellens R, Grandcolas P (2003) Electron microscopic identification of the intestinal protozoan flagellates of the xylophagus cockroach Parasphaeria boleiriana from Brazil. Parasitol Res 90:249–256
Chavez-Munguya B, Omana-Molina M, Gonzalez-Lazaro M, Gonzalez-Robles A, Cedillo-Rivera R, Bonilla P, Martynez-Palomo A (2007) Ultrastructure of cyst differentiation in parasitic protozoa. Parasitol Res 100:1169–1175
Chen L (1933) Zuchtungsversuche an parasitischen protozoen vonPeriplaneta orientalis. Z Parasitenkd 6:207–219
Clavel A, Varea M, Doiz O, Lopez L, Quilez J, Castillo FJ, Rubio C, Gomez-Lus R (1999) Visualization of hydatid elements: comparison of several techniques. J Clin Microbiol 37(5):1561–1563
El-Sayed NM, Hikal WM (2014) Several staining techniques to enhance the visibility of Acanthamoeba cysts. Parasitol Res 114(3):823–830
Farmer JN (1980) The protozoa. In: Farmer JN (ed) Introduction to protozoology. The C.V. Mosby Company, London, pp 265–273
Garcia LS (2007) Macroscopic and microscopic examination of fecal specimens. In: Garcia LS (ed) Diagnostic medical parasitology (Part II), 5th edn. ASM Press, Washington, pp 782–830
Johnston WW, Elson CC (2008) Respiratory tract. In: Bibbo M, Wilbur DC (eds) Comprehensive cytopathology, 3rd edn. Saunders, Elsevier, pp 303–361
Kessel RG, Beams HW (1990) Freeze fracture and scanning electron microscope studies on the nuclear envelope and perinuclear cytomembranes (parabasal apparatus) in the protozoan, Lophomonas blattarum. J Submicrosc Cytol Pathol 22:367–378
Khan S, Kumar VA, Venkitachalam A, Vishwam V, Dinesh K, Karim S (2015) Detached ciliary tufts masquerading as free-living amoebae. Int J Infect Dis 30:142–143
Kiernan JA (2008) Histological and histochemical methods: theory and practice, 4th edn. Scion, Oxford
Kirby H (1950) Collection and cultivation of methods for symbiotic protozoa. In: Kirby H (ed) Materials and methods in the study of protozoa. University of California Press, Berkeley
Koss LG (1992) Diagnostic cytology and its histopathologic bases (vol. 2). JB Lippincott, Philadelphia, pp 1452–1509
Kudo RR (1954) Protozoology, 4th edn. Charles C Thomas Publisher, Springfield
Kuritzkes D, Rein M, Horowitz S, Droege G, Waldon MA, Bell DA, Fuller AF, Ellman LL, Dickersin GR, Swartz MN, Wolfson JS (1988) Detached ciliary tufts mistaken for peritoneal parasites: a warning. Rev Infect Dis 10:1044–1047
Martinez-Giron R (2013) Protozoal infections. In: Barrios R, Haque AK (eds) Parasitic diseases of the lungs. Springer, New York, pp 47–68
Martinez-Giron R, Doganci L (2010) Lophomonas blattarum: a bronchopulmonary pathogen. Acta Cytol 54(5):1050–1051
Martinez-Giron R, van Woerden HC (2013) Lophomonas blattarum and bronchopulmonary disease. J Med Microbiol 62(11):1641–1648
Martinez-Giron R, van Woerden HC (2014) Bronchopulmonary lophomoniasis: emerging disease or unsubstantiated legend? Parasit Vectors 23(7):284
Martinez-Giron R, van Woerden HC, Doganci L (2011) Lophomonas misidentification in bronchoalveolar lavages. Intern Med 50(21):2721, author reply 2723
Pai HH, Ko YC, Chen ER (2003) Cockroaches (Periplaneta americana and Blatella germanica) as potential mechanical disseminators of Entamoeba histolytica. Acta Trop 87:355–359
Ribas A, Martinez-Giron R, Ponte-Mittelbrum C, Alonso-Cuervo R, Iglesias-Llaca F (2007) Immunosupression, flagellated protozoa in the human airways and metronidazole: observations on the state of the art. Transpl Int 20:811–812
Shakoor S, Beg M, Mahmood S, Bandea R, Sriram R, Noman F, Ali F, Visvesvara GS, Zafar A (2011) Primary amebic meningoencephalitis caused by Naegleria fowleri, Karachi, Pakistan. Emerg Infect Dis 17:258–261
Skipper R, DeStephano DB (1989) A rapid stain for Campylobacter pylori in gastrointestinal tissue sections using Diff-Quik®. J Histotechnol 12:303–304
Strand MA, Brooks MA (1977) Pathogens of Blattidae (cockroaches). Bull World Health Organ 55(1):289–296
Wang Y, Tang Z, Ji S, Zhang Z, Chen J, Cheng Z, Cheng D, Liu Z, Li L (2006) Pulmonary Lophomonas blattarum infection in patients with kidney allograft transplantation. Transpl Int 19:1006–1013
Wu Z, Liu Y (2010) Blattarum lophomoniasis: a newly discovered parasitosis. J Pathog Biol 7:21
Yamada Y, Yoshihara S (2010) Creola bodies in infancy with respiratory syncytial virus bronchiolitis predict the development of asthma. Allergol Int 59(4):375–380
Yao G (2008) Bronchopulmonary infection with Lophomonas blattarum: two cases report and literature review. J Med Col PLA 23:176–182
York MK (2004) Gram stain. In: Isenberg HD (ed) Clinical microbiology procedures handbook. American Society of Microbiology, Washington
Yoshihara S, Yamada Y, Abe T, Linden A, Arisaka O (2006) Association of epithelial damage and signs of neutrophil mobilization in the airways during acute exacerbations of paediatric asthma. Clin Exp Immunol 144(2):212–216
Zaragatzki E, Hess M, Grabensteiner E, Abdel-Ghaffar F, Al-Rasheid KAS, Mehlhorn H (2010) Light and transmission electron microscopic studies on the encystation of Histomonas meleagridis. Parasitol Res 106:977–983
Zerpa R, Ore E, Patino L, Espinoza YA (2010) Lophomonas sp. in respiratory tract secretions in hospitalized children with severe lung disease. Rev Peru Med Exp Salud Publ 27:575–577
Zhang X, Xu L, Wang LL, Liu S, Li J, Wang X (2011) Bronchopulmonary infection with Lophomonas blattarum: a case report and literature review. J Int Med Res 39:944–949
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Alam-Eldin, Y.H., Abdulaziz, A.M. Identification criteria of the rare multi-flagellate Lophomonas blattarum: comparison of different staining techniques. Parasitol Res 114, 3309–3314 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00436-015-4554-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00436-015-4554-4