Abstract
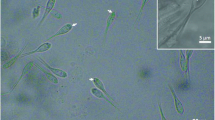
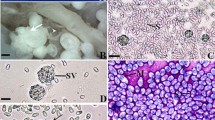
Morphological and molecular procedures were used to describe a new species of microsporidian that infects the muscles of the sub-opercular region and the caudal fins of the freshwater Aequidens plagiozonatus in Brazil. This microsporidian forms whitish xenomas containing variable number of spores, reaching up to ~0.4 mm in diameter. The mature spores, pyriformin shape, with slightly round ends, measured 3.4 ± 0.5 μm long and 1.9 ± 0.3 μm wide (n = 50) and showed characteristics typical of Microsporidia. The average thickness of the spore wall was 100 (96–108) nm (n = 50), and the spore wall was composed of two layers, a thin, electron-dense exospore and a thick electron-transparent endospore. The exospore was surrounded by a thin, irregular layer of granular material. The anchoring disc was mushroom-like, located in the apical region of the spore in an eccentric position relative to the spore axis, rendering bilateral asymmetry to the spore. The anterior part of the polar filament (PF) (manubrium) measured approximately 125 (122–128) nm thick (n = 30), and the angle of tilt between the anterior PF and the spore axis was ~45°; the posterior part was packed in 8–9 coils. Phylogenetic analysis showed a strongly supported clade containing family Spragueidae Weissenberg, 1976, family Tetramicridae Matthews and Matthews, 1980, Microsporidium sp. RBS1, and Kabatana spp. In conclusion, the available morphological, ultrastructural, and molecular data shows that this microsporidian is a new species belonging to group 4, classified as Potaspora aequidens n. sp. This is the second species described in the genus Potaspora.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abdel-Ghaffar F, Abdel-Rahman B, Morsy K, Mehlhorn H, Al Quraishy S, Al-Rasheid K, Abdel-Gaber R (2012) Morphological and molecular biological characterization of Pleistophora aegyptiaca sp. nov. infecting the Red Sea fish Saurida tumbil. Parasitol Res 110:741–752
Azevedo C, Matos E (2002) Fine structure of a new species, Loma myrophis (phylum Microsporidia), parasite of the Amazonian fish Myrophis platyrhynchus (Teleostei, Ophichthidae). Eur J Protistol 37:445–452
Azevedo C, Matos E (2003) Amazonspora Hassar n. gen. and n. sp. (Phylum Microsporídia, Fam. Glugeidae), a parasite of the amazonian teleost Hassar orestis (Fam. Doradidae). J Parasitol 89(2):336–341
Casal G, Matos E, Teles-Grilo ML, Azevedo C (2008) A new microsporidian parasite, Potaspora morhaphis n. gen., n. sp. (Microsporidia) infecting the Teleostean fish, Potamorhaphis guianensis from the River Amazon. Morphological, ultrastructural and molecular characterization. J Parasitol 135:1053–1064
Casal G, Matos E, Teles-Grilo ML, Azevedo C (2009) Morphological and genetical description of Loma psittaca sp. n. isolated from the Amazonian fish species Colomesus psittacus. Parasitol Res 105(5):1261–1271
Casal G, Matos E, Teles-Grilo L, Azevedo C (2010) Ultrastructural and molecular characterization of a new microsporidium parasite from the amazonian fish, Gymnorhamphichthys rondoni (Rhamphichthyidae). Parasitology 96(6):1155–1163
Casal G, Matos E, Garcia P, Al-Quraishy S, Azevedo C (2012) Ultrastructural and molecular studies of Microgemma carolinus n. sp. (Microsporidia), a parasite of the fish Trachinotus carolinus (Carangidae) in Southern Brazil. Parasitology 139:1720–1728
Cheney SA, Lafranchi-Tristem NJ, Canning EU (2000) Phylogenetic relationships of Pleistophora-like microsporidia based on small subunit ribosomal DNA sequences and implications for the source of Trachipleistophora hominis infections. J Eukaryot Microbiol 47:280–287
Franzen C (2008) Microsporidia: a review of 150 years of research. Open Parasitol J2:1–34
Gatehouse HS, Malone LA (1998) The ribosomal RNA gene region of Nosema apis (Microspora): DNA sequence for small and large subunit rRNA genes and evidence of a large tandem repeat unit size. J Invertebr Pathol 71:97–105
Hall TA (1999) BioEdit: a user-friendly biological sequence alignment editor and analysis program for Windows 95/98/NT. Nucl Acid 41:95–98
Lom J, Dyková I (1992) Protozoan parasites of fishes. Elsevier, Amsterdam, 315 p
Lom J, Nilsen F (2003) Fish microsporidia: fine structural diversity and phylogeny. Int J Parasitol 33:107–127
Mathis A (2000) Microsporidia: emerging advances in understanding the basic biology of these unique organisms. Int J Parasitol 30:795–804
Mathis A, Weber R, Deplazes P (2005) Zoonotic potential of the Microsporidia. Clin Microbiol Rev 18(3):423–445
Matos E, Azevedo C (2004) Ultrastructural description of Microsporidium brevirostris sp. n., parasite of the Teleostean Brachyhypopomus brevirostris (Hypopomidae) from the Amazon River. Acta Protozool 43:261–267
Morsy K, Abdel-Ghaffar F, Mehlhorn H, Abdel-Rahman B, Abdel-Gaber R (2012) Ultrastructure and molecular phylogenetics of a new isolate of Pleistophora pagri sp. nov. (Microsporidia, Pleistophoridae) from Pagrus pagrus in Egypt. Parasitol Res 111:1587–1597
Nilsen F (2000) Small subunit ribosomal DNAphylogeny of Microsporidia with particular referenceto genera that infect fish. J Parasitol 86:128–133
Nilsen F, Endresen C, Hordvik I (1998) Molecular phylogeny of microsporidians with particular reference to muscle infecting species of fishes. J Eukaryot Microbiol 45:535–543
Posada D (2008) jModelTest: phylogenetic model averaging. Mol Biol Evol 25:1253–1256
Ronquist MAF, Huelsenbeck JP (2003) MrBayes 3: Bayesian phylogenetic inference under mixed models. Bioinformatics 19:1572–1574
Stentiford GD, Feist SW, Stone DM, BatemanKS DAM (2013) Microsporidia: diverse, dynamic, and emergent pathogens in aquatic systems. Trends Parasitol 29:567–578
Swofford DL (1998) Phylogenetic analysis using parsimony (*and other methods). Sinauer Associates, Sunderland
Vávra J, Lukes J (2013) Microsporidia and “the art of living together.”. Adv Parasitol 82:254–319
Vossbrinck CR, Vossbrinck BAD (2005) Molecular phylogeny of the Microsporidia: ecological, ultrastructural and taxonomic considerations. Fol Parasitol 52:131–142
Vossbrinck CR, Baker MD, Didier ES, Debrunner-VossbrinckBA SJA (1993) Ribosomal DNA sequences of Encephalitozoon hellem and Encephalitozoon cuniculi: speciesidentification and phylogenetic construction. J Eukaryot Microbiol 40:354–362
Wittner M, Weiss LM (1999) The Microsporidia and Microsporidiosis. ASM Press, Washington, DC
Xu Y, Weiss LM (2005) The microsporidian polar tube: a highly specialised invasion organelle. Int J Parasitol 35:941–953
Acknowledgments
We are grateful to The Edilson Matos Research Laboratory (LPEM–UFPA), “Coordenação de Aperfeiçoamento de Pessoal de Nível Superior” (CAPES), “Conselho Nacional de Desenvolvimento Científico e Tecnológico” (CNPq, Universal Research Program), Special Visitant Researcher-CAPES (88881.064967/2014-01), and “Fundação Amazônia Paraense de Amparo à Pesquisa” (FAPESPA) (Brazil). This study was partially supported by Eng. António de Almeida Foundation (Porto, Portugal); FCT (Lisbon, Portugal), within the scope of the PhD fellowship grant SFRH/BD/92661/2013 to S.R. and King Saud University (Riyadh, Saudi Arabia), within the scope of Project no. RGP-002. This work complies with the current laws of the countries in which it was performed.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Videira, M., Casal, G., Rocha, S. et al. Potaspora aequidens n. sp. (Microsporidia, Tetramicridae), a parasite infecting the freshwater fish Aequidens plagiozonatus (Teleostei, Cichlidae) from Brazil. Parasitol Res 114, 2435–2442 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00436-015-4438-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00436-015-4438-7