Abstract
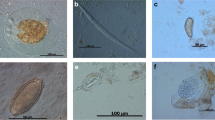
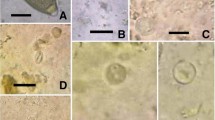
In general, the knowledge on parasites infecting Antarctic birds is scarce. The present study intends to extend the knowledge on gastrointestinal parasites of Emperor Penguins (Aptenodytes forsteri) at the Atka Bay, Antarctica. Fecal samples of 50 individual Emperor Penguins were collected at the Atka Bay and analyzed using the sodium-acetate-formaldehyde (SAF) method for the identification of intestinal helminth eggs and/or protozoan parasite stages. In addition, coproantigen ELISAs were performed to detect Cryptosporidium and Giardia infections. Overall, 13 out of 50 penguins proved parasitized (26 %). The following stages of gastrointestinal parasites were identified: One Capillaria sp. egg, Tetrabothrius spp. eggs, Diphyllobothrium spp. eggs, and proglottids of the cestode Parorchites zederi. The recorded Capillaria infection represents a new host record for Emperor Penguins. All coproantigen ELISAs for the detection of Cryptosporidium spp. and Giardia spp. were negative. This paper provides current data on parasites of the Emperor Penguin, a protected endemic species of the Antarctica.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Anderson RC (2002) Nematode parasites of vertebrates, their development and transmission. CABI Publishing, 2nd edn. 650 pp
Baird W (1853) Descriptions of some new species of entozoa from the collection of the British Museum. Proc Zool Soc London 21:18–25
Barbosa A, Palacios MJ (2009) Health of Antarctic birds: a review of their parasites, pathogens and diseases. Polar Biol 32:1095–1115
Blajin, Rukhadze (1929) On a method for staining flukes and tapeworm segments as whole microscopical preparations. J Trop Med Hyg 33:342–345
Bush O, Lafferty AD, Lotz JM, Shostak AW (1997) Parasitology meets ecology on its own terms: Margolis et al. revisited. J Parasitol 83:575–583
Cherel Y, Kooyman GL (1998) Food of emperor penguins (Aptenodytes forsteri) in the Western Ross Sea, Antarctica. Mar Biol 130:335–344
Chilton NB, Huby-Chilton F, Gasser RB, Beveridge I (2006) The evolutionary origins of nematodes within the order Strongylida are related to predilection sites within hosts. Mol Phylogenet Evol 40:118–128
Cielecka D, Wojciechowska A, Zdzitowiecki K (1992) Cestodes from penguins on King George Island (South Shetlands, Antarctica). Acta Parasitol 37:65–72
Clark J, Kerry K (2000) Diseases and parasites of penguins. Penguin Conserv 13:5–24
Diamant A, Banet A, Paperna I, von Westernhagen H, Broeg K, Kruener G, Koerting W, Zander S (1999) The use of fish metabolic, pathological and parasitological indices in pollution monitoring II. The Red Sea and Mediterranean. Helgoland Mar Res 53:195–208
Diaz JI, Fusaro B, Longarzo L, Coria NR, Vidal V, Jerez S, Ortiz J, Barbosa A (2013) Gastrointestinal helminthes of Gentoo penguins (Pygoscelis papua) from Stranger Point, 25 de Mayo/King George Island, Antarctica. Parasitol Res 112:1877–1881
Dzikowski R, Paperna I, Diamant A (2003) Use of fish parasite species richness indices in analyzing anthropogenically impacted coastal marine ecosystems. Helgoland Mar Res 57:220–227
Fonteneau F, Geiger S, Marion L, Le Maho Y, Robin JP, Kinsella JM (2011) Gastrointestinal helminths of King penguins (Aptenodytes patagonicus) at Crozet Archipelago. Polar Biol 34:1249–1252
Fredes F, Madariaga C, Raffo E, Valencia J, Herrera M, Godoy C, Alcaíno H (2007) Gastrointestinal parasite fauna of gentoo penguins (Pygoscelis papua) from the Península Munita, Bahía Paraíso, Antarctica. Antarct Sci 19:93–94
Fretwell PT, Larue MA, Morin P, Kooyman GL, Wienecke B, Ratcliffe N, Fox AJ, Fleming AH, Porter C, Trathan PN (2012) An emperor penguin population estimate: the first global, synoptic survey of a species from space. PLoS One 7:e33751
Fuhrmann O (1921) Die Cestoden der Deutschen Südpolar Expedition 1901–1903. In: Drygalski E (ed) Deutsche Südpolar Expedition 1901–1903, 16 Zoologie 8:467–542
Georgiev BB, Vasileva GP, Chipev NH, Dimitrova ZM (1996) Cestodes of seabirds at Livingston Island, South Shetlands. Bulgarian Antarctic Res Life Sciences 111–127
Hechinger RF, Lafferty KD, Huspeni TC, Andrew JB, Armand MK (2007) Can parasites be indicators of free-living diversity? Relationships between species richness and the abundance of larval trematodes and of local benthos and fishes. Oecologia 151:82–92
Hoberg EP (1996) Faunal diversity among avian parasite assemblages: the interaction of history, ecology and biogeography. Bull Scand Soc Parasitol 6:65–89
Hoberg EP (2005) Economic, environmental and medical importance: Marine birds and their helminth parasites. In: Rohde K (ed) Marine parasitology. CSIRO, Sydney, pp 414–421
Hudson PJ, Dobson AP, Lafferty KD (2006) Is a healthy ecosystem one that is rich in parasites? Trends Ecol Evol 21:381–385
Johnston TH (1937) Cestoda. In: Johnston TH (ed) Australasian Antarctic expedition 1911–14, Sci Rep, Ser C Zoology and Botany 10:5–74
Jones HI (1988) Notes on parasites in penguins (Spheniscidae) and petrels (Procellariidae) in the Antarctic and sub-Antarctic. J Wildl Dis 24:166–167
Kahlil LF, Jones A, Bray RA (1994) Keys to the cestode parasites of vertebrates. CAB International, Wallingford
Katoh K, Standley EM (2013) MAFFT multiple sequence alignment software version 7: Improvements in performance and usability. Mol Biol Evol 30:772–780
Kooyman GL, Kooyman TG (1995) Diving behavior of emperor penguins nurturing chicks at Coulman Island, Antarctica. Condor 97:536–549
Kooyman GL, Cherel Y, Le Maho Y, Croxall JP, Thorson PH, Ridoux V, Kooyman CA (1992) Diving behavior and energetics during foraging cycles in king penguins. Ecol Monogr 62:143–463
Lauckner G (1985) Diseases of Aves (Marine Birds). In: Kinne O (ed) Diseases of marine animals, vol IV, Part 2, Reptilia, Aves. Mammalia. Biologische Anstalt Helgoland, Hamburg, pp 805–847
Leiper RT, Atkinson EL (1914) Helminthes of the British Antarctic Expedition, 1910–1913. Proc Zool Soc London 222–226
Leiper RT, Atkinson EL (1915) Parasitic worms with a note on free-living nematoda. Brit Antartic (‘Terra Nova’) Exped 1910. Nat Hist Rep Zool 11:19–60
Littlewood DTJ, Olson PD (2001) Small subunit rDNA and the Platyhelminthes: Signal, noise, conflict and compromise. In: Littlewood DTJ, Bray RA (eds) Interrelationships of the Platyhelminthes. Taylor & Francis, London, pp 262–278
MacKenzie K, Williams HH, Williams B, McVicar AH, Siddall R (1995) Parasites as indicators of water quality and the potential use of helminth transmission in marine pollution studies. Adv Parasit 35:85–144
Marcogliese DJ (2003) Food webs and biodiversity: are parasites the missing link? J Parasitol 89:106–113
Marcogliese DJ (2005) Parasites of the superorganism: Are they indicators of ecosystem health? Int J Parasitol 35:705–716
Mawson PM (1953) Parasitic nematoda collected by the Australian National Antarctic Research Expedition: Heard Island and Macquarie Island 1948–1951. Parasitology 43:291–297
Nadler SA, Carreno RA, Mejía-Madrid H, Ullberg J, Pagan C, Houston R, Hugot JP (2007) Molecular phylogeny of clade III nematodes reveals multiple origins of tissue parasitism. Parasitology 134:1421–1442
Overstreet RM (1997) Parasitological data as monitors of environmental health. Parassitologia 39:169–175
Palacios MJ, Valera F, Barbosa A (2012) Experimental assessment of the effects of gastrointestinal parasites on offspring quality in chinstrap penguins (Pygoscelis antarctica). Parasitology 139:819–824
Prudhoe S (1969) Cestodes from fish, birds and whales. B.A.N.Z. Antarctic Research Expedition 1929–1931. Rep Ser B 8:171–193
Schmidt GD (1986) CRC handbook of tapeworm identification. CRC Press, Boca Raton
Steig EJ, Schneider DP, Rutherford RD, Mann ME, Comisso JC, Shindell DT (2009) Warming of the Antarctis ice-sheet surface since the 1957 International Geophysical year. Nature 457:459–463
Tamura K, Stecher G, Peterson D, Filipski A, Kumar S (2013) MEGA6: Molecular evolutionary genetics analysis version 6.0. Mol Biol Evol 30:2725–2729
Vidal V, Ortiz J, Diaz JI, Ruiz de Ybañez MR, Amat MT, Palacios MJ, Benzal J, Valera F, de la Cruz C, Motas M, Barbosa A (2012) Gastrointestinal parasites in Chinstrap Penguins from Deception Island, South Shetlands, Antarctica. Parasitol Res 111:723–727
Wienecke B, Robertson G, Kirkwood R, Lawton K (2007) Extreme dives by free-ranging emperor penguins. Polar Biol 30:133–142
Williams TD (1995) The penguins. Spheniscidae. (Birds Families of the World, No. 2). Oxford University Press, p 328
Acknowledgments
We are thankful to the Alfred Wegener Institute for Polar and Marine Research for logistical support and sample acquisition. Furthermore, we thank the German Federal Environment Agency for the sampling permission. We are grateful to Christine Henrich, Agnes Mohr, and Birgit Reinhardt for technical assistance. Special thanks to Boyko B. Georgiev (Institute of Biodiversity and Ecosystem Research, Bulgarian Academy of Sciences, Sofia, Bulgaria) and Krzysztof Tomczuk (Faculty of Veterinary Medicine, Lublin, Poland) for providing us with assistive literature.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kleinertz, S., Christmann, S., Silva, L.M.R. et al. Gastrointestinal parasite fauna of Emperor Penguins (Aptenodytes forsteri) at the Atka Bay, Antarctica. Parasitol Res 113, 4133–4139 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00436-014-4085-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00436-014-4085-4