Abstract
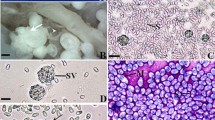
A new species of Microsporidia found in the marine teleost Sparus aurata collected from Hurghada coasts along the Red Sea, Egypt was described based on light and ultrastructural studies. Twenty three (30.6 %) out of 75 of the examined fish were parasitized with a microsporidian parasite. Numerous macroscopic whitish cysts embedded in the peritoneal cavity were observed to infect many organs of the body including muscles, connective tissues, and the intestinal epithelium. The infection was developed as tumor-like masses of often up to 5 mm in diameter inducing an enormous hypertrophy to the infected organs. Fresh spores appeared mostly ovoid to pyriform in shape reaching a size of 1.7 ± 0.5 (1.5–2.5) μm × 1.3 ± 0.4 (1–2) μm; they possessed a large vacuole at the posterior end. These spores were located within a sporophorous vesicle which was bound by a thick amorphous wall. The ultrastructural features support the placement of the present species within the genus Microsporidium. The developmental stages were enclosed within a xenoma structure that was bounded by a double-layered cyst wall. The life cycle of the microsporidian pathogen described herein included four stages: proliferation (merogony), sporogony, sporoblast, spores, and liberation. Mature spores appeared electron dense, uninucleate, and were ellipsoidal in shape. At the anterior end of the spore, the anchoring disk was found in a central position. There was a definite number (5–11) of turns of the polar tube. A 538-bp region of the SSU rDNA gene of the studied species was sequenced (GenBank accession number: KF0220444). Multiple sequence alignment calculated a high degree of similarity (>92 %) with six microsporidian species. The most closely related sequence was provided by the GenBank entry AF151529 for Microsporidium prosopium isolated from Hyperoplus lanceolatus differing in 67 nucleotide positions in its SSU rDNA with the highest percentage of identity (97.2 %) and the lowest divergence value (0.20). Variations in the morphology of the spores and developmental stages between the two species revealed that the two species are different. The site of infection in the host and description of the onset of parasite development are strong criteria for the placement of the microsporidian parasite of the fish S. aurata within the genus Microsporidium as a new species, and we propose to name it Microsporidium aurata nov. sp.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abdel-Ghaffar F et al (2009) Ultrastructure, development, and host–parasite relationship of a new species of the genus Pleistophora—a microsporidian parasite of the marine fish Epinephelus chlorostigma. Parasitol Res 106:39–46
Abdel-Ghaffar F, Bashtar AR, Mehlhorn H, Al-Rasheid K, Morsy K (2011) Microsporidian parasites: a danger facing marine fishes of the Red Sea. Parasitol Res 108(1):219–225
Abdel-Ghaffar F, Bashtar AR, Morsy K, Mehlhorn H, Al Quraishy S, Al-Rasheid K, Abdel-Gaber R (2012) Morphological and molecular biological characterization of Pleistophora aegyptiaca sp. nov. infecting the Red Sea fish Saurida tumbil. Parasitol Res 110(2):741–752
Awakura T (1974) Studies on the microsporidian infection in salmonid fishes. Sci Rep Hokkaido Fish Hatchery 29:1–93
Azevedo C, Matos E (2002) Fine structure of a new species, Loma myrophis (Phylum Microsporidia), parasite of the Amazonian fish Myrophis platyrhynchus (Teleostei, Ophichthidae). Europ J Protistol 37:445–452
Azevedo C, Matos E (2003) Amazonspora hassar n. gen. and n. sp. (Phylum Microsporidia, fam. Glugeidae), a parasite of the Amazonian teleost Hassar orestis (fam. Doradidae). J Parasitol 89:336–341
Baker ND, Vossbrink CR, Maddox JV, Undeen AH (1994) Phylogenetic relationships among Vairimorpha and Nosema species (Microspora) based on ribosomal RNA sequence data. J Invert Pathol 64:100–106
Baker MD, Vossbrinck CR, Didier ES, Maddox JV, Shadduck JA (1995) Small- subunit ribosomal DNA phylogeny of various microsporidia with emphasis on AIDS-related forms. J Eukaryot Microbiol 42:564–570
Bell AS, Yokoyama H, Aoki T, Takahashi M, Maruyama K (1999) Single and nested polymerase chain reaction assays for the detection of Microsporidium seriolae (Microspora), the causative agent of ‘Beko’ disease in yellowtail Seriola quinqueradiata. Dis Aquat Org 37:127–134
Bell AS, Aoki T, Yokoyama H (2001) Phylogenetic relationships among microsporidia based on rdna sequence data, with particular reference to fish-infecting; Microsporidium Balbiani 1884 species. J Eukaryot Microbiol 48(3):258–265
Bush AO, Lafferty KD, Lotz JM, Shostak AW (1997) Parasitology meets ecology on its own terms: Margolis et al. revisited. J Parasitol 83:575–583
Canning EU (1976) Microsporidia in vertebrates: host-parasite relations at the organismal level. In: Bulla LA, Cheng TC (eds) Comparative pathobiology. Biology of the microsporidia, Plenum, New York 1:137–202
Canning EU, Lom J (1986) The microsporidia of vertebrates. Academic, New York, p 289
Caullery M, Mesnil F (1905) Sur des haplosporidies parasites de poissons marins. C R Soc Biol 58:640–643
Cavalier-Smith T (1983) In Endocytobiology II: Intracellular Space as Oligogenetic (Schenk, H.E.A. and Schwemmler, W.S., ed.), p. 1027–1034, Walter de Gruyter and Co.
Dykova I (1995) Phylum microspora. In: Woo PTK (ed) Fish diseases and disorders. protozoan and metazoan infections. CAB International, Cambridge 1:149–179
Dyková I, Lom J (1978) Tissue reaction to Glugea plecoglossi infection by its natural host, Plecoglossus altivelis. Folia Parasitol (Praha) 27:213–216
Egusa S (1982) A microsporidian species from yellowtail juveniles, Seriola quinqueradiata, with “Beko” disease. Fish Pathology 16:187–192 (In Japanese)
Egusa S, Hatai K, Fujimaki Y (1988) Notes on Microsporidium species, the etiological agent of “Beko” disease in red sea bream juveniles, Pagrus major. Fish Pathology 23:263–267 (In Japanese)
Faye N (1992) Microsporidies des poisons des cotes senegalaises: faunistique, biologie, ultrastructure. Thesis, Universite Montpellier11, Sciences et Techniques du Languedoc
Faye A, Toguebaye BS, Bouix G (1991) Microfilum lutjanin.g. n. sp. (Protozoa Microsporida), a gill parasite of the golden African snapper Lutjanus fulgens (Valenciennes, 1830) (Teleostei, Lutjanidae): developmental cycle and ultrastructure. J Protozool 38:30–40
Faye N, Toguebaye BS, Bouix G (1996) Ultrastructure and development of Neonosemoides tilapiae (Sakiti and Bouix, 1987) n.g., n. comb. (Protozoa, Microspora) from African cichlid fish. Europ J Protistol 32:320–326
Gurley RR (1893) On the classification of Myxosporidia, a group of protozoan parasites infesting fishes. Bull U S Fish Comm 11:407–420
Hall TA (1999) BioEdit: a user-friendly biological sequence alignment editor and analysis program for Windows 95/98/NT. Nucl Acids Symp Ser 41:95–98
Hatakeyama Y, Kawakami Y, Iwano H, Inoue T, Ishihara R (1997) Analysis and taxonomic inferences of small subunit ribosomal RNA sequence of five microsporidia pathogenic to the silkworm, Bombyx mori. J Seric Sci Jpn 66:242–252
Hatakeyama Y, Bansal AK, Iwano H, Kawakami Y, Ishihara R (2000) Characterization of SSU-rRNA sequence of a new microsporidium Nosema sp. (Nosematidae: Microsporidia), isolated from Antheraea mylitta Drury (Lepidoptera: Saturniidae) in India. J Seric 39:131–134
Hedrick RP, Groff JM, Baxa D (1991) Experimental infections with Nucleospora salmonis n. g., n. sp.: an intranuclear microsporidium from Chinook salmon (Onchorhynchus tschawytscha). Am Fish Soc News 19: 5
Hung HW, Lo CF, Tseyg CC, Peng SE, Chou CM, Kou GH (1998) The small subunit ribosomal RNA gene sequence of Pleistophora anguillarum and the use of PCR primers for diagnostic detection of the parasite. J Euk Microbiol 45(5):556–560
Kawakami Y, Inoue T, Kikuchi M, Takayanagi M, Sunairi M, Ando T, Ishihara R (1992) Primary and secondary structures of 5S ribosomal RNA of Nosema bombycis (Nosematidae: Microsporidia). J Seric Sci Jpn 61:321–327
Larsson JIR (1999) Identification of microsporidia. Acta Protozool 38:161–197
Liu H, Pan G, Dang X, Li T, Zhou Z (2013) Characterization of active ribosomal RNA harboring MITEs insertion in microsporidian Nosema bombycis genome. Parasitol Res 112(3):1011–1020
Lom J (2002) A catalogue of described genera and species of microsporidians parasitic in fish. Syst Parasitol 53:81–99
Lom J, Arthur JR (1989) A guideline for the preparation of species descriptions in Myxosporea. J Fish Dis 12:151–156
Lom J, Dykova I (1992) Protozoan parasites of fishes. Elsevier, Amsterdam
Lom J, Nilsen F (2003) Fish Microsporidia: fine structural diversity and phylogeny. Int J Parasitol 33:107–127
Lom J, Pekkarinen M (1999) Ultrastructural observations on Loma acerinae (Jírovec, 1930) comb. nov. (Phylum Microsporidia). Acta Protozool 38:61–74
Lom J, Dykova I, Shaharom F (1990) Microsporidiurn arthuri n. sp. parasite of Pangasius sutchi (Pangasiidae, Siluroidea) in South-East Asia. Dis Aquat Org 8:65–67
Lom J, Dyková I, Tonguthai K (1999) Kabataia gen. n., a new genus proposed for Microsporidium spp. infecting trunk muscles of fishes. Dis Aquat Org 38:39–46
Lom J, Dyková I, Tonguthai K (2000) Kabatana gen. n., new name for the microsporidian genus Kabataia Lom, Dykova et Tonguthai, 1999. Folia Parasitol (Praha) 47:78
Lom J, Nilsen F, Dyková I (2001) Thelohania contejeani Henneguy, 1892: dimorphic life cycle and taxonomic affinities, as indicated by ultrastructural and molecular study. Parasitol Res 87:860–872
Mansour L, Ben Hassine OK, Vivares CP, Cornillot E (2012) Spraguea lophii (Microsporidia) parasite of the teleost fish, Lophius piscatorius from Tunisian coasts: evidence for an extensive chromosome length polymorphism. Parasitol Int 62(1):66–74
Matos E, Corral L, Azevedo C (2003) Ultrastructural details of the xenoma of Loma myrophis (phylum Microsporidia) and extrusion of the polar tube during autoinfection. Dis Aquat Org 54:203–207
Matthews RA, Matthews BF (1980) Cell and tissue reactions of turbot Scophthalmus maximus (L.) to Tetramicra brevifilum gen.n., sp.n. (Microspora). J Fish Dis 3:495–515
Miki S, Awakura T (1977) The fine structure of Glugea takedai Awakura, 1974 (Microsponda, Nosematidae). Sci Rep Hokkaido Fish Hatchery No 32:1–19
Morrison CM, Sprague V (1981a) Electron microscopical study of a new genus and new species of microsporida in the gills of Atlantic cod Gadus morhua L. J Fish Dis 4:15–32
Morrison CM, Sprague V (1981b) Microsporidian parasites in the gills of salmonid fishes. J Fish Dis 4:371–386
Morsy K, Abdel-Ghaffar F, Mehlhorn H, Bashtar AR, Abdel-Gaber R (2012) Ultrastructure and molecular phylogenetics of a new isolate of Pleistophora pagri sp. nov. (Microsporidia, Pleistophoridae) from Pagrus pagrus in Egypt. Parasitol Res 111(4):1587–1597
Muller A, Trammer T, Chioralia G, Seitz HM, Diehl V, Franzen C (2000) Ribosomal RNA of Nosema algerae and phylogenetic relationship to other microsporidia. Parasitol Res 86:18–23
Nilsen F, Endresen C, Hordvik I (1998) Molecular phylogeny of microsporidians with particular reference to muscle infecting species of fishes. J Euk Microbiol 45:535–543
Ralphs JR, Matthews RA (1986) Hepatic microsporidiosis due to Microgemma hepaticus n. gen., n. sp. in juvenile grey mullet Chelon labrosus. J Fish Dis 9:225–242
Rao SN, Muthulakshmi M, Kanginakudru S, Nagaraju J (2004) Phylogenetic relationships of three new microsporidian isolates from the silkworm, Bombyx mori. J Invertbr Pathol 86:87–95
Rao SN, Nath BS, Saratchandra B (2005) Characterization and phylogenetic relationships among microsporidia infecting silkworm, Bombyx mori, using inter simple sequence repeat (ISSR) and small subunit rRNA (SSUrRNA) sequence analysis. Genome 48:355–366
Rao N, Nath BS, Bhuvaneswari G, Raje S (2007) Genetic diversity and phylogenetic relationships among microsporidia infecting the silkworm, Bombyx mori, using random amplification of polymorphic DNA: morphological and ultrastructural characterization. J Invert Pathol 96:193–204
Raynaud L, Delbac F, Broussolle V, Rabodonirina M, Girault V, Wallon M, Cozon G, Vivares CP, Peyron F (1998) Identification of Encephalitozoon intestinalis in travellers with chronic diarrhea by specific PCR amplification. J Clin Microbiol 36:37–40
Refardt D, Decaestecker E, Johnson PTJ, Vavra J (2008) Morphology, molecular phylogeny and ecology of Binucleata daphniae n. g., sp. n. (Fungi: Microsporidia), a parasite of Daphnia magna Straus, 1820 (Crustacea: Branchiopoda). J Eukaryot Microbiol 55(5):393–408
Sambrook J, Fritsch EF, Maniatis T (1989) “Chapter 14: in vitro amplification of DNA by the polymerase chain reaction”, in molecular 133 cloning: a laboratory manual, 2nd edn. Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory, New York
Sano M, Sato J, Yokoyama H (1998) Occurrence of Beko disease caused by Microsporidiurn seriolae (Microspora) in hatchery-reared juvenile yellowtail. Fish Pathology 33:11–16
Schubert G (1969a) Ultracytologische Untersuchungen an der Spore der Mikrosporidienart. Heterosporis finki, gen. n., sp. n. Parasitol Res 32:59–79
Schubert G (1969b) Elektronenmikroskopische Untersuchungen zur Sporonten und Sporenentwicklung der Mikrosporidienart Heterosporis finki. Parasitol Res 32:80–92
Shaw RW, Kent ML (1999) Fish microsporidia. In: Wittner M, Weiss LM (eds) The Microsporidia and microsporidiosis. ASM, Washington, DC, pp 502–516
Sprague V, Becnel JJ, Edwin IH (1992) Taxonomy of phylum Microspora. Crit Rev Microbiol 18:285–395
Swofford DL (1998) PAUP* Phylogenetic analysis using parsimony and other methods. V. 4.0 Beta. Sinauer associates, Sunderland
Thélohan P (1891) Sporozoaires nouveaux, parasites des muscles des poissons. C R Acad Biol 3:27–29
Thompson JD, Gibson TJ, Plewniak F, Jeanmougin F, Higgins DG (1997) The CLUSTAL_X windows interface: flexible strategies for multiple sequence alignment aided by quality analysis tools. Nucleic Acids Res 25:4876–4882
Tsai SJ, Lo CF, Soichi Y, Wang CH (2003) The characterization of microsporidian isolates (Nosematidae: Nosema) from five important lepidopteran pests in Taiwan. J Invertbr Pathol 83:51–59
Undeen AH, Cockburn AF (1989) The extraction of DNA from microsporidian spores. J Invertbr Pathol 54:132–133
Vávrá, J, Sprague V (1976) Biology of the microsporidia. In: Bulla, L. A., Jr. & Cheng, T. C. (ed.), Comparative Pathobiology, Plenum Press, New York 1:1–369
Vinckier D (1975) Nosemoides gen. n., N. vivieri (Vinckier, Devauchelle and Prensier, 1970) comb. nov (Microsporidie): étude de la differenciation sporoblastique et génèse des differentes structures de la spore. J Protozool 22:170–184
Vossbrinck CR, Baker MD, Didier ES, Debrunner-Vossbrinck BA, Shadduck JA (1993) Ribosomal RNA sequences of Encephalitozoon hellem and Encephalitozoon cuniculi: species identification and phylogenetic construction. J Euk Microhiol 40:354–362
Weiser J (1977) Contribution to the classification of Microsporidia. Vest CS Spol Zool 41:308–320
Weiss LM (2001) Microsporidia Cincinnati. J Eukaryot Microbiol (Suppl.): 475–495
Weissenberg R (1949) Cell growth and cell transformation by intra-cellular parasites. Anat Rec 103:517–518
Weissenberg R (1968) Intracellular development of the microsporidian Glugea anomala in hypertrophying migratory cells of the fish Gasterosteus aculeatus, an example of the formation of the xenoma tumors. J Protozool 15:44–57
Weissenberg R (1976) Microsporidian interactions with host cells. In: Bulla LA, Cheng TC (eds) Comparative pathobiology. Biology of the Microsporidia, Plenum, New York 1: 203–237
Acknowledgments
The authors extend their appreciation to the Distinguished Scientist Fellowship Program at King Saud University, Saudi Arabia for funding this work. Also, this work is supported by the Faculty of Science, Cairo University, Egypt.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Morsy, K., Bashtar, A.R., Abdel-Ghaffar, F. et al. Morphological and phylogenetic description of a new xenoma-inducing microsporidian, Microsporidium aurata nov. sp., parasite of the gilthead seabream Sparus aurata from the Red Sea. Parasitol Res 112, 3905–3915 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00436-013-3580-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00436-013-3580-3