Abstract
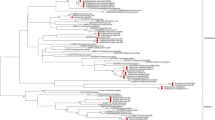
Classification of Demodex mites has long depended on hosts and morphological characteristics. However, the fact that two species coexist in the same host and phenotype is easily influenced by environment causes difficulty and indeterminacy in traditional classification. Genotype, which directly reflects the molecular structure characteristics, is relatively stable. In this study, species identification of four phenotypes of human Demodex mites was conducted. Mites were morphologically classified into four phenotypes: long- and short-bodied Demodex folliculorum with finger-like terminus and Demodex brevis with finger- or cone-like terminus. The mitochondrial 16S ribosomal DNA (rDNA) fragment of individual mite was amplified, cloned, sequenced, and aligned. Sequence divergences, genetic distances, transition/transversion rates, and phylogenetic trees were analyzed. The results demonstrated that the 16S rDNA sequence of three phenotypes with finger-like terminus was 337 bp, and that of phenotype with cone-like terminus was 342 bp. The divergences, genetic distances, and transition/transversion rates among the three phenotypes with finger-like terminus were 0.0–2.7 %, 0.000–0.029, and 5.0–7/0 (5/1–7/0), respectively, indicating an intraspecific variation. Yet, those between these three phenotypes and the one with cone-like terminus were 21.6–22.8 %, 2.510–2.589, and 0.47–0.59 (22/47–27/46), respectively, suggesting an interspecific variation. The five phylogenetic trees showed that the three phenotypes with finger-like terminus clustered into one branch, while the phenotype with cone-like terminus clustered into another. In conclusion, terminus is a major morphological characteristic for the identification of human Demodex species. The three phenotypes with finger-like terminus belong to D. folliculorum, while the phenotype with cone-like terminus belongs to D. brevis. Molecular identification can verify and replenish morphological identification.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Desch CE, Nutting WB (1972) Demodex folliculorum (Simon) and Demodex brevis (Akbulatova) of man: redescription and reevaluation. J Parasit 58:167–177
de Rojas M, Riazzo C, Callejón R, Guevara D, Cutillas C (2012) Molecular study on three morphotypes of Demodex mites (Acarina: Demodicidae) from dogs. Parasitol Res 111:2165–2172
Hebert PDN, Ratnasingham S, deWaard JR (2003a) Barcoding animal life: cytochrome c oxidase subunit 1 divergences among closely related species. Proc R Soc Lond B 270(Suppl):S96–S99
Hebert PD, Cywinska A, Ball SL, deWaard JR (2003b) Biological identifications through DNA barcodes. Proc R Soc Lond B 270:313–321
Hillier A, Desch CE (2002) Large-bodied Demodex mite infestation in 4 dogs. J Am Vet Med Assoc 220:623–627
Kumar S, Nei M, Dusley J, Tamura K (2008) MEGA: a biologist centric software for evolutionary analysis of DNA and protein sequences. Brief Bioinform 9:299–306
Li CP (2009) Medical arthropodology. People’s Medical Publishing House, Beijing
Mueller RS, Bettenay SV (1999) An unusual presentation of canine demodicosis caused by a long-bodied Demodex mite in a Lakeland Terrier. Aust Vet Pract 29:128-+
Sastre N, Ravera I, Villanueva S, Altet L, Bardagi M, Sanchez A, Francino O, Ferrer L (2012) Phylogenetic relationships in three species of canine Demodex mite based on partial sequences of mitochondrial 16S rDNA. Vet Dermatol 23:509–e101
Tamura K, Dudley J, Nei M, Kumar S (2007) MEGA4: molecular analysis (MEGA) software version 4.0. Mol Biol Evol 24:1596–1599
Thompson JD, Gibson TJ, Plewniak F, Jeanmougin F, Higgins DG (1997) The ClustalX windows interface: flexible strategies for multiple sequence alignment aided by quality analysis tools. Nucleic Acid Res 25:4876–4882
Xie HX, Liu SL, Xu YH, Xu MQ (1982) Taxonomy of the family Demodecidae and new subspecies. Acta Zootaxonomica Sin 7:256–269
Zhao YE, Guo N, Li C, Lu ZH (2007) The dynamic observation of the morphologic structure and activity of human Demodex in different stages. Chin J Vector Bio Control 18:120–123
Zhao YE, Guo N, Wu LP (2009) The effect of temperature on the viability of Demodex folliculorum and Demodex brevis. Parasitol Res 105:1623–1628
Zhao YE, Wu LP, Peng Y, Cheng H (2010) Retrospective analysis of the association between Demodex infestation and rosacea. Arch Dermatol 146:896–902
Zhao YE, Guo N, Wu LP (2011a) Influence of temperature and medium on viability of Demodex folliculorum and Demodex brevis (Acari: Demodicidae). Exp Appl Acarol 54:421–425
Zhao YE, Guo N, Xun M, Xu JR, Wang M, Wang DL (2011b) Sociodemographic characteristics and risk factor analysis of Demodex infestation (Acari: Demodicidae). J Zhejiang Univ-Sci B 12:998–1007
Zhao YE, Peng Y, Wang XL, Wu LP, Wang M, Yan HL, Xiao SX (2011c) Facial dermatosis associated with Demodex: a case–control study. J Zhejiang Univ-Sci B 12:1008–1015
Zhao YE, Wu LP (2012a) Phylogenetic relationships in Demodex mites (Acari: Demodicidae) based on mitochondrial 16S rDNA partial sequences. Parasitol Res 111:1113–1121
Zhao YE, Wu LP (2012b) RAPD-SCAR marker and genetic relationship analysis of three Demodex species (Acari: Demodicidae). Parasitol Res 110:2395–2402
Zhao YE, Xu JR, Li H, Wu LP, Wang ZH (2012a) Complete sequence analysis of 18S rDNA based on genomic DNA extraction from individual Demodex mites (Acari: Demodicidae). Exp Parasitol 131:45–51
Zhao YE, Wu LP, Hu L, Xu JR (2012b) Association of blepharitis with Demodex: a meta-analysis. Ophthalmic Epidemiol 19:95–102
Zhao YE, Hu L, Wu LP, Ma JX (2012c) A meta-analysis of association between acne vulgaris and Demodex infestation. J Zhejiang Univ-Sci B 13:192–202
Zhao YE, Wang ZH, Xu Y, Xu JR, Liu WY, Wei M, Wang CY (2012d) Cloning and sequence analysis of chitin synthase gene fragments of Demodex mites. J Zhejiang Univ-Sci B 13:763–768
Zhao YE, Wu LP, Hu L, Xu Y, Wang ZH, Liu WY (2012e) Sequencing for complete rDNA sequences (18S, ITS1, 5.8S, ITS2, and 28S rDNA) of Demodex and phylogenetic analysis of Acari based on 18S and 28S rDNA. Parasitol Res 111:2109–2114
Zhao YE, de Rojas M (2013) Advances on the research on systematics of Demodex. Int J Med Parasit Dis 40:166–170
Zhao YE, Ma JX, Hu L, Wu LP, de Rojas M (2013) Identification between Demodex folliculorum (Acari: Demodicidae) isolates from China and Spain based on mitochondrial cox1 sequences. J Zhejiang Univ Sci B. doi:10.1631/jzus.B1200363
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by a grant from the National Natural Science Foundation of China (no. 81271856).
Conflict of interest
None.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhao, YE., Hu, L. & Ma, JX. Molecular identification of four phenotypes of human Demodex mites (Acari: Demodicidae) based on mitochondrial 16S rDNA. Parasitol Res 112, 3703–3711 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00436-013-3558-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00436-013-3558-1