Abstract
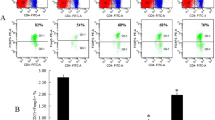
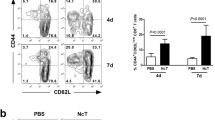
As one of food-borne parasitic diseases, toxoplasmosis entails the risk of developing reactivation in immunocompromised patients. The synthetic dipeptide pidotimod is a potent immunostimulating agent that improves the immunodefenses in immunodepression. To investigate the efficacy of pidotimod as a preventive treatment, we used a murine model of reactivated toxoplasmosis with cyclophosphamide (CY)-induced immunosuppression. Pidotimod administration significantly restored the body weight and spleen organ index, increased survival time (from 70 to 90 %), and decreased the parasitemia (from 80 to 35 %) of CY-induced mice with reactivated toxoplasmosis. Cytokine profiles and CD4+ T cells subpopulation analyses by Cytometric Bead Array and flow cytometry demonstrated that pidotimod treatment resulted in a significant upregulation of pro-inflammatory cytokines (IFN-γ, TNF-α, and IL-2) and Th1 cells (from 3.73 ± 0.39 to 5.88 ± 0.46 %) after CY induction in infected mice. Additionally, histological findings and parasite DNA quantification revealed that mice administered with pidotimod had a remarkable reduction of parasite burden (two-log) and amelioration of histopathology in the brains. The in vitro studies showed that pidotimod significantly restored concanavalin A-induced splenocyte proliferation and pro-inflammatory cytokines in the supernatants of splenocyte culture. It could be concluded that the administration of pidotimod in immunocompromised mice significantly increases the Th1-biased immune response, prolongs survival time, and ameliorates the load of parasites in the blood. This is the first report of the preventive effect of pidotimod on reactivated toxoplasmosis.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adams K, Allen JA, Brooker PC, Henderson L, Jones E, Proudlock RJ, Mailland F, Coppi G (1994) Genotoxicity testing of pidotimod in vitro and in vivo. Drug Res (Stuttg) 44(12A):1454–1459
Barragan A, Sibley LD (2002) Transepithelial migration of Toxoplasma gondii is linked to parasite motility and virulence. J Exp Med 195(12):1625–1633
Chiarenza A, Iurato MP, Barbera N, Lempereur L, Cantarella G, Scapagnini U, Bernardini R (1994) Modulating effects of the synthetic thymic dipeptide pidotimod on the immune system in the aging rat. Pharmacol Toxicol 74(4–5):262–266
Coppi G, Amico-Roxas M, Berte F, Bussi R, Gnemi P, Harling RJ, Mailland F, Manzardo S, Massey JE, Spencer-Briggs DJ et al (1994) Toxicological evaluation of pidotimod. Drug Res (Stuttg) 44(12A):1448–1453
Cortez E, Stumbo AC, Oliveira M, Barbosa HS, Carvalho L (2009) Statins inhibit Toxoplasma gondii multiplication in macrophages in vitro. Int J Antimicrob Agents 33(2):185–186
Dellacasa-Lindberg I, Hitziger N, Barragan A (2007) Localized recrudescence of Toxoplasma infections in the central nervous system of immunocompromised mice assessed by in vivo bioluminescence imaging. Microbes Infect 9(11):1291–1298
Di Renzo M, Pasqui AL, Bruni F, Saletti M, Bova G, Chiarion C, Girardello R, Ferri P, Auteri A (1997) The in vitro effect of pidotimod on some immune functions in cancer patients. Immunopharmacol Immunotoxicol 19(1):37–51
Du XF, Jiang CZ, Wu CF, Won EK, Choung SY (2008) Synergistic immunostimulating activity of pidotimod and red ginseng acidic polysaccharide against cyclophosphamide-induced immunosuppression. Arch Pharm Res 31(9):1153–1159
Frawley R, White K Jr, Brown R, Musgrove D, Walker N, Germolec D (2011) Gene expression alterations in immune system pathways in the thymus after exposure to immunosuppressive chemicals. Environ Health Perspect 119(3):371–376
Gazzinelli R, Xu Y, Hieny S, Cheever A, Sher A (1992) Simultaneous depletion of CD4+ and CD8+ T lymphocytes is required to reactivate chronic infection with Toxoplasma gondii. J Immunol 149(1):175–180
Gazzinelli RT, Eltoum I, Wynn TA, Sher A (1993) Acute cerebral toxoplasmosis is induced by in vivo neutralization of TNF-alpha and correlates with the down-regulated expression of inducible nitric oxide synthase and other markers of macrophage activation. J Immunol 151(7):3672–3681
Gharavi MJ, Jalali S, Khademvatan S, Heydari S (2011) Detection of IgM and IgG anti-Toxoplasma antibodies in renal transplant recipients using ELFA, ELISA and ISAGA methods: comparison of pre- and post-transplantation status. Ann Trop Med Parasitol 105(5):367–371
Giagulli C, Noerder M, Avolio M, Becker PD, Fiorentini S, Guzman CA, Caruso A (2009) Pidotimod promotes functional maturation of dendritic cells and displays adjuvant properties at the nasal mucosa level. Int Immunopharmacol 9(12):1366–1373
Giampietri A, Bonmassar E, Goldin A (1978) Drug induced modulation of immune responses in mice: effects of 5-(3,3-dimethyl-1-triazeno)-imidazole-4-carboxamide (DTIC) and cyclophosphamide (Cy). J Immunopharmacol 1(1):61–86
Guiton R, Vasseur V, Charron S, Arias MT, Van Langendonck N, Buzoni-Gatel D, Ryffel B, Dimier-Poisson I (2010) Interleukin 17 receptor signaling is deleterious during Toxoplasma gondii infection in susceptible BL6 mice. J Infect Dis 202(3):427–435
Ho IC, Vorhees P, Marin N, Oakley BK, Tsai SF, Orkin SH, Leiden JM (1991) Human GATA-3: a lineage-restricted transcription factor that regulates the expression of the T cell receptor alpha gene. EMBO J 10(5):1187–1192
Israelski DM, Remington JS (1993) Toxoplasmosis in patients with cancer. Clin Infect Dis 17(Suppl 2):S423–S435
Jensen KD, Wang Y, Wojno ED, Shastri AJ, Hu K, Cornel L, Boedec E, Ong YC, Chien YH, Hunter CA, Boothroyd JC, Saeij JP (2011) Toxoplasma polymorphic effectors determine macrophage polarization and intestinal inflammation. Cell Host Microbe 9(6):472–483
Jost C, Reiter-Owona I, Liesenfeld O (2007) The timing of sulfadiazine therapy impacts the reactivation of latent Toxoplasma infection in IRF-8−/− mice. Parasitol Res 101(6):1603–1609
Katlama C, De Wit S, O’Doherty E, Van Glabeke M, Clumeck N (1996) Pyrimethamine–clindamycin vs. pyrimethamine–sulfadiazine as acute and long-term therapy for toxoplasmic encephalitis in patients with AIDS. Clin Infect Dis 22(2):268–275
Kelly MN, Kolls JK, Happel K, Schwartzman JD, Schwarzenberger P, Combe C, Moretto M, Khan IA (2005) Interleukin-17/interleukin-17 receptor-mediated signaling is important for generation of an optimal polymorphonuclear response against Toxoplasma gondii infection. Infect Immun 73(1):617–621
Lachenmaier SM, Deli MA, Meissner M, Liesenfeld O (2011) Intracellular transport of Toxoplasma gondii through the blood–brain barrier. J Neuroimmunol 232(1–2):119–130
Manzardo S, Falcone A, Pinzetta A, Ieva G, Coppi G (1994) General pharmacology of pidotimod and testing for drug interactions. Drug Res (Stuttg) 44(12A):1441–1447
Mazur L, Czyzewska A, Bochenek M (2002) Flow cytometric detection of apoptotic bone marrow cells with fractional DNA content after application of WR-2721, cyclophosphamide, cisplatin, and exposure of mice to gamma rays. Hum Exp Toxicol 21(6):335–341
Mehlhorn H, Dankert W, Hartman PG, Then RL (1995) A pilot study on the efficacy of epiroprim against developmental stages of Toxoplasma gondii and Pneumocystis carinii in animal models. Parasitol Res 81(4):296–301
Meneceur P, Bouldouyre MA, Aubert D, Villena I, Menotti J, Sauvage V, Garin JF, Derouin F (2008) In vitro susceptibility of various genotypic strains of Toxoplasma gondii to pyrimethamine, sulfadiazine, and atovaquone. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 52(4):1269–1277
Migliorati G, Coppi G, D’Adamio F, Pagliacci C, Nicoletti I, Riccardi C (1992) Immunopharmacology of pidotimod: effect on natural killer cell activity and thymocyte cell death. Pharmacol Res 26(Suppl 2):154–155
Migliorati G, Nicoletti I, Riccardi C (1994) Immunomodulating activity of pidotimod. Drug Res (Stuttg) 44(12A):1421–1424
Montoya JG, Liesenfeld O (2004) Toxoplasmosis. Lancet 363(9425):1965–1976
Scholer N, Krause K, Kayser O, Muller RH, Borner K, Hahn H, Liesenfeld O (2001) Atovaquone nanosuspensions show excellent therapeutic effect in a new murine model of reactivated toxoplasmosis. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 45(6):1771–1779
Silva NM, Vieira JC, Carneiro CM, Tafuri WL (2009) Toxoplasma gondii: the role of IFN-gamma, TNFRp55 and iNOS in inflammatory changes during infection. Exp Parasitol 123(1):65–72
Song X, Shen J, Wen H, Zhong Z, Luo Q, Chu D, Qi Y, Xu Y, Wei W (2011) Impact of Schistosoma japonicum infection on collagen-induced arthritis in DBA/1 mice: a murine model of human rheumatoid arthritis. PLoS One 6(8):e23453
Sumyuen MH, Garin YJ, Derouin F (1996) Effect of immunosuppressive drug regimens on acute and chronic murine toxoplasmosis. Parasitol Res 82(8):681–686
Suzuki Y, Joh K, Kwon OC, Yang Q, Conley FK, Remington JS (1994) MHC class I gene(s) in the D/L region but not the TNF-alpha gene determines development of toxoplasmic encephalitis in mice. J Immunol 153(10):4649–4654
Xavier GA, Cademartori BG, Cunha Filho NA, Farias NA (2013) Evaluation of seroepidemiological toxoplasmosis in HIV/AIDS patients in the south of Brazil. Rev Inst Med Trop Sao Paulo 55(1):25–30
Yang X, Huang B, Chen J, Huang S, Zheng H, Lun ZR, Shen J, Wang Y, Lu F (2012) In vitro effects of aqueous extracts of Astragalus membranaceus and Scutellaria baicalensis Georgi on Toxoplasma gondii. Parasitol Res 110(6):2221–2227
Yoshida H, Miyazaki Y, Wang S, Hamano S (2007) Regulation of defense responses against protozoan infection by interleukin-27 and related cytokines. J Biomed Biotechnol 2007(3):79401
Zhao Q, Zhang M, Hong L, Zhou K, Lin Y (2010) Evaluation of drug effects on Toxoplasma gondii nuclear and plastid DNA replication using real-time PCR. Parasitol Res 106(5):1257–1262
Acknowledgments
This work was funded by the National Basic Research Program of China (973 Program, Grant No. 2010CB530001) and Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant Nos. 81171605 and 81271864). Our thanks to Prof. Geoff Hide at University of Salford, Salford, UK for his kind language polishing and comments.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Xing-Xing Huo and Lin Wang contributed equally to this work.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Huo, XX., Wang, L., Chen, ZW. et al. Preventive effect of pidotimod on reactivated toxoplasmosis in mice. Parasitol Res 112, 3041–3051 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00436-013-3488-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00436-013-3488-y