Abstract
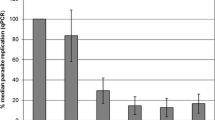
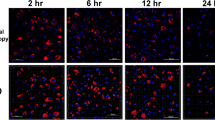
Toxoplasma (T.) gondii is known to infect various cell types including macrophages. In the present study, we generated monocyte-derived macrophage cultures from chicken blood. By flow cytometrical analysis, 84.5 % of the cultivated cells showed typical macrophage properties. Macrophage cultures were cultivated at either 37 °C or 40 °C, respectively, and were infected 72 to 96 h post isolationem with tachyzoites of the T. gondii type II strain ME49 at a rate of 7.5 tachyzoites per host cell. Light microscopical investigations revealed incorporation of tachyzoites into the macrophages and gradual destruction of the infected macrophage culture. Parasite multiplication was observed by a quantitative real time PCR (qPCR) based on the 529-bp fragment specific for T. gondii. Samples were drawn 1 h post infectionem (p.i.), as well as 12, 24, 36, 48, and 72 h p.i. The parasite replication curve showed a transient decrease of parasite stages 12 h p.i. followed by a tachyzoite multiplication. The comparison of different culture conditions showed a significantly higher replication rate of T. gondii at 37 °C (median value 48 h p.i., 289.2 % of the initial tachyzoite number) compared to cultures incubated at 40 °C (median value 48 h p.i., 73.1 % of the initial tachyzoite number) throughout the observation period (P < 0.05). In general, replication rates were significantly lower than in a standard VERO cell cultures at 37 °C (P < 0.05). The observed differences were attributed to the physiological chicken macrophage reaction at 40 °C probably approximating the situation in vivo.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Anderson SE Jr, Remington JS (1974) Effect of normal and activated human macrophages on Toxoplasma gondii. J Exp Med 139:1154–1174
Bennett B (1966) Isolation and cultivation in vitro of macrophages from various sources in the mouse. Am J Pathol 48(1):165–181
Berndt A, Wilhelm A, Jugert C, Pieper J, Sachse K, Methner U (2007) Chicken cecum immune response to Salmonella enterica serovars of different levels of invasiveness. Infect Immun 75:5993–6007
Bouchot A, Millot JM, Charpentier S, Bonhomme A, Villena I, Aubert D, Pinon JM (2001) Membrane potential changes after infection of monocytes by Toxoplasma gondii. Int J Parasitol 31:1114–1120
Canessa A, Pistoia V, Roncella S, Merli A, Melioli G, Terragna A, Ferrarini M (1988) An in vitro model for Toxoplasma infection in man. Interaction between CD4+ monoclonal T cells and macrophages results in killing of trophozoites. J Immunol 140:3580–3588
Channon JY, Seguin RM, Kasper LH (2000) Differential infectivity and division of Toxoplasma gondii in human peripheral blood leukocytes. Infect Immun 68:4822–4826
DaMatta RA, Seabra SH, Manhães L, de Souza W (2000) Nitric oxide is not involved in the killing of Trypanosoma cruzi by chicken macrophages. Parasitol Res 86:239–243
da Silva DS, Bahia-Oliveira LM, Shen SK, Kwok OC, Lehman T, Dubey JP (2003) Prevalence of Toxoplasma gondii in chickens from an area in southern Brazil highly endemic to humans. J Parasitol 89:394–396
Davies DE, Lloyd JB (1989) Monocyte-to-macrophage transition in vitro. A systematic study using human cells isolated by fractionation on Percoll. J Immunol Methods 118:9–16
Davison F, Kaspers B, Schat KA (2008) Avian Immunology. Academic Press by Elsevier Ltd., London
de Camargo MC, Antunes CM, Chiari Cde A (1995) Epidemiology of Toxoplasma gondii infection in the municipality of Ribeirâo das Neves, MG. I. Importance of domestic animals as sources of T. gondii infection in humans. Rev Soc Bras Med Trop 28:211–214
de Almeida MC, Silva AC, Barral A, Barral Netto M (2000) A Simple Method for Human Peripheral Blood Monocyte Isolation. Mem Inst Oswaldo Cruz 95:221–223
Devada K, Anandan R, Dubey JP (1998) Serologic prevalence of Toxoplasma gondii in chickens in Madras, India. J Parasitol 84:621–622
Diab MR, El-Bahy MM (2008) Toxoplasma gondii: virulence of tachyzoites in serum free media at different temperatures. Exp Parasitol 118:75–79
Dubey JP, Graham DH, Blackston CR, Lehmann T, Gennari SM, Ragozo AM, Nishi SM, Shen SK, Kwok OC, Hill DE, Thulliez P (2002) Biological and genetic characterisation of Toxoplasma gondii isolates from chickens (Gallus domesticus) from São Paulo, Brazil: unexpected findings. Int J Parasitol 32:99–105
Dubey JP, Edelhofer R, Marcet P, Vianna MC, Kwok OC, Lehmann T (2005) Genetic and biologic characteristics of Toxoplasma gondii infections in free-range chickens from Austria. Vet Parasitol 133:299–306
Dubey JP, Velmurugan GV, Chockalingam A, Pena HF, de Oliveira LN, Leifer CA, Gennari SM, Bahia Oliveira LM, Su C (2008) Genetic diversity of Toxoplasma gondii isolates from chickens from Brazil. Vet Parasitol 157:299–305
Dubey JP (2010) Toxoplasma gondii infections in chickens (Gallus domesticus): prevalence, clinical disease, diagnosis and public health significance. Zoonoses Public Health 57:60–73
Dubey JP, Velmurugan GV, Rajendran C, Yabsley MJ, Thomas NJ, Beckmen KB, Sinnett D, Ruid D, Hart J, Fair PA, McFee WE, Shearn-Bochsler V, Kwok OC, Ferreira LR, Choudhary S, Faria EB, Zhou H, Felix TA, Su C (2011a) Genetic characterisation of Toxoplasma gondii in wildlife from North America revealed widespread and high prevalence of the fourth clonal type. Int J Parasitol 41:1139–1147
Dubey JP, Rajendran C, Ferreira LR, Martins J, Kwok OC, Hill DE, Villena I, Zhou H, Su C, Jones JL (2011b) High prevalence and genotypes of Toxoplasma gondii isolated from goats, from a retail meat store, destined for human consumption in the USA. Int J Parasitol 41:827–833
Dubey JP, Passos LM, Rajendran C, Ferreira LR, Gennari SM, Su C (2011c) Isolation of viable Toxoplasma gondii from feral guinea fowl (Numida meleagris) and domestic rabbits (Oryctolagus cuniculus) from Brazil. J Parasitol 97:842–845
Edvinsson B, Lappalainen M, Evengård B (2006) ESCMID Study Group for Toxoplasmosis. Real-time PCR targeting a 529-bp repeat element for diagnosis of toxoplasmosis. Clin Microbiol Infect 12:131–136
Enbergs H, Kriesten K (1969) Fine structure of the hen's monocytes. Z Zellforsch Mikrosk Anat 97:377–382
Fouts AE, Boothroyd JC (2007) Cellular Response to Infection. Ajioka J., Soldati D. Toxoplasma Molecular and cellular biology, Horizont Bioscience, Norfolk, UK, pp 171–190
Guillermo LV, DaMatta RA (2004) Nitric oxide inhibition after Toxoplasma gondii infection of chicken macrophage cell lines. Poult Sci 83:776–782
Hwang IY, Quan JH, Ahn MH, Ahmed HA, Cha GH, Shin DW, Lee YH (2010) Toxoplasma gondii infection inhibits the mitochondrial apoptosis through induction of Bcl-2 and HSP70. Parasitol Res 107:1313–1321
Jensen MD, Wallach DF, Lin PS (1974) Comparative growth characteristics of VERO cells on gas-permeable and conventional supports. Exp Cell Res 84:271–281
Jones TC, Yeh S, Hirsch JG (1972) The interaction between Toxoplasma gondii and mammalian cells. I. Mechanism of entry and intracellular fate of the parasite. J Exp Med 136:1157–1172
Jones TC, Len L, Hirsch JG (1975) Assessment in vitro of immunity against Toxoplasma gondii. J Exp Med 141:466–482
Kaneto CN, Costa AJ, Paulillo AC, Moraes FR, Murakami TO, Meireles MV (1997) Experimental toxoplasmosis in broiler chicks. Vet Parasitol 69:203–210
Kasper LH, Khan IA, Ely KH, Buelow R, Boothroyd JC (1992) Antigen-specific (p30) mouse CD8+ T cells are cytotoxic against Toxoplasma gondii-infected peritoneal macrophages. J Immunol 148:1493–1498
Lambert H, Barragan A (2010) Modelling parasite dissemination: Host cell subversion and immune evasion by Toxoplasma gondii. Cell Microbiol 12:292–300
Lambert H, Dellacasa-Lindberg I, Barragan A (2011) Migratory responses of leukocytes infected with Toxoplasma gondii. Microbes Infect 13:96–102
Lüder CG, Gross U (2005) Apoptosis and its modulation during infection with Toxoplasma gondii: molecular mechanisms and role in pathogenesis. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol 289:219–237
Marim FM, Silveira TN, Lima DS Jr, Zamboni DS (2010) A method for generation of bone marrow-derived macrophages from cryopreserved mouse bone marrow cells. PLoS One 5:e15263
Meirelles MN, De Souza W (1985) Killing of Trypanosoma cruzi and Leishmania mexicana, and survival of Toxoplasma gondii, in chicken macrophages in vitro. J Submicrosc Cytol 17:327–334
Mordue DG, Sibley LD (2003) A novel population of Gr-1+−activated macrophages induced during acute toxoplasmosis. J Leukoc Biol 74:1015–1025
Murray HW (1986) Cellular resistance to protozoal infection. Annu Rev Med 37:61–69
Nguyen BT, Stadtsbaeder S (1976) Spontaneous interaction in vitro between lymphocytes and syngeneic peritoneal macrophages of mice. Infect Immun 13:884–889
Onaga H, Tajima M, Ishii T (1983) Activation of macrophages by culture fluid of antigen-stimulated spleen cells collected from chickens immunized with Eimeria tenella. Vet Parasitol 13:1–11
Ong YC, Boyle JP, Boothroyd JC (2011) Strain-dependent host transcriptional responses to Toxoplasma infection are largely conserved in mammalian and avian hosts. PLoS One 6(10):e26369. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0026369
Pfefferkorn ER, Pfefferkorn LC (1976) Toxoplasma gondii: Isolation and preliminary characterization of temperature- sensitive mutants. Exp Parasitol 39:365–376
Pieper J, Methner U, Berndt A (2011) Characterization of avian gamma/delta T-cell subsets after Salmonella Typhimurium infection of chicks. Infect Immun 79:822–829
Quéré P, Pierre J, Hoang MD, Esnault E, Domenech J, Sibille P, Dimier-Poisson I (2013) Presence of dendritic cells in chicken spleen cell preparations and their functional interaction with the parasite Toxoplasma gondii. Vet Immunol Immunopathol 153:57–69
Seabra SH, de Souza W, DaMatta RA (2002) Toxoplasma gondii partially inhibits nitric oxide production of activated murine macrophages. Exp Parasitol 100:62–70
Unno A, Suzuki K, Xuan X, Nishikawa Y, Kitoh K, Takashima Y (2008) Dissemination of extracellular and intracellular Toxoplasma gondii tachyzoites in the blood flow. Parasitol Int 57:515–518
Vissers MC, Jester SA, Fantone JC (1988) Rapid purification of human peripheral blood monocytes by centrifugation through Ficoll-Hypaque and Sepracell-MN. J Immunol Methods 110:203–207
Wigley P, Hulme SD, Bumstead N, Barrow PA (2002) In vivo and in vitro studies of genetic resistance to systemic salmonellosis in the chicken encoded by the SAL1 locus. Microbes Infect 4:1111–1120
Zia-Ali N, Fazaeli A, Khoramizadeh M, Ajzenberg D, Dardé M, Keshavarz-Valian H (2007) Isolation and molecular characterization of Toxoplasma gondii strains from different hosts in Iran. Parasitol Res 101:111–115
Acknowledgements
The study was funded by a grant of the Karl-Enigk-Stiftung. The authors wish to thank the cooperating institutes of the Centre for Infectious Diseases of the Faculty of Veterinary Medicine, University of Leipzig, for the consistent technical support.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Malkwitz, I., Berndt, A., Daugschies, A. et al. Long-term investigations on Toxoplasma gondii-infected primary chicken macrophages. Parasitol Res 112, 3115–3122 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00436-013-3486-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00436-013-3486-0