Abstract
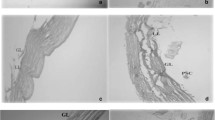
Cystic echinococcosis, caused by the metacestode stage of Echincoccus granulosus, remains endemic in many regions around the world. The present work evaluated whether or not a superabsorbent polymer (SAP) and ultrasound contrast agent (UCA) alone or in combination could enhance damage efficacy of high-intensity focused ultrasound (HIFU) on hydatid cysts in vitro. HIFU of 100 W acoustic power, with the aid of 0.1 ml UCA and 0.1 g SAP alone or in combination, was used to ablate hydatid cysts in vitro. The comparison of ultrasound image for each layer of hydatid cyst before and after HIFU ablation was made immediately, and the protoscolices of the cysts were stained by eosin exclusion assay, and the structures of protoscolices were observed by light microscopy. To understand the destructive effects of HIFU, the pathological changes in cyst walls of hydatid cyst ablated with HIFU were examined. The results demonstrated that HIFU had some lethal effect on hydatid cysts: echo enhancement of ultrasound image, increase of mortality rate of protoscolices, serious structural damage of protoscolices, and complete destruction or even disappearance of laminated layer and germinal layer was observed in the group of HIFU combined with UCA and SAP alone or in combination. It was found that the destructive effect of HIFU aided with a combination of UCA and SAP to hydatid cysts was more effective than that of HIFU just aided with UCA or SAP alone. These results suggested that UCA and SAP might be used as a HIFU enhancing agent to improve the efficacy of HIFU ablation to hydatid cysts, which could be a possible therapeutic option for cystic echinococcosis.















Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abdul-Salam J, Farah M (1988) Hydatidosis in camels in Kuwait. Parasitol Res 74(3):267–270
Al-Bataineh O, Jenne J, Huber P (2012) Clinical and future applications of high intensity focused ultrasound in cancer. Cancer Treat Rev 38(5):346–353
Arif SH, Malik AA, Khaja AR, Dass TA, Naikoo ZA (2011) Role of albendazole in the management of hydatid cyst liver. Saudi J Gastroenterol 17(5):343–347
Borden MA, Qin S, Ferrara KW (2010) Ultrasound contrast agents. In: Molecular imaging. BC Decker Inc., Hamilton, pp.425–444
Chartier-Kastler E, Yonneau L, Conort P, Haertig A, Bitker MO, Richard F (2000) High intensity focused ultrasound (HIFU) in urology. Prog Urol 10(6):1108–1117
Crouzet S, Murat FJ, Pasticier G, Cassier P, Chapelon JY, Gelet A (2010) High intensity focused ultrasound (HIFU) for prostate cancer: current clinical status, outcomes and future perspectives. Int J Hyper 26(8):796–803
Davis A, Pawlowski Z, Dixon H (1986) Multicentre clinical trials of benzimidazolecarbamates in human echinococcosis. B WHO 64(3):383–388
Deng FL, Jiang ZD, Zhou JZ, Li R, Shen JL, Sun LQ (2010) Analysis of clinical complications of focused ultrasound intreatment of uterine fibroids. Ultrasound Clin Med 12(005):326–328
Ding H, Wang WP, Huang BJ, Wei RX, He NA, Qi Q, Li CL (2005) Imaging of focal liver lesions low-mechanical-index real-time ultrasonography with SonoVue. J Ultras Med 24(3):285–297
Elissondo M, Dopchiz M, Ceballos L, Alvarez L, Sánchez Bruni S, Lanusse C, Denegri G (2006) In vitro effects of flubendazole on Echinococcus granulosus protoscoleces. Parasitol Res 98(4):317–323
Elissondo M, Ceballos L, Dopchiz M, Andresiuk V, Alvarez L, Sánchez Bruni S, Lanusse C, Denegri G (2007) In vitro and in vivo effects of flubendazole on Echinococcus granulosus metacestodes. Parasitol Res 100(5):1003–1009
Elissondo MC, Ceballos L, Alvarez L, Sánchez Bruni S, Lanusse C, Denegri G (2009) Flubendazole and ivermectin in vitro combination therapy produces a marked effect on Echinococcus granulosus protoscoleces and metacestodes. Parasitol Res 105(3):835–842
Frider B, Larrieu E (2010) Treatment of liver hydatidosis: how to treat an asymptomatic carrier? World J Gastroentero 16(33):4123–4129
Illing R, Kennedy J, Wu F, Ter Haar G, Protheroe A, Friend P, Gleeson F, Cranston D, Phillips R, Middleton M (2005) The safety and feasibility of extracorporeal high-intensity focused ultrasound (HIFU) for the treatment of liver and kidney tumours in a Western population. Brit J Cancer 93(8):890–895
Junghanss T, da Silva AM, Horton J, Chiodini PL, Brunetti E (2008) Clinical management of cystic echinococcosis: state of the art, problems, and perspectives. AmJTrop Med Hyg 79(3):301–311
Kennedy J, Ter Haar G, Cranston D (2003) High intensity focused ultrasound: surgery of the future? Brit J Radiol 76(909):590–599
Kiatkamjornwong S (2007) Superabsorbent polymers and superabsorbent polymer composites. Sci Asia 33(s1):39–43
Kong J, Ye B, Zhang J, Han XM, Yang YH, Li FQ (2011) Effect of high intensity focused ultrasound on Echinococcus granulosus protoscolices with the aid of microbubble contrast agent. Chin J Zoon 27(8):687–691
Li XJ, Wang Y (2008) Experimental research on ultrasonicwave promoting traditional Chinese medicine penetrating skin. J Pract Med Techn 13(15):1650–1650
Li CX, Xu GL, Li JJ, Luo GY, Zhang R, Shan HB (2003) Discussion on the prevention and treatment of the high-intensity focused ultrasound treatment of malignant complications. Chin J Ultrasonogr 5(12):310–311
Li CX, Xu GL, Jiang ZY, Li JJ, Luo GY, Shan HB, Zhang R, Li Y (2004) Analysis of clinical effect of high-intensity focused ultrasound on liver cancer. World J Gastroentero 10(15):2201–2204
Liu XT, Hong M, Xu GL, Li CX, LI JJ, Luo Q (2004) Observation and nursing of the complication of 200 cases of malignant tumor with high intensity focusing ultrasound. Chin J Prac Nurs 20(7):9–10
Luo W, Zhou XD, Ren XL, He GB, He JG, Zheng MJ, Zhang M (2007) Enhanced effects of ultrasound contrast agent on HIFU ablation: pathological study. Chin J Ultras Med 23(3):173–175
Men S, Hekimoğlu B, Yücesoy C, Arda I, Baran I (1999) Percutaneous treatment of hepatic hydatid cysts: an alternative to surgery. Am J Roentgenol 172(1):83–89
Moazeni M, Larki S (2010) In vitro effectiveness of acidic and alkline solutions on scolices of hydatid cyst. Parasitol Res 106(4):853–856
Moro P, Schantz P (2006) Echinococcosis: historical landmarks and progress in research and control. Ann Trop Med Parasit 100(8):703–714
Moro P, Schantz PM (2009) Echinococcosis: a review. Int J Infect Dis 13(2):125–133
Righetti R, Kallel F, Stafford RJ, Price RE, Krouskop TA, Hazle JD, Ophir J (1999) Elastographic characterization of HIFU-induced lesions in canine livers. Ultrasound Med Biol 25(7):1099–1113
Robbin ML (2001) Ultrasound contrast agents: a promising future. Radiol Clin N Am 39(3):399–414
Schneider M, Arditi M, Barrau MB, Brochot J, Broillet A, Ventrone R, Yan F (1995) BR1: a new ultrasonographic contrast agent based on sulfur hexafluoride-filled microbubbles. Invest Radiol 30(8):451–457
Sha WH, Li YY, Nie YQ, Wang ZB, Li FQ, Li CY, Wang YQ, Gong XB, Ma P (2004) Focal region of high intensity focused ultrasound combined with ultrasound contrast agent on rabbit liver. Chin J Ultrasonogr 13(4):299–302
Smego RA, Bhatti S, Khaliq AA, Beg MA (2003) Percutaneous aspiration-injection-reaspiration drainage plus albendazole or mebendazole for hepatic cystic echinococcosis: a meta-analysis. Clin Infect Dis 37(8):1073–1083
Stojkovic M, Zwahlen M, Teggi A, Vutova K, Cretu CM, Virdone R, Nicolaidou P, Cobanoglu N, Junghanss T (2009) Treatment response of cystic echinococcosis to benzimidazoles: a systematic review. PLoS Negl Trop Dis 3(9):e524
Tung YS, Liu HL, Wu CC, Ju KC, Chen WS, Lin WL (2006) Contrast-agent-enhanced ultrasound thermal ablation. Ultrasound Med Biol 32(7):1103–1110
Urrea-París M, Casado N, Moreno M, Rodriguez-Caabeiro F (2001) Chemoprophylactic praziquantel treatment in experimental hydatidosis. Parasitol Res 87(6):510–512
Varcasia A, Garippa G, Pipia AP, Scala A, Brianti E, Giannetto S, Battelli G, Poglayen G, Micagni G (2008) Cystic echinococcosis in equids in Italy. Parasitol Res 102(4):815–818
Wang JA, Zou XY, Ye B, Zhang CW, Zhao FS (2007a) Pathological change in hydatid cysts of Echinococcus granulosus treated with high intensity focused ultrasound. Chin J Parasitol Parasit Dis 25(6):462–465
Wang JA, Zou XY, Ye B, Zhang CW, Zhao FS, Han XM, Yang YH, Li FQ (2007b) The heat effect of irradiation with high intensity focused ultrasound on the hydatid cysts of Echinococcus granulosus. Chin J Zoon 23(6):576–579
Wang JA, Zou XY, Ye B, Zhang CW, Zhao FS, Han XM, Li FQ, Zou JZ (2009) High intensity focus ultrasound kills hydatid cysts of Echinococcus granulosus. Acta Acad Med Mil Tert 31(14):1333–1336
Wen H, Zhao XD (2008) Atlas of echinococcosis: Chinese–English edition. Science Press, Duluth. p. 29
Wu F, Wang ZB, Chen WZ, Zhu H, Bai J, Zou JZ, Li KQ, Jin CB, Xie FL, Su HB (2004) Extracorporeal high intensity focused ultrasound ablation in the treatment of patients with large hepatocellular carcinoma. Ann Surg Oncol 11(12):1061–1069
Xiong SH, Wang ZB, Li FQ, Tian YB, Hu K, Gong XB, Ma P (2004) Research of hepatic biological focal region of high-intensity focused ultrasound and its real-time monitoring with ultrasonography in vivo. Chin J Med Imag Tech 19(9):1113–1115
Xu HX, Lu MD, Liu GJ, Xie XY, Xu ZF, Zheng YL, Liang JY (2006) Imaging of peripheral cholangiocarcinoma with low-mechanical index contrast-enhanced sonography and SonoVue initial experience. J Ultras Med 25(1):23–33
Yalcin E, Kiper N, Tan C, Ozcelik U, Dogru D, Cobanoglu N, Kose M, Pekcan S, Aslan AT, Ersoy F (2010) The role of human leucocyte antigens in children with hydatid disease: their association with clinical condition and prognosis. Parasitol Res 106(4):795–800
Zderic V, Brayman AA, Sharar SR, Crum LA, Vaezy S (2006) Microbubble-enhanced hemorrhage control using high intensity focused ultrasound. Ultrason 45(1):113–120
Zhang XN, Tang LH, Zhang Q (2004) The effect of albendazole to confront the echinococcosis and the progress of new drugs. J Chin Clin Med 5(12):43–45
Zhang L, Zhu H, Jin C, Zhou K, Li K, Su H, Chen W, Bai J, Wang Z (2009) High-intensity focused ultrasound (HIFU): effective and safe therapy for hepatocellular carcinoma adjacent to major hepatic veins. Eur Radiol 19(2):437–445
Zhang J, Kong J, Ye B, Zou XY, Wu WH (2012a) Preparation and water absorptive properties of starch based super absorbent resin for hydatid fluid. Chin J Zoon 27(12):1090–1093
Zhang J, Ye B, Kong J, Cai H, Zhao Y, Han X, Li F (2012b) In vitro protoscolicidal effects of high intensity focused ultrasound enhanced by a superabsorbent polymer. Parasitol Res 2012. doi:10.1007/s00436-00012-03176-00433
Zhou YF (2011) High intensity focused ultrasound in clinical tumor ablation. World J Clin Oncol 2(1):8–27
Zohuriaan-Mehr MJ, Kabiri K (2008) Superabsorbent polymer materials: a review. Iran Polym J 17(6):451–477
Zou JZ, Wu F (2000) Ultrasonography of 164 cases with malignant tumor treated by high intensity focused ultrgsound. Chin J Ultrasonogr 9(012):739–741
Zou X, Ye B, Wang J, Zhang C, Han X, Li F (2007) Effects of HIFU on hydatid cysts of Echinococcus granulosus: two exposure pattern comparison. Chin J Ultrasound Med 23(8):574–577
Zou XY, Ye B, Wang JA, Gong XB (2008) Effect of high intensity focused ultrasound on the enzymatic activity of Echinococcus granulosus protoscolices. Chin J Zoon 23(11):1097–1100
Zou XY, AN W, LongZhao H, Zhang J, Wu WH, Ye B (2009) Echinococcus granulosus: protoscolicidal effect of high intensity focused ultrasound. Exp Parasitol 121(4):312–316
Acknowledgments
This study was funded by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 30972567). The authors appreciate the assistance of HIFU Therapeutic Center, the Affiliated Hospital of Qinghai University, are grateful to Hailong Zhao in Department of Pathogenic Biology, Medical College, Qinghai University, and appreciate Ms. Komal Dhingra in Batch 2010, Overseas students office, Chongqing Medical University, for her helping us to polish this paper’s manuscript in English.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
This project was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 30972567).
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Cai, H., Chen, LL., Ye, B. et al. The destructive effects of high-intensity focused ultrasound on hydatid cysts enhanced by ultrasound contrast agent and superabsorbent polymer alone or in combination. Parasitol Res 112, 707–717 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00436-012-3191-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00436-012-3191-4